走读网络协议栈 bind (tcp) 的(Linux - 5.0.1 下载)内核源码。
原理:bind 将IP地址/端口信息绑定在 socket 相关数据结构上,并且根据通过端口映射,将 socket 指针保存在内核哈希表里。
1. 概述
bind 为创建的 socket 绑定IP地址/端口。(IP/PORT - TCP/UDP)。
bind 详细文档参考(文档 - 链接可能要翻墙)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
/*
* sockfd:socket 文件描述符。
* myaddr:指向特定于协议的的地址结构的指针。。
* addrlen:struct sockaddr 地址结构长度。
* return:返回操作结果,若成功返回 0,否则返回 -1。
*/
#include <sys/socket.h>
int bind(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *myaddr, socklen_t addrlen);
上述文字来源:《UNIX 网络编程_卷1》
2. 概述
bind 核心逻辑将 socket 和地址端口关联起来。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
/* net/ipv4/af_inet.c */
int __inet_bind(struct sock *sk, struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len,
bool force_bind_address_no_port, bool with_lock) {
...
struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
...
/* socket 绑定地址。 */
inet->inet_rcv_saddr = inet->inet_saddr = addr->sin_addr.s_addr;
...
/* socket 绑定端口。 */
inet->inet_sport = htons(inet->inet_num);
inet->inet_daddr = 0;
inet->inet_dport = 0;
...
}
在实现过程中,有一些特殊功能需要注意。
-
端口可以设置为 0 吗?
答:可以,系统会分配一个随机端口。但是服务程序一般都指定特定的端口,而不是由系统随机分配。
-
地址端口可以重复绑定吗?
答:可以,了解一下这两个设置项:SO_REUSEADDR / SO_REUSEPORT。
-
SO_REUSEADDR 是为了解决 TCP_TIME_WAIT 问题。
-
SO_REUSEPORT 是为了解决惊群问题,允许多个进程共同使用相同的地址端口。
-
3. 结构
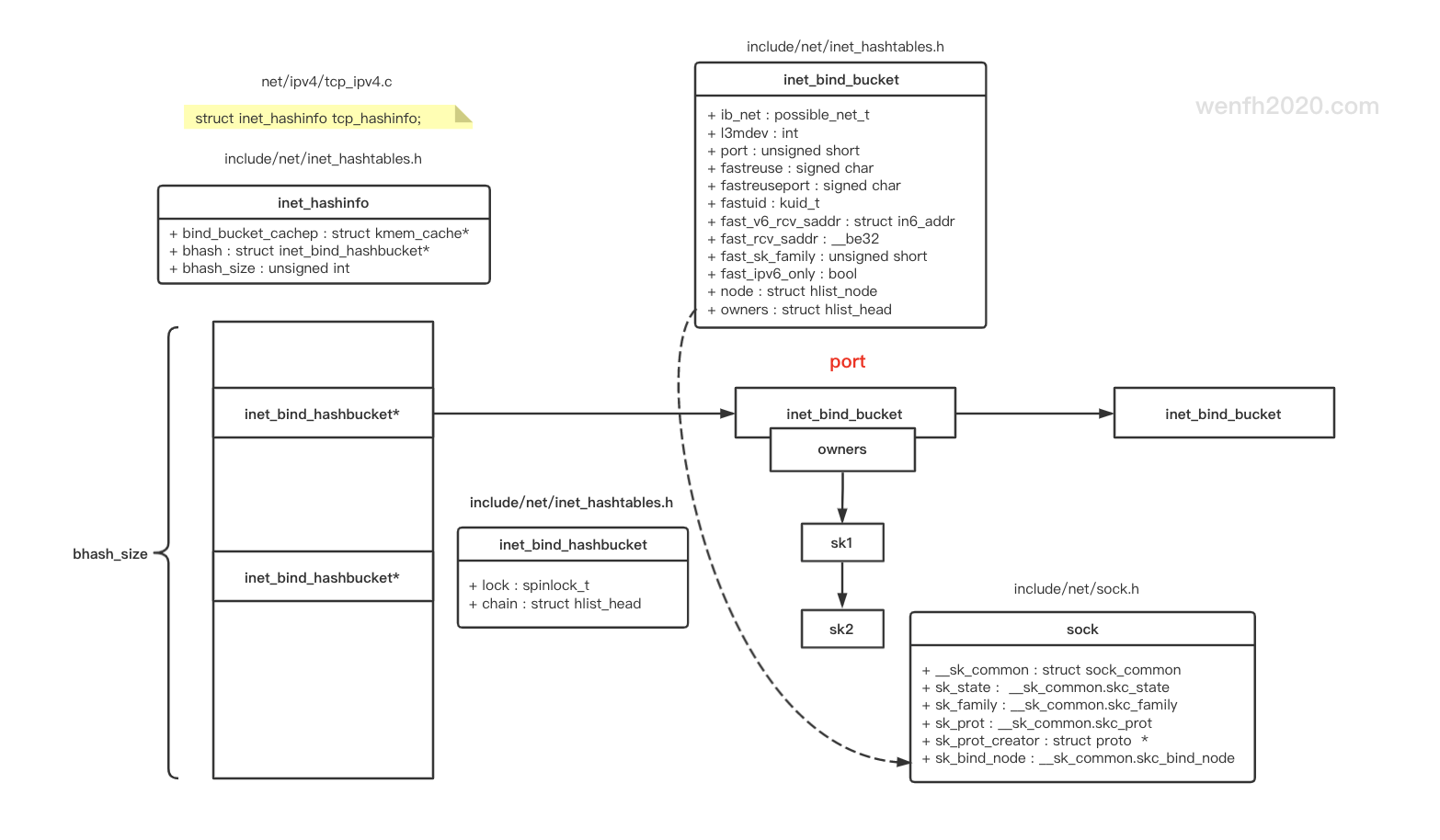
地址和端口会保存在对应的 socket 结构体中,对应的网络端口信息也会存储在内核的哈希表里。
3.1. socket 结构关系

3.2. 哈希表
-
哈希存储IP地址/端口相关数据结构信息。
哈希表时间复杂度是 O(1),非常快。
但是这里也有缺点,因为哈希表是由数组和链表的组合结构,自身有冲突链表(哈希链),而且
inet_bind_bucket有owners链表,保存共享端口的 socket 数据。【注意】
tcp 连接三次握手成功后,在 accept 调用前, client 的 socket.sock 信息也会保存到 owners,参考
__inet_inherit_port的使用。查询数据时,可能需要遍历两个链表,而且在同一个网域下,以端口作为哈希索引,导致不同的 IP 地址相同端口的数据也会在同一个
inet_bind_bucket里。所以inet_bind_bucket要使用fastreuse和fastreuseport去优化,尽量避免链表遍历。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
/* net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c */
struct inet_hashinfo tcp_hashinfo;
/* include/net/inet_hashtables.h */
