EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 是 2016 年 4.5+ 内核新添加的一个 epoll 的标识(代码改动较小,详看:github)。
它降低了多个进程/线程通过 epoll_ctl 添加共享 fd 引发的惊群概率,使得一个事件发生时,只唤醒一个正在 epoll_wait 阻塞等待唤醒的进程/线程(而不是全部唤醒)。
而 Ngnix 在 1.11.3 之后相应添加了 NGX_EXCLUSIVE_EVENT 功能标识(代码改动较小,详看:github),它使用了 EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 特性。
对比 nginx 在应用层的解决方案:accept_mutex,NGX_EXCLUSIVE_EVENT 它从内核层面避免惊群问题,它更简洁高效。
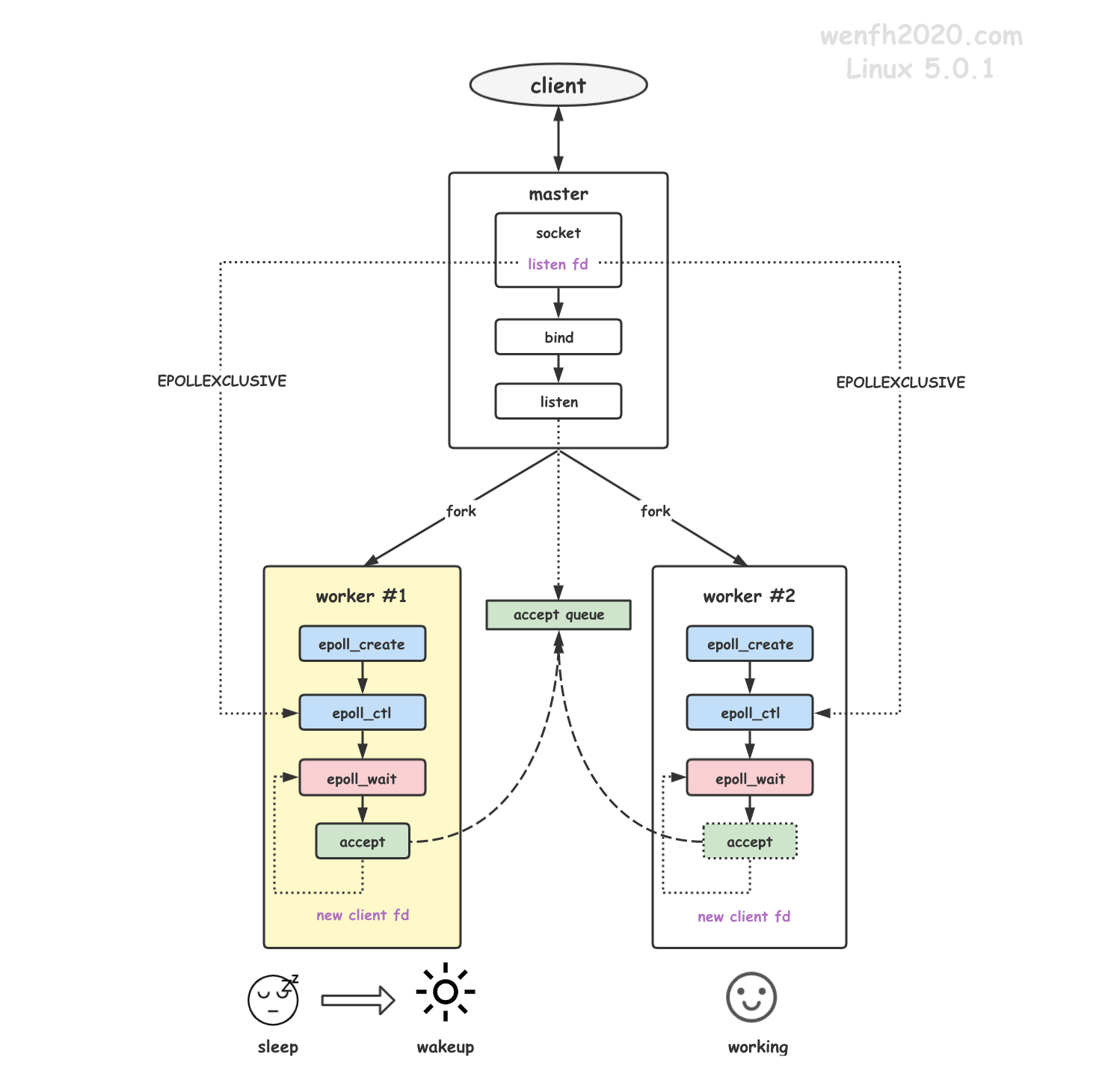
该功能的工作原和使用相对简单:进程使用 epoll_ctl 添加 listen socket fd 时,把 EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 属性添加进去就可以了。多个进程通过 epoll_wait 等待 listen socket 事件,当有新链接到来时,内核只唤醒一个等待的进程。
我们从应用层(nginx)和内核去分析 epoll 的 EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 属性工作原理。
- 探索惊群 ①
- 探索惊群 ② - accept
- 探索惊群 ③ - nginx 惊群现象
- 探索惊群 ④ - nginx - accept_mutex
- 探索惊群 ⑤ - nginx - NGX_EXCLUSIVE_EVENT(★)
- 探索惊群 ⑥ - nginx - reuseport
- 探索惊群 ⑦ - 文件描述符透传
1. nginx
1.1. 概述
nginx 在 2016 年提交了代码修改,为了支持 Linux 4.5+ 版本的 EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 特性,主要是为了避免内核惊群问题。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Events: support for EPOLLEXCLUSIVE.
This flag appeared in Linux 4.5 and is useful for avoiding thundering herd
problem.
The current Linux kernel implementation walks the list of exclusive waiters,
and queues an event to each epfd, until it finds the first waiter that has
threads blocked on it via epoll_wait().
master
release-1.21.4
…
release-1.11.3
@VBart
VBart committed on 15 Jul 2016
1 parent b60534e commit 5c2dd3913aad5c4bf7d9056e1336025c2703586b
高版本的 linux 内核系统,nginx 安装默认启用 EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 属性的支持。
1
2
3
4
5
6
# CHANGES
Changes with nginx 1.11.3 26 Jul 2016
*) Change: now the "accept_mutex" directive is turned off by default.
*) Feature: now nginx uses EPOLLEXCLUSIVE on Linux.
