std::sort 是标准库里比较经典的算法,它是一个复合排序,结合了几种算法的优点。
1. 概述
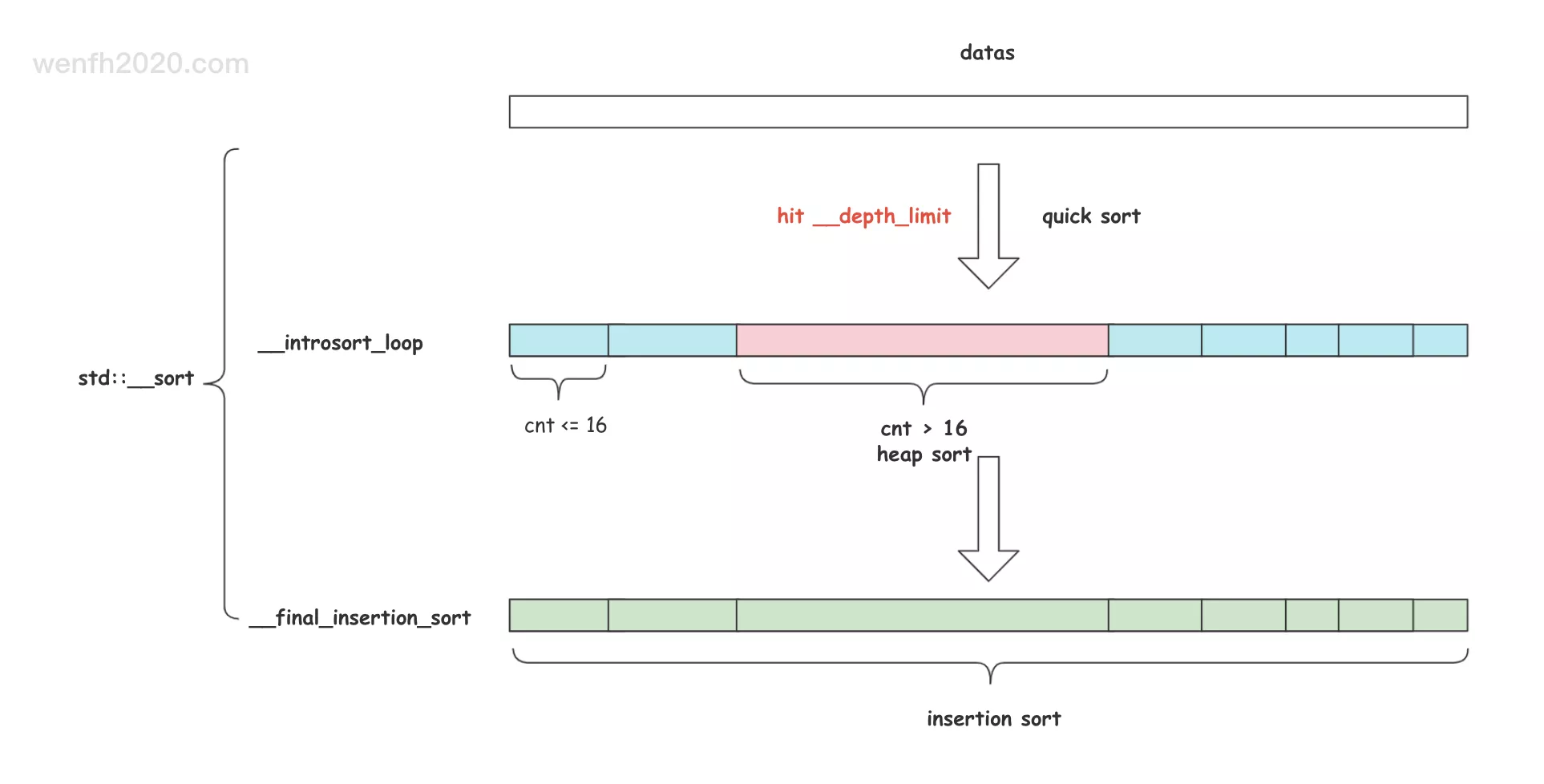
std::sort 主要是三种算法的结合体:插入排序,快速排序,堆排序。
1.1. 算法优缺点
| 算法 | 时间复杂度 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 插入排序 | O(N*N) | 当数据量很少时,效率比较高。 | 当数据量比较大时,时间复杂度比较高。 |
| 快速排序 | 平均 O(N*logN),最坏 O(N*N) | 大部分时候性能比较好。 | 算法时间复杂度不稳定,数据量大时递归深度很大,影响程序工作效率。 |
| 堆排序 | O(N*logN) | 算法时间复杂度稳定,比较小,适合数据量比较大的排序。 | 堆排序在建堆和调整堆的过程中会产生比较大的开销,数据量少的时候不适用。 |
1.2. 算法结合
std::sort 根据上文提到的几种算法的优缺点,对排序算法进行整合。
- 快速排序,递归排序到一定深度后,数据已经被分为多个子区域,子区域里面的数据可能是无序的,但是子区域之间已经是有序了。
- 在这多个子区域里,如果某个子区域数据个数大于阈值(16),采用堆排序,使得某个子区域内部有序。
- 剩下的没有被堆排序的小区域,数据量都是小于阈值的,最后整个数据区域采用插入排序。
这种被优化的快速排序+堆排序,被称为
内省排序(introspective sort)。
2. 源码
2.1. 测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
/* g++ -g -O0 -W -std=c++11 main.cpp -o test && ./test */
#include <time.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#define MAX_LEN 1000000
#define LIMT_CNT 100
int main() {
int limit = 0;
std::vector<int> nums;
nums.reserve(MAX_LEN);
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_LEN; i++) {
nums.push_back(rand());
}
std::sort(nums.begin(), nums.end(), std::less<int>());
for (auto v : nums) {
std::cout << v << " " << std::endl;
if (++limit > LIMT_CNT) {
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
2.2. 调试
动手调试源码,逻辑会更清晰 😁。(ubuntu 调试环境搭建)
2.3. stl 源码分析
2.3.1. 函数调用关系
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
std::sort
|-- std::__sort
|-- __introsort_loop
|-- __unguarded_partition_pivot # 将某个区域的数据根据哨兵分离出两个子区域,并返回这两个子区域的分界位置 __cut。
|-- __introsort_loop # 递归。
|-- __partial_sort -- if (__depth_limit == 0) # 快排到达指定深度,数据量大于阈值,采用堆排序。