struct inet_bind_hashbucket {
spinlock_t lock;
struct hlist_head chain;
};
/* hash 结构,保存了端口对应的 socket 信息。 */
struct inet_hashinfo {
...
/* Ok, let's try this, I give up, we do need a local binding
* TCP hash as well as the others for fast bind/connect.
*/
struct kmem_cache *bind_bucket_cachep;
struct inet_bind_hashbucket *bhash;
unsigned int bhash_size;
...
};
/* Networking protocol blocks we attach to sockets.
* socket layer -> transport layer interface
*/
struct proto {
char name[32];
...
int (*get_port)(struct sock *sk, unsigned short snum);
...
union {
struct inet_hashinfo *hashinfo;
...
} h;
...
}
/* net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c */
struct proto tcp_prot = {
.name = "TCP",
...
.get_port = inet_csk_get_port,
...
.h.hashinfo = &tcp_hashinfo,
...
};
/* include/net/inet_hashtables.h */
struct inet_bind_bucket {
possible_net_t ib_net;
int l3mdev;
unsigned short port; /* 端口号。 */
signed char fastreuse; /* SO_REUSEADDR 选项。*/
signed char fastreuseport; /* SO_REUSEPORT 选项。*/
kuid_t fastuid; /* SO_REUSEPORT 选项的用户 id。*/
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IPV6)
struct in6_addr fast_v6_rcv_saddr;
#endif
__be32 fast_rcv_saddr;
unsigned short fast_sk_family;
bool fast_ipv6_only;
struct hlist_node node; /* bucket 列表,保存哈希冲突的 bucket。*/
struct hlist_head owners; /* socket 信息。 */
};
- 哈希表操作逻辑。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
/* net/ipv4/tcp.c
* 初始化哈希表。 */
void __init tcp_init(void) {
...
tcp_hashinfo.bhash =
alloc_large_system_hash("TCP bind",
sizeof(struct inet_bind_hashbucket),
tcp_hashinfo.ehash_mask + 1,
17, /* one slot per 128 KB of memory */
0,
&tcp_hashinfo.bhash_size,
NULL,
0,
64 * 1024);
tcp_hashinfo.bhash_size = 1U << tcp_hashinfo.bhash_size;
for (i = 0; i < tcp_hashinfo.bhash_size; i++) {
spin_lock_init(&tcp_hashinfo.bhash[i].lock);
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&tcp_hashinfo.bhash[i].chain);
}
...