用 strace 去监控进程的系统调用,当 nginx 进程启动后,epoll_ctl 关注 listen socket fd,并添加 EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 属性标识。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# strace -f -s 512 -o /tmp/nginx.log /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
# grep -E 'listen|epoll_create|EPOLLEXCLUSIVE' /tmp/nginx.log
128804 epoll_create(100) = 5
# 主进程创建了 listen socket,fd == 6。
128804 listen(6, 511) = 0
128807 epoll_create(25012 <unfinished ...>
128807 <... epoll_create resumed>) = 10
128806 epoll_create(25012 <unfinished ...>
128806 <... epoll_create resumed>) = 8
128809 epoll_create(25012 <unfinished ...>
128809 <... epoll_create resumed>) = 14
128808 epoll_create(25012 <unfinished ...>
128808 <... epoll_create resumed>) = 12
# 每个子进程关注 fd == 6 事件,并添加 EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 属性标识。
128807 epoll_ctl(10, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, 6, {EPOLLIN|EPOLLEXCLUSIVE, {u32=732094480, u64=140132630061072}}) = 0
128809 epoll_ctl(14, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, 6, {EPOLLIN|EPOLLEXCLUSIVE, {u32=732094480, u64=140132630061072}} <unfinished ...>
128806 epoll_ctl(8, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, 6, {EPOLLIN|EPOLLEXCLUSIVE, {u32=732094480, u64=140132630061072}} <unfinished ...>
128808 epoll_ctl(12, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, 6, {EPOLLIN|EPOLLEXCLUSIVE, {u32=732094480, u64=140132630061072}}) = 0
1.2. 源码
配置了多进程的 nginx,它的子进程在启动时,将监听的共享 listen socket 通过 epoll_ctl 添加到 epoll。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
(gdb) bt
#0 ngx_epoll_add_event (ev=0x0, event=140737488348208, flags=93824993537200) at src/event/modules/ngx_epoll_module.c:580
#1 0x00005555555a6734 in ngx_event_process_init (cycle=0x555555692cb0) at src/event/ngx_event.c:889