|-- __final_insertion_sort # 插入排序整个排序区域。
2.3.2. 排序源码
排序源码:内省排序 + 插入排序。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
/* /usr/include/c++/9/bits/stl_algo.h */
template<typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
inline void
sort(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last,
_Compare __comp) {
...
std::__sort(__first, __last, __gnu_cxx::__ops::__iter_comp_iter(__comp));
}
template<typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
inline void
__sort(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last,
_Compare __comp) {
if (__first != __last) {
/* 内省排序:
* 快速排序递归一定深度,如果对应区域内数据量大于阈值,对应区域内数据采用堆排序。
* std::__lg() 计算递归深度限制。*/
std::__introsort_loop(__first, __last,
std::__lg(__last - __first) * 2, __comp);
/* 插入排序。 */
std::__final_insertion_sort(__first, __last, __comp);
}
}
2.3.2.1. 内省排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
/* /usr/include/c++/9/bits/stl_algo.h */
template<typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Size, typename _Compare>
void
__introsort_loop(_RandomAccessIterator __first,
_RandomAccessIterator __last,
_Size __depth_limit, _Compare __comp) {
while (__last - __first > int(_S_threshold)) {
if (__depth_limit == 0) {
/* 子区域采用堆排序。 */
std::__partial_sort(__first, __last, __last, __comp);
return;
}
--__depth_limit;
/* 递归排序,并返回排序区域被分成两个区域后,区域的分界位置 __cut。 */
_RandomAccessIterator __cut =
std::__unguarded_partition_pivot(__first, __last, __comp);
/* 快速排序(递归)。*/
std::__introsort_loop(__cut, __last, __depth_limit, __comp);
__last = __cut;
}
}
/// This is a helper function...