}
/* 添加 hash bucket。
* net/ipv4/inet_connection_sock.c
* Allocate and initialize a new local port bind bucket.
* The bindhash mutex for snum's hash chain must be held here.
*/
struct inet_bind_bucket *inet_bind_bucket_create(struct kmem_cache *cachep,
struct net *net,
struct inet_bind_hashbucket *head,
const unsigned short snum,
int l3mdev)
{
struct inet_bind_bucket *tb = kmem_cache_alloc(cachep, GFP_ATOMIC);
if (tb) {
write_pnet(&tb->ib_net, net);
tb->l3mdev = l3mdev;
tb->port = snum;
tb->fastreuse = 0;
tb->fastreuseport = 0;
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&tb->owners);
hlist_add_head(&tb->node, &head->chain);
}
return tb;
}
/* 哈希表与 socket 相互建立联系。 */
void inet_bind_hash(struct sock *sk, struct inet_bind_bucket *tb,
const unsigned short snum) {
inet_sk(sk)->inet_num = snum;
sk_add_bind_node(sk, &tb->owners);
inet_csk(sk)->icsk_bind_hash = tb;
}
static inline void sk_add_bind_node(struct sock *sk, struct hlist_head *list) {
hlist_add_head(&sk->sk_bind_node, list);
}
4. 内核源码逻辑
4.1. 函数堆栈
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
inet_bind(struct socket * sock, struct sockaddr * uaddr, int addr_len) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/af_inet.c:436)
__sys_bind(int fd, struct sockaddr * umyaddr, int addrlen) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:1482)
__do_sys_bind() (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:1493)
__se_sys_bind() (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:1491)
__x64_sys_bind(const struct pt_regs * regs) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:1491)
do_syscall_64(unsigned long nr, struct pt_regs * regs) (/root/linux-5.0.1/arch/x86/entry/common.c:290)
entry_SYSCALL_64() (/root/linux-5.0.1/arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:175)
4.2. 函数调用关系
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
#------------------- *用户态* ---------------------------
bind
#------------------- *内核态* ---------------------------
__x64_sys_bind # 内核系统调用。
|-- __sys_bind # net/socket.c
|-- sockfd_lookup_light # net/socket.c - 通过 fd 查找对应的 socket.
|-- move_addr_to_kernel # net/socket.c - 将用户态的参数数据拷贝进内核。
|-- __inet_bind # net/ipv4/af_inet.c
|-- inet_csk_get_port # net/ipv4/inet_connection_sock.c - 端口分配和保存逻辑。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(bind, int, fd, struct sockaddr __user *, umyaddr, int, addrlen) {
return __sys_bind(fd, umyaddr, addrlen);
}
int __sys_bind(int fd, struct sockaddr __user *umyaddr, int addrlen) {
...
/* 根据 fd 找出对应的 socket。 */
sock = sockfd_lookup_light(fd, &err, &fput_needed);
...
err = sock->ops->bind(sock, (struct sockaddr *)&address, addrlen);
...
}
int inet_bind(struct socket *sock, struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len) {
struct sock *sk = sock->sk;
...
return __inet_bind(sk, uaddr, addr_len, false, true);
}
int __inet_bind(struct sock *sk, struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len,
bool force_bind_address_no_port, bool with_lock) {
struct sockaddr_in *addr = (struct sockaddr_in *)uaddr;
struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
struct net *net = sock_net(sk);
unsigned short snum;
...
snum = ntohs(addr->sin_port);
...
/* socket 绑定地址。 */
inet->inet_rcv_saddr = inet->inet_saddr = addr->sin_addr.s_addr;
...
/* Make sure we are allowed to bind here. */
if (snum || !(inet->bind_address_no_port || force_bind_address_no_port)) {
/* 内核保存端口信息到内核哈希表。
* inet_csk_get_port*/
if (sk->sk_prot->get_port(sk, snum)) {
...
}
...
}
...