#2 0x00005555555b3b62 in ngx_worker_process_init (cycle=0x555555692cb0, worker=0) at src/os/unix/ngx_process_cycle.c:900
#3 0x00005555555b31e9 in ngx_worker_process_cycle (cycle=0x555555692cb0, data=0x0) at src/os/unix/ngx_process_cycle.c:704
#4 0x00005555555afeda in ngx_spawn_process (cycle=0x555555692cb0, proc=0x5555555b31a4 <ngx_worker_process_cycle>, data=0x0, name=0x55555564274f "worker process", respawn=-3) at src/os/unix/ngx_process.c:199
#5 0x00005555555b2427 in ngx_start_worker_processes (cycle=0x555555692cb0, n=4, type=-3) at src/os/unix/ngx_process_cycle.c:344
#6 0x00005555555b1c0a in ngx_master_process_cycle (cycle=0x555555692cb0) at src/os/unix/ngx_process_cycle.c:130
#7 0x000055555556da39 in main (argc=1, argv=0x7fffffffe438) at src/core/nginx.c:383
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
/* src/event/ngx_event.h */
#if (NGX_HAVE_EPOLLEXCLUSIVE)
#define NGX_EXCLUSIVE_EVENT EPOLLEXCLUSIVE
#endif
/* src/event/ngx_event.c */
static ngx_int_t
ngx_event_process_init(ngx_cycle_t *cycle) {
...
ls = cycle->listening.elts;
for (i = 0; i < cycle->listening.nelts; i++) {
...
#if (NGX_HAVE_EPOLLEXCLUSIVE)
if ((ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_EPOLL_EVENT)
&& ccf->worker_processes > 1) {
/* ngx_add_event -> ngx_epoll_add_event */
if (ngx_add_event(rev, NGX_READ_EVENT, NGX_EXCLUSIVE_EVENT) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
continue;
}
#endif
...
}
...
}
2. 内核
2.1. 概述
看看 linux 在 github 提交的 EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 功能描述要点:
- EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 是 2016 年 4.5+ 内核新添加的一个 epoll 的标识。
- epoll 通过 epoll_ctl 添加共享 fd 时,需要添加 EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 标识即可,使用相对简单。
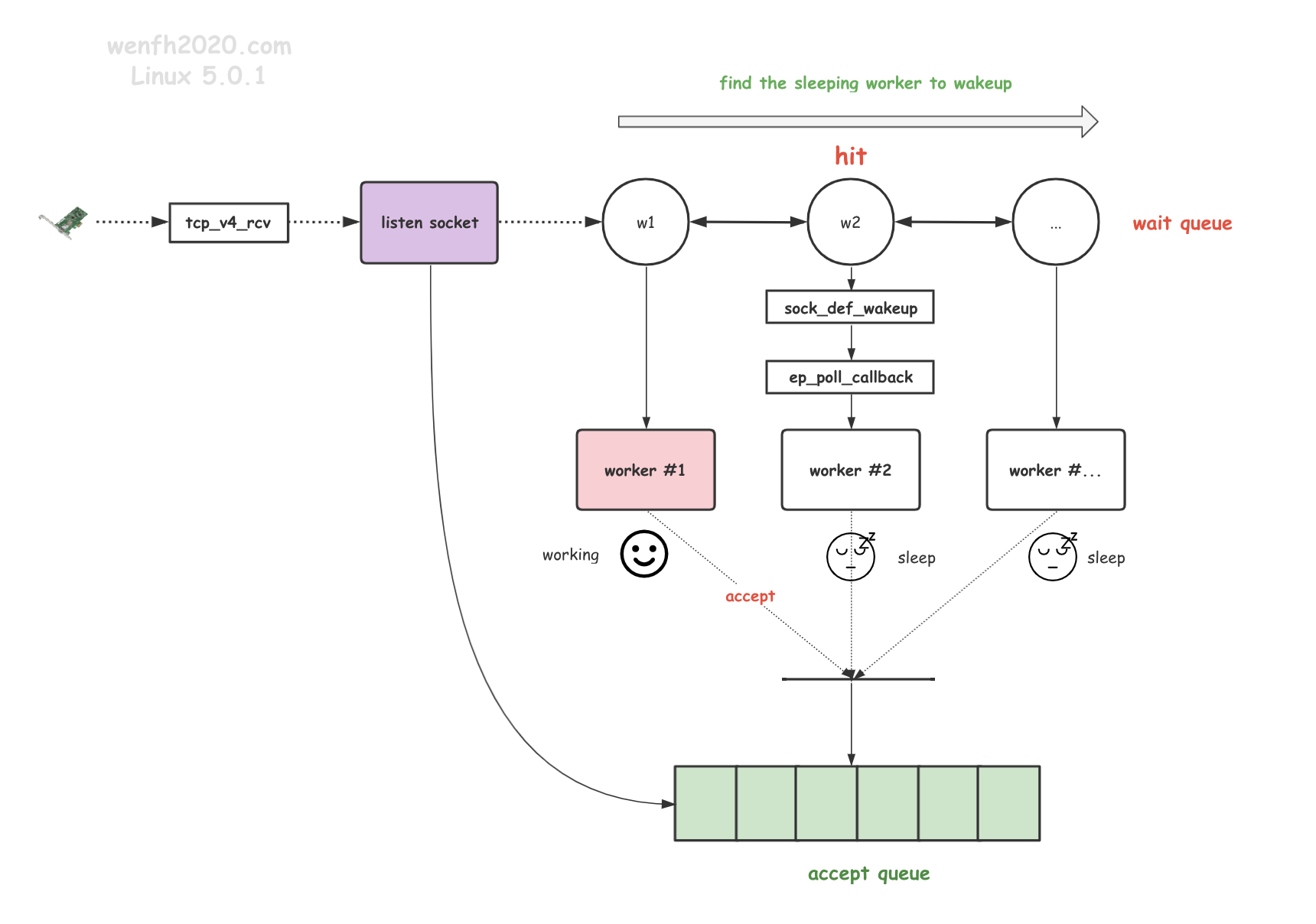