template<typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
inline _RandomAccessIterator
__unguarded_partition_pivot(_RandomAccessIterator __first,
_RandomAccessIterator __last, _Compare __comp) {
/* 数据区域中间位置。 */
_RandomAccessIterator __mid = __first + (__last - __first) / 2;
/* 比较三个值:第一个位置 ,最后一个位置,中间位置这三个值。
* 哪个位置上的数据处于中间的(a < b < c 取 b)作为快速排序的哨兵。
* 那么将哨兵数据与第一个位置数据置换。 */
std::__move_median_to_first(__first, __first + 1, __mid, __last - 1, __comp);
/* 第一个位置上的数据是哨兵,那么从 [__first + 1, __last) 这个区间的数据,
* 根据哨兵的值,将这个区域的数据分成左右两部分,
* 例如:小于哨兵的数据放在区域左边,大于哨兵的数据放在区域右边。*/
return std::__unguarded_partition(__first + 1, __last, __first, __comp);
}
/* 三个数取中值,放在 __result 位置。*/
template<typename _Iterator, typename _Compare>
void __move_median_to_first(_Iterator __result,_Iterator __a, _Iterator __b,
_Iterator __c, _Compare __comp) {
if (__comp(__a, __b)) {
if (__comp(__b, __c))
std::iter_swap(__result, __b);
else if (__comp(__a, __c))
std::iter_swap(__result, __c);
else
std::iter_swap(__result, __a);
}
else if (__comp(__a, __c))
std::iter_swap(__result, __a);
else if (__comp(__b, __c))
std::iter_swap(__result, __c);
else
std::iter_swap(__result, __b);
}
/* 根据哨兵,将数据区域分成两部分,并返回区域分界位置。 */
template<typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
_RandomAccessIterator
__unguarded_partition(_RandomAccessIterator __first,
_RandomAccessIterator __last,
_RandomAccessIterator __pivot, _Compare __comp) {
while (true) {
while (__comp(__first, __pivot))
++__first;
--__last;
while (__comp(__pivot, __last))
--__last;
if (!(__first < __last))
return __first;
std::iter_swap(__first, __last);
++__first;
}
}
2.3.2.2. 插入排序
- 源码分析。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
/* /usr/include/c++/9/bits/stl_algo.h */
template <typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
void
__final_insertion_sort(_RandomAccessIterator __first,
_RandomAccessIterator __last, _Compare __comp) {
if (__last - __first > int(_S_threshold)) {
std::__insertion_sort(__first, __first + int(_S_threshold), __comp);
std::__unguarded_insertion_sort(__first + int(_S_threshold), __last, __comp);
} else
std::__insertion_sort(__first, __last, __comp);
}
/// This is a helper function for the sort routine.