/* socket 端口。 */
inet->inet_sport = htons(inet->inet_num);
inet->inet_daddr = 0;
inet->inet_dport = 0;
...
}
4.3. 端口存储逻辑
端口分配和保存逻辑,要注意端口冲突情况。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
/* Obtain a reference to a local port for the given sock,
* if snum is zero it means select any available local port.
* We try to allocate an odd port (and leave even ports for connect())
*/
int inet_csk_get_port(struct sock *sk, unsigned short snum) {
bool reuse = sk->sk_reuse && sk->sk_state != TCP_LISTEN;
struct inet_hashinfo *hinfo = sk->sk_prot->h.hashinfo;
int ret = 1, port = snum;
struct inet_bind_hashbucket *head;
struct net *net = sock_net(sk);
struct inet_bind_bucket *tb = NULL;
kuid_t uid = sock_i_uid(sk);
int l3mdev;
l3mdev = inet_sk_bound_l3mdev(sk);
/* 如果传入的端口为 0,内核从合法的端口范围内,自动分配一个端口给 socket。 */
if (!port) {
head = inet_csk_find_open_port(sk, &tb, &port);
if (!head)
return ret;
if (!tb)
goto tb_not_found;
goto success;
}
/* 通过哈希表查找对应端口的信息。 */
head = &hinfo->bhash[inet_bhashfn(net, port, hinfo->bhash_size)];
spin_lock_bh(&head->lock);
/* 哈希表是由数组和链表组成的,哈希槽上保存的是哈希冲突的(多个)bucket,
* 它们用链表串联一起,遍历链表找出对应端口所在的 bucket。 */
inet_bind_bucket_for_each(tb, &head->chain)
if (net_eq(ib_net(tb), net) && tb->l3mdev == l3mdev &&
tb->port == port)
goto tb_found;
tb_not_found:
/* 如果哈希表里没有 bucket,新建一个,保存对应的端口信息。 */
tb = inet_bind_bucket_create(hinfo->bind_bucket_cachep, net, head, port, l3mdev);
...
/* 将对应端口的 socket 保存在哈希表的 bucket 里,在这个过程中,需要判断
* 端口冲突情况,要注意 SO_REUSEADDR 和 SO_REUSEPORT 这两个设置项,
* 它们允许端口重复使用。 */
tb_found:
if (!hlist_empty(&tb->owners)) {
if (sk->sk_reuse == SK_FORCE_REUSE)
goto success;
if ((tb->fastreuse > 0 && reuse) || sk_reuseport_match(tb, sk))
goto success;
if (inet_csk_bind_conflict(sk, tb, true, true))
goto fail_unlock;
}
success:
if (hlist_empty(&tb->owners)) {
tb->fastreuse = reuse;
if (sk->sk_reuseport) {
tb->fastreuseport = FASTREUSEPORT_ANY;
tb->fastuid = uid;
tb->fast_rcv_saddr = sk->sk_rcv_saddr;
tb->fast_ipv6_only = ipv6_only_sock(sk);
tb->fast_sk_family = sk->sk_family;
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IPV6)
tb->fast_v6_rcv_saddr = sk->sk_v6_rcv_saddr;
#endif
} else {
tb->fastreuseport = 0;
}
} else {
if (!reuse)
tb->fastreuse = 0;
if (sk->sk_reuseport) {
/* We didn't match or we don't have fastreuseport set on
* the tb, but we have sk_reuseport set on this socket
* and we know that there are no bind conflicts with
* this socket in this tb, so reset our tb's reuseport
* settings so that any subsequent sockets that match
* our current socket will be put on the fast path.
*
* If we reset we need to set FASTREUSEPORT_STRICT so we
* do extra checking for all subsequent sk_reuseport
* socks.