- 它尽量避免 epoll_ctl 添加共享 fd 引发的惊群问题:多进程通过 epoll_wait 等待资源,当资源到来时,内核查找遍历查找一个正在睡眠的进程,唤醒它去处理资源。(只唤醒一个,这样避免了无差别地全部唤醒正在等待的所有进程。)
- 该标识测试性能成果:程序负载从原来时长 860 秒 降低到 24 秒。(这么强大 🐂❓感觉我翻译得不正确 😂,还是参考下面的英文原文吧...)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
epoll: add EPOLLEXCLUSIVE flag
Currently, epoll file descriptors or epfds (the fd returned from
epoll_create[1]()) that are added to a shared wakeup source are always
added in a non-exclusive manner. This means that when we have multiple
epfds attached to a shared fd source they are all woken up. This creates
thundering herd type behavior.
Introduce a new 'EPOLLEXCLUSIVE' flag that can be passed as part of the
'event' argument during an epoll_ctl() EPOLL_CTL_ADD operation. This new
flag allows for exclusive wakeups when there are multiple epfds attached
to a shared fd event source.
The implementation walks the list of exclusive waiters, and queues an
event to each epfd, until it finds the first waiter that has threads
blocked on it via epoll_wait(). The idea is to search for threads which
are idle and ready to process the wakeup events. Thus, we queue an event
to at least 1 epfd, but may still potentially queue an event to all epfds
that are attached to the shared fd source.
Performance testing was done by Madars Vitolins using a modified version
of Enduro/X. The use of the 'EPOLLEXCLUSIVE' flag reduce the length of
this particular workload from 860s down to 24s.
Sample epoll_clt text:
EPOLLEXCLUSIVE
Sets an exclusive wakeup mode for the epfd file descriptor that is
being attached to the target file descriptor, fd. Thus, when an event
occurs and multiple epfd file descriptors are attached to the same
target file using EPOLLEXCLUSIVE, one or more epfds will receive an
event with epoll_wait(2). The default in this scenario (when
EPOLLEXCLUSIVE is not set) is for all epfds to receive an event.