template <typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
void
__insertion_sort(_RandomAccessIterator __first,
_RandomAccessIterator __last, _Compare __comp) {
if (__first == __last) return;
for (_RandomAccessIterator __i = __first + 1; __i != __last; ++__i) {
/* 如果当前数据比第一个数据还要小(如果是从小到大排序),
* [__first, __i) 区域数据向右移动一个位置,__i 数据放在首位。 */
if (__comp(__i, __first)) {
typename iterator_traits<_RandomAccessIterator>::value_type
__val = _GLIBCXX_MOVE(*__i);
_GLIBCXX_MOVE_BACKWARD3(__first, __i, __i + 1);
*__first = _GLIBCXX_MOVE(__val);
} else
/* __i 位置上的数据作为要插入的数据,
* 从右到左(__i 位置开始)逐个数据进行比较排序,直到不满足条件再停下来。 */
std::__unguarded_linear_insert(__i,
__gnu_cxx::__ops::__val_comp_iter(__comp));
}
}
template <typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
void
__unguarded_linear_insert(_RandomAccessIterator __last, _Compare __comp) {
typename iterator_traits<_RandomAccessIterator>::value_type
__val = _GLIBCXX_MOVE(*__last);
_RandomAccessIterator __next = __last;
--__next;
while (__comp(__val, __next)) {
*__last = _GLIBCXX_MOVE(*__next);
__last = __next;
--__next;
}
*__last = _GLIBCXX_MOVE(__val);
}
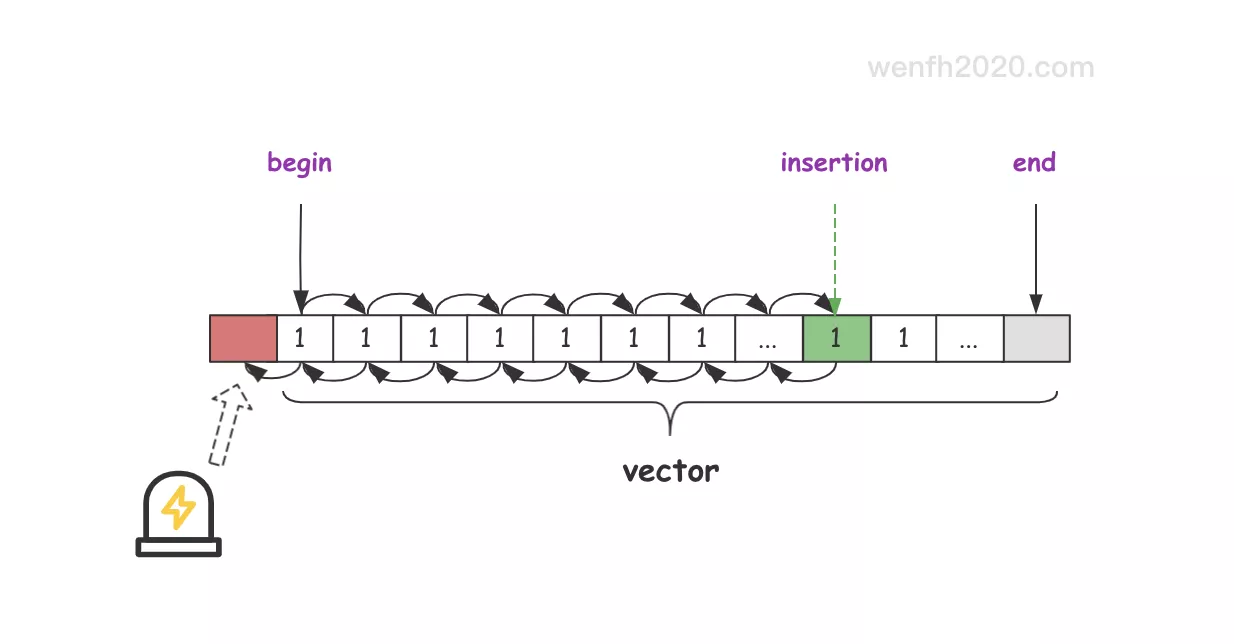
注意,因为__unguarded_linear_insert内部 while 循环没有作边界检查,所以 __comp 函数两个参数的比较必须是 v1 > v2 或者 v1 < v2,不能 v1 >= v2 或者 v1 <= v2 这样的,否则程序可能会因为内存越界崩溃( 参考下面错误示例)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
/* g++ main.cpp -o test && ./test */
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main() {
std::vector<int> nums;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
nums.push_back(1);
}
std::sort(nums.begin(), nums.end(), [](int v1, int v2) {
return v1 <= v2;
});
return 0;
}
3. 小结
- std::sort 采用的是分治思维,先采用快速排序,将整个区域分成多个子区域,每个子区域内部根据数据量采用不同算法。
- 分治后,各个子区域局部有序后再通过整个区域进行排序。
4. 参考
- 十大排序算法
- 快排的改良版——内省式排序
- C++中使用std::sort自定义排序规则时要注意的崩溃问题
- 《STL 源码剖析》- (389 - 400)