*/
if (!sk_reuseport_match(tb, sk)) {
tb->fastreuseport = FASTREUSEPORT_STRICT;
tb->fastuid = uid;
tb->fast_rcv_saddr = sk->sk_rcv_saddr;
tb->fast_ipv6_only = ipv6_only_sock(sk);
tb->fast_sk_family = sk->sk_family;
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IPV6)
tb->fast_v6_rcv_saddr = sk->sk_v6_rcv_saddr;
#endif
}
} else {
tb->fastreuseport = 0;
}
}
if (!inet_csk(sk)->icsk_bind_hash)
/* 将 socket 与哈希表绑定。 */
inet_bind_hash(sk, tb, port);
WARN_ON(inet_csk(sk)->icsk_bind_hash != tb);
ret = 0;
fail_unlock:
spin_unlock_bh(&head->lock);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(inet_csk_get_port);
4.4. 端口冲突
冲突的必要:新旧 socket 都绑定在相同设备上,而且IP地址/端口相同。
这个判断端口冲突的逻辑,有点烧脑,主要检查两个选项场景: SO_REUSEADDR 和 SO_REUSEPORT。
先检查 SO_REUSEADDR 的使用场景,再检查 SO_REUSEPORT 的使用场景。
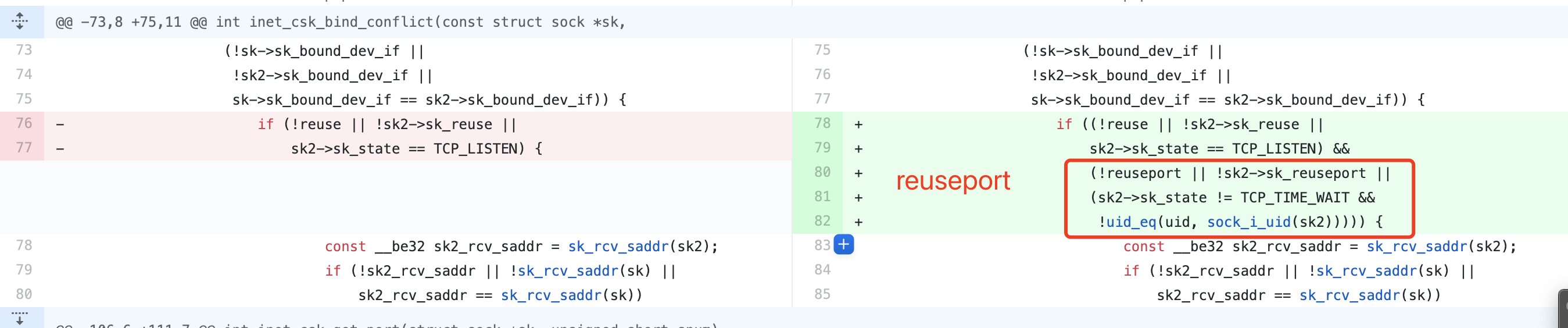
SO_REUSEADDR 是为了解决前一个 socket 处于 TCP_TIME_WAIT 没完全退出的问题。
SO_REUSEPORT 是为了解决惊群问题的,允许多个进程共同使用同一个IP地址/端口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
static int inet_csk_bind_conflict(const struct sock *sk,
const struct inet_bind_bucket *tb,
bool relax, bool reuseport_ok)
{
struct sock *sk2;
bool reuse = sk->sk_reuse;
bool reuseport = !!sk->sk_reuseport && reuseport_ok;
kuid_t uid = sock_i_uid((struct sock *)sk);
/*
* Unlike other sk lookup places we do not check
* for sk_net here, since _all_ the socks listed
* in tb->owners list belong to the same net - the
* one this bucket belongs to.
*/
/* 遍历已经 bind 端口的 socket. */
sk_for_each_bound(sk2, &tb->owners) {
/* 如果 sk2 也绑定到同一个设备上,那么进行检查。 */
if (sk != sk2 && (!sk->sk_bound_dev_if || !sk2->sk_bound_dev_if || sk->sk_bound_dev_if == sk2->sk_bound_dev_if)) {
/* 当前或者前一个 socket 没有设置 SO_REUSEADDR,或者前一个 socket 已经处于 listen 状态了。 */
if ((!reuse || !sk2->sk_reuse || sk2->sk_state == TCP_LISTEN) &&
/* 当前或者前一个 socket 没有设置 SO_REUSEPORT */
(!reuseport || !sk2->sk_reuseport || rcu_access_pointer(sk->sk_reuseport_cb) ||
/* 或者 sk2 不处于 TCP_TIME_WAIT 状态并且两个 uid 不一样。 */
(sk2->sk_state != TCP_TIME_WAIT && !uid_eq(uid, sock_i_uid(sk2))))) {
/* 两个地址一样。 */
if (inet_rcv_saddr_equal(sk, sk2, true))
break;
}
if (!relax && reuse && sk2->sk_reuse && sk2->sk_state != TCP_LISTEN) {
if (inet_rcv_saddr_equal(sk, sk2, true))
break;
}
}
}
return sk2 != NULL;
}