EPOLLEXCLUSIVE may only be specified with the op EPOLL_CTL_ADD.
...
v4.5-rc1
@almostivan
@torvalds
almostivan authored and torvalds committed on 21 Jan 2016
2.2. 原理
epoll_ctl 关注添加 fd 的事件时,通过 add_wait_queue_exclusive 函数,将 WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE 标识的等待事件添加到 fd 的等待唤醒队列中。
当 fd 发生对应的事件时,wake_up_interruptible_all (__wake_up_common) 遍历 lisetn socket fd 的等待事件队列,但只唤醒一个带有 WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE 标识的等待事件的进程。
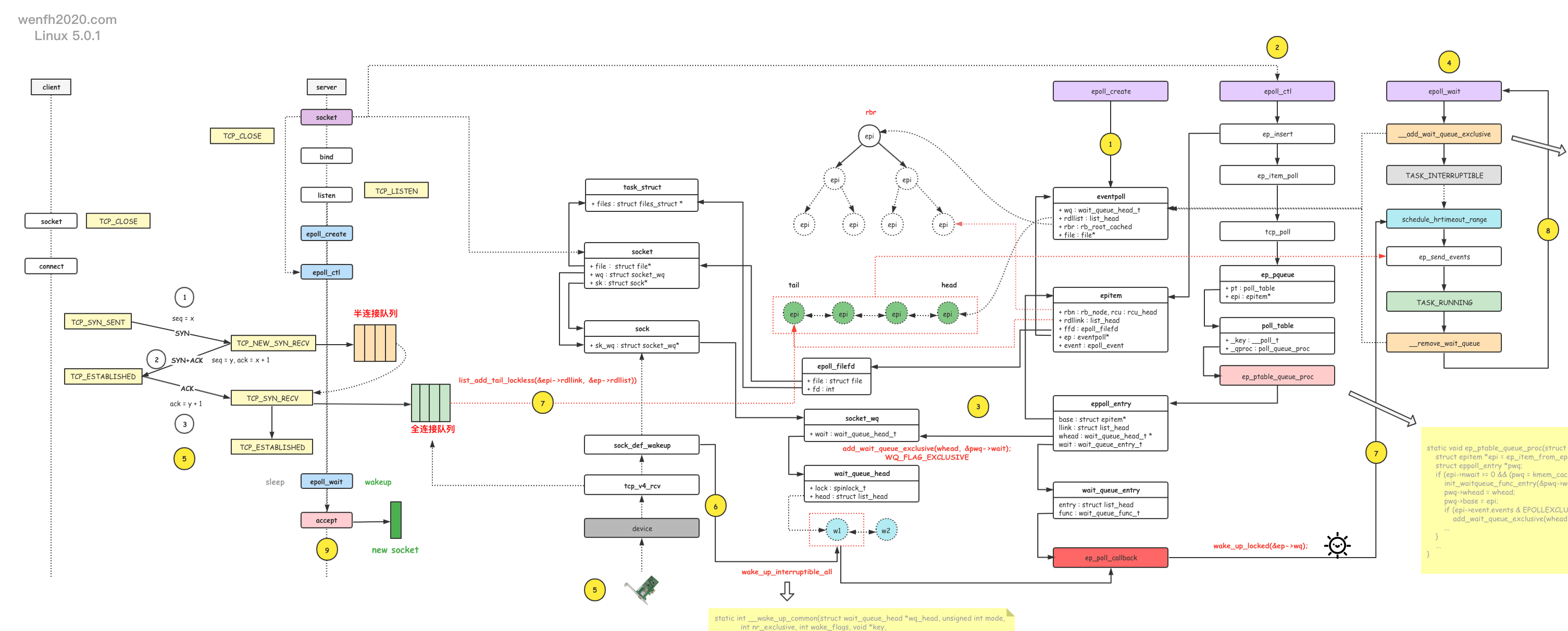
小结:惊群问题其实就是一个等待唤醒的问题。
-
添加等待事件:
- 等待 socket 事件发生:epoll_ctl -> add_wait_queue_exclusive -> socket.wq
- 等待阻塞的进程唤醒:epoll_wait -> __add_wait_queue_exclusive ->eventpoll.wq
-
唤醒:
tcp_v4_rcv -> wake_up_interruptible_all -> socket.wq -> ep_poll_callback -> wake_up_locked -> eventpoll.wq -> epoll_wait
2.2.1. fd 等待队列
因为是分析 tcp 协议的 nginx 程序,这个 fd 指向的是 socket 数据结构。
而进程通过 epoll_ctl 关注的是 fd 事件,当进程在等待 fd 的事件时,会将等待事件添加到 socket 的等待队列 socket.wq 中去,当 socket 触发事件时会通过等待事件唤醒进程。
流程:epoll_ctl -> listen socket -> add_wait_queue_exclusive <+ep_poll_callback+> -> socket.wq
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
/* include/linux/net.h*/
struct socket {
...
