获取本地时间是比较常用的操作,可通过 gettimeofday 函数获取本地时间,然后根据需要转化成对应的时间单位:毫秒,微秒,秒。
1. gettimeofday
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
#include <sys/time.h>
int gettimeofday(struct timeval *tp, struct timezone *tzp);
struct timeval {
time_t tv_sec; /* seconds since Jan. 1, 1970 */
suseconds_t tv_usec; /* and microseconds */
};
2. 单位
2.1. 毫秒
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
long long mstime() {
struct timeval tv;
long long mst;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
mst = ((long long)tv.tv_sec) * 1000;
mst += tv.tv_usec / 1000;
return mst;
}
2.2. 微秒
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
long long ustime() {
struct timeval tv;
long long ust;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
ust = ((long)tv.tv_sec) * 1000000;
ust += tv.tv_usec;
return ust;
}
2.3. 秒(double)
1
2
3
4
5
double time_now() {
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, 0);
return ((tv).tv_sec + (tv).tv_usec * 1e-6);
}
3. 格式化
[年]-[月]-[日] [时]-[分]-[秒].[毫秒]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <iostream>
void format() {
int off;
time_t t;
char buf[64];
struct tm* tm;
struct timeval tv;
t = time(NULL);
tm = localtime(&t);
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
/* 时间精度:秒。 */
off = strftime(buf, sizeof(buf), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", tm);
std::cout << "[" << buf << "]" << std::endl;
/* 时间精度:毫秒。 */
snprintf(buf + off, sizeof(buf) - off, ".%03d", (int)tv.tv_usec / 1000);
std::cout << "[" << buf << "]" << std::endl;
}
int main() {
format();
return 0;
}
1
2
3
# g++ test_time.cpp -o test_time && ./test_time
[2020-10-16 10:07:22]
[2020-10-16 10:07:22.916]
4. c++11 时间接口
c++11 提供了时间获取接口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
int main() {
auto t1 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {
std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
}
auto t2 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto spend_s = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
auto spend_ms = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(t2 - t1);
std::cout << "spend: " << spend_s.count() << " s"
<< std::endl
<< "spend: " << spend_ms.count() << " ms"
<< std::endl;
return 0;
}
5. 性能
5.1. 问题
高并发系统里,从火焰图里看到:平平无奇的 mstime() 接口,却是资源吃货!
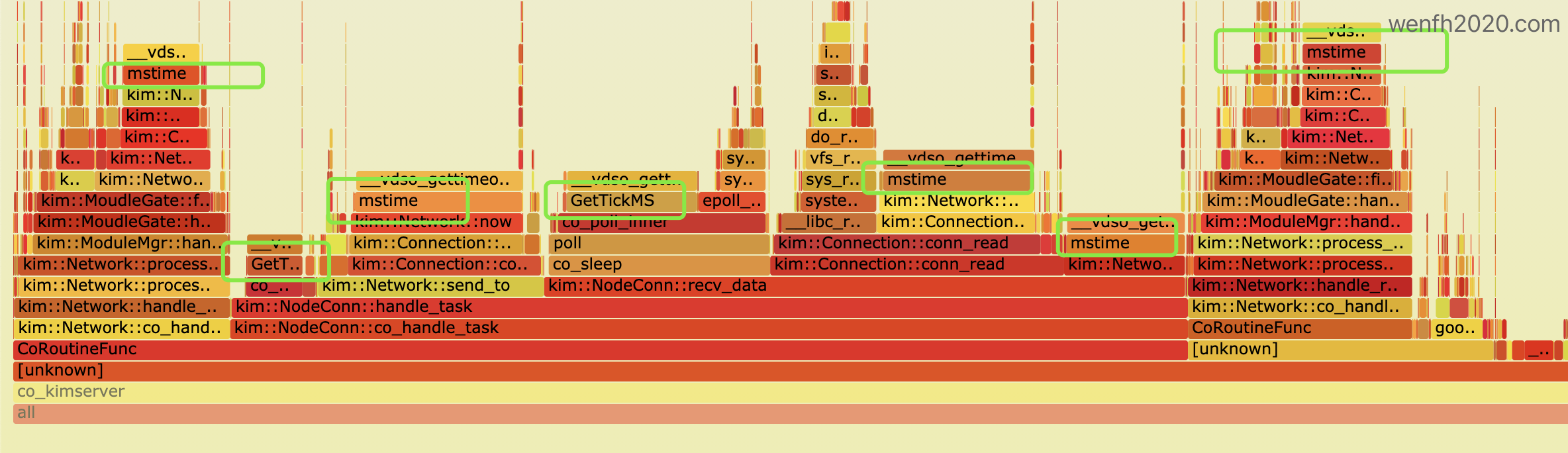
火焰图参考:如何生成火焰图🔥
5.2. 优化
一般业务,对时间精度要求不高。可以按照两个方面优化:
- 放在时钟里定时设置。
- 根据使用频率设置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
class Network {
...
protected:
int m_time_index = 0;
uint64_t m_now_time = 0;
void on_repeat_timer() {
m_now_time = mstime();
}
uint64_t now() {
if ((++m_time_index % 10) == 0) {
m_now_time = mstime();
}
return m_now_time;
}
...
};
有空的朋友,可以阅读一下 libev 的源码,看看它是怎么获取当前时间的。
1
2
3
ev_tstamp ev_now (struct ev_loop *loop) {
return ((loop)->ev_rt_now);
}