struct socket_wq *wq; /* socket 等待队列。 */
...
};
/* Set exclusive wakeup mode for the target file descriptor
* include/uapi/linux/eventpoll.h*/
#define EPOLLEXCLUSIVE ((__force __poll_t)(1U << 28))
/* fs/eventpoll.c
* This is the callback that is used to add our wait queue to the
* target file wakeup lists.
*
* 添加等待事件到 fd 的等待唤醒队列中。这个 fd 是通过 epoll_ctl 关注的,
* 而 ep_poll_callback 是触发等待事件回调函数。
*/
static void ep_ptable_queue_proc(struct file *file, wait_queue_head_t *whead, poll_table *pt) {
struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_epqueue(pt);
struct eppoll_entry *pwq;
if (epi->nwait >= 0 && (pwq = kmem_cache_alloc(pwq_cache, GFP_KERNEL)) {
init_waitqueue_func_entry(&pwq->wait, ep_poll_callback);
pwq->whead = whead;
pwq->base = epi;
/* 添加排它性(WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE)等待事件到 fd 的等待队列。 */
if (epi->event.events & EPOLLEXCLUSIVE)
add_wait_queue_exclusive(whead, &pwq->wait);
...
}
...
}
/* kernel/sched/wait.c
* 添加排它性等待事件到等待队列。*/
void add_wait_queue_exclusive(struct wait_queue_head *wq_head, struct wait_queue_entry *wq_entry) {
unsigned long flags;
wq_entry->flags |= WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE;
spin_lock_irqsave(&wq_head->lock, flags);
__add_wait_queue_entry_tail(wq_head, wq_entry);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&wq_head->lock, flags);
}
2.2.2. epoll_wait 等待事件
epoll_wait -> __add_wait_queue_exclusive -> eventpoll.wq
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
/* epoll 结构对象。*/
struct eventpoll {
...
/* 使用当前 epoll 的进程等待队列。 */
wait_queue_head_t wq;
...
};
/* fs/eventpoll.c */
static int ep_poll(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event __user *events,
int maxevents, long timeout) {
...
fetch_events:
...
eavail = ep_events_available(ep);
if (eavail)
/* 如果就绪队列有数据,那就不用阻塞等待了,epoll_wait 将数据从
* 内核拷贝到用户空间,然后从内核返回到用户空间。*/
goto send_events;
...
/* 如果没有就绪事件,进程将进入睡眠等待状态,添加等待事件到等待队列。
* 当 epoll 关注的文件有对应的事件发生,会触发 ep_poll_callback 函数(epoll_ctl 里绑定的),
* 唤醒等待队列里的对应进程。 */
if (!waiter) {
waiter = true;
init_waitqueue_entry(&wait, current);
spin_lock_irq(&ep->wq.lock);
/* epoll 往等待队列中,添加当前进程的等待事件,等待唤醒。 */
__add_wait_queue_exclusive(&ep->wq, &wait);
spin_unlock_irq(&ep->wq.lock);
}
for (;;) {
/* 将进程设置为可被中断唤醒的睡眠状态。 */
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
...
/* 再检查是否有就绪事件发生,如果有就不睡了。 */
eavail = ep_events_available(ep);
if (eavail)
break;
...
/* 进入超时等待睡眠状态。 */
if (!schedule_hrtimeout_range(to, slack, HRTIMER_MODE_ABS)) {
timed_out = 1;
break;
}
}
/* 上面循环退出,进程恢复运行状态。 */
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
send_events:
...
if (waiter) {
spin_lock_irq(&ep->wq.lock);
/* epoll 从等待队列中,删除当前进程的等待事件。 */
__remove_wait_queue(&ep->wq, &wait);
spin_unlock_irq(&ep->wq.lock);
}
}
2.2.3. 唤醒流程
socket 触发等待事件,唤醒 socket.wq 等待队列上的进程。
流程:tcp_v4_rcv -> wake_up_interruptible_all -> socket.wq -> ep_poll_callback -> wake_up_locked -> eventpoll.wq -> epoll_wait
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
/* kernel/sched/wait.c
* This is the callback that is passed to the wait queue wakeup
* mechanism. It is called by the stored file descriptors when they
* have events to report. */
static int __wake_up_common(struct wait_queue_head *wq_head, unsigned int mode,
int nr_exclusive, int wake_flags, void *key,
wait_queue_entry_t *bookmark) {
wait_queue_entry_t *curr, *next;
int cnt = 0;
...
/* 遍历等待队列,调用唤醒函数去唤醒进程。 */
list_for_each_entry_safe_from(curr, next, &wq_head->head, entry) {
unsigned flags = curr->flags;
int ret;
...
/* 调用进程唤醒回调函数:ep_poll_callback。*/
ret = curr->func(curr, mode, wake_flags, key);
if (ret < 0)
break;
/* ret 是 epoll 的回调函数 ep_poll_callback 返回结果。
* 如果该 epoll 没有正在阻塞等待,那么循环不会退出,继续寻找下一个等待的 epoll 进行唤醒。
* WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE 属性,是否只唤醒一个进程。
* nr_exclusive 一般是 1,如果上述条件都满足,这个循环就退出了。*/
if (ret && (flags & WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE) && !--nr_exclusive)
break;
...
}
...
}
/* fs/eventpoll.c
* This is the callback that is passed to the wait queue wakeup
* mechanism. It is called by the stored file descriptors when they
* have events to report.
*/
static int ep_poll_callback(wait_queue_entry_t *wait, unsigned mode, int sync, void *key) {
...
int ewake = 0;
...
/* If this file is already in the ready list we exit soon */
if (!ep_is_linked(epi)) {
list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
ep_pm_stay_awake_rcu(epi);
}
...
/* 这个地方很重要,判断当前 epoll 是否有进程正在通过 epoll_wait 进行等待。
* 如果没有,那么 ewake == 0,那么 __wake_up_common 会寻找下一个睡眠等待的进程。 */
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq)) {
if ((epi->event.events & EPOLLEXCLUSIVE) &&
!(pollflags & POLLFREE)) {
switch (pollflags & EPOLLINOUT_BITS) {
case EPOLLIN:
if (epi->event.events & EPOLLIN)
ewake = 1;
break;
case EPOLLOUT:
if (epi->event.events & EPOLLOUT)
ewake = 1;
break;
case 0:
ewake = 1;
break;
}
}
/* 唤醒 epoll_wait 阻塞等待的进程。 */
wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);
}
...
out_unlock:
...
if (!(epi->event.events & EPOLLEXCLUSIVE))
ewake = 1;
...
return ewake;
}
3. 效果
3.1. 对比惊群效果
用 strace 可以抓到 nginx 运行的进程系统调用日志,发现依然有 accept 返回错误,但是出现概率要比直接惊群的效果要好。
strace 监控进程,会影响该进程的处理速度,因为 strace 处理监控系统调用,还要将日志写到磁盘。
在 ubuntu 20.04 / 5.11.0-37-generic 开启 16 个进程测试,通过 grep 查看 strace 打印的 accept 日志,了解惊群的数据。发现 EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 特性的 accept 的错误非常少,4295 个 accept,只有 66 个是返回错误的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# strace -f -s 512 -o /tmp/nginx.log /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
# grep accept4 /tmp/nginx.log | grep =
...
128808 <... accept4 resumed>{sa_family=AF_INET, sin_port=htons(48848), sin_addr=inet_addr("172.16.230.15")}, [112->16], SOCK_NONBLOCK) = 9
128809 <... accept4 resumed>{sa_family=AF_INET, sin_port=htons(48846), sin_addr=inet_addr("172.16.230.15")}, [112->16], SOCK_NONBLOCK) = 9
128806 <... accept4 resumed>{sa_family=AF_INET, sin_port=htons(48840), sin_addr=inet_addr("172.16.230.15")}, [112->16], SOCK_NONBLOCK) = 13
128808 <... accept4 resumed>{sa_family=AF_INET, sin_port=htons(48844), sin_addr=inet_addr("172.16.230.15")}, [112->16], SOCK_NONBLOCK) = 10
128807 <... accept4 resumed>{sa_family=AF_INET, sin_port=htons(48842), sin_addr=inet_addr("172.16.230.15")}, [112->16], SOCK_NONBLOCK) = 12
...
128808 <... accept4 resumed>0x7ffecef630a0, [112], SOCK_NONBLOCK) = -1 EAGAIN (Resource temporarily unavailable)
128807 <... accept4 resumed>0x7ffecef630a0, [112], SOCK_NONBLOCK) = -1 EAGAIN (Resource temporarily unavailable)
128806 <... accept4 resumed>0x7ffecef630a0, [112], SOCK_NONBLOCK) = -1 EAGAIN (Resource temporarily unavailable)
128809 <... accept4 resumed>0x7ffecef630a0, [112], SOCK_NONBLOCK) = -1 EAGAIN (Resource temporarily unavailable)
...
# grep accept4 /tmp/nginx.log | grep = | wc -l
4295
# grep accept /tmp/nginx.log | grep EAGAIN | wc -l
66
对比 nginx 在低版本内核(ubuntu 14.04/4.4.0-142-generic)的惊群现象,3519 个 accept,519 个错误,EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 特性避免惊群效果已经非常好了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
# strace -f -s 512 -o /tmp/nginx.log /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
# grep accept4 /tmp/nginx.log | grep = | wc -l
3519
# grep accept /tmp/nginx.log | grep EAGAIN | wc -l
519
3.2. 问题原因
上面测试发现 EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 仍然有 accept 错误。
这里忽略了一个重要的知识点,虽然每个子进程的 epoll 实例都是独立的,但是 epoll_ctl 关注的 listen socket 默认采用了 LT 模式,而 LT 模式下,epoll 的就绪队列上的节点不会在当前的 epoll_wait 中删除,而是在下一次的 epoll_wait 中重新检查事件是否处理完毕,再决定是否删除。
同一个进程在两次的 epoll_wait 之间的时间段内,共享的 listen socket 就可能接入很多新链接,导致前面唤醒的进程,accept 完一个链接资源后,执行第二次 epoll_wait 后,再去检查 epoll 就绪队列上的 listen socket 的就绪节点,发现 listen socket 上的完全队列还有数据,就绪节点仍然有效,所以 epoll_wait 返回有效数据给 accept 获取。但是这个资源可能由其它新的唤醒进程去处理的,被旧的进程处理掉了,所以新的进程被唤醒后,执行 accept,发现已经没有资源了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
while (1) {
...
n = epoll_wait(...);
if (n > 0) {
if (is_able_accept) {
accept(...);
}
}
...
}
4. 小结
- EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 工作原理:每次内核只唤醒一个睡眠的进程处理资源。
- 程序从内核层面只唤醒某个睡眠的进程,避免无差别唤醒所有进程处理新来的资源,降低了惊群出现的概率,提高了程序的工作效率。
- 降低了惊群概率,但是无法完全避免惊群,因为 listen socket 的资源是共享的,被唤醒的进程处理资源情况不能实时确定,导致后面唤醒的进程在获取资源时,发现共享资源已经被前面唤醒的进程处理完了。

