rdb 文件是一个经过压缩的二进制文件,是 redis 持久化方式之一。本章主要讲 rdb 应用场景。
1. 配置
redis 有两种持久化方式,分别为:aof 和 rdb,默认开启 rdb,本章重点讲 rdb。
1
2
| # redis.conf
appendonly no
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| standardConfig configs[] = {
...
createBoolConfig("appendonly", NULL, MODIFIABLE_CONFIG, server.aof_enabled, 0, NULL, updateAppendonly),
...
}
void initServer(void) {
...
server.aof_state = server.aof_enabled ? AOF_ON : AOF_OFF;
...
}
|
2. 异步持久化
redis 主逻辑是在单进程,单线程里实现的。像持久化这种耗大量性能的操作,主进程一般会通过 fork 子进程异步进行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| // 主进程 fork 子进程存盘
int rdbSaveBackground(char *filename, rdbSaveInfo *rsi) {
...
if ((childpid = redisFork()) == 0) {
...
/* Child */
retval = rdbSave(filename,rsi);
...
}
...
}
|
3. 应用场景
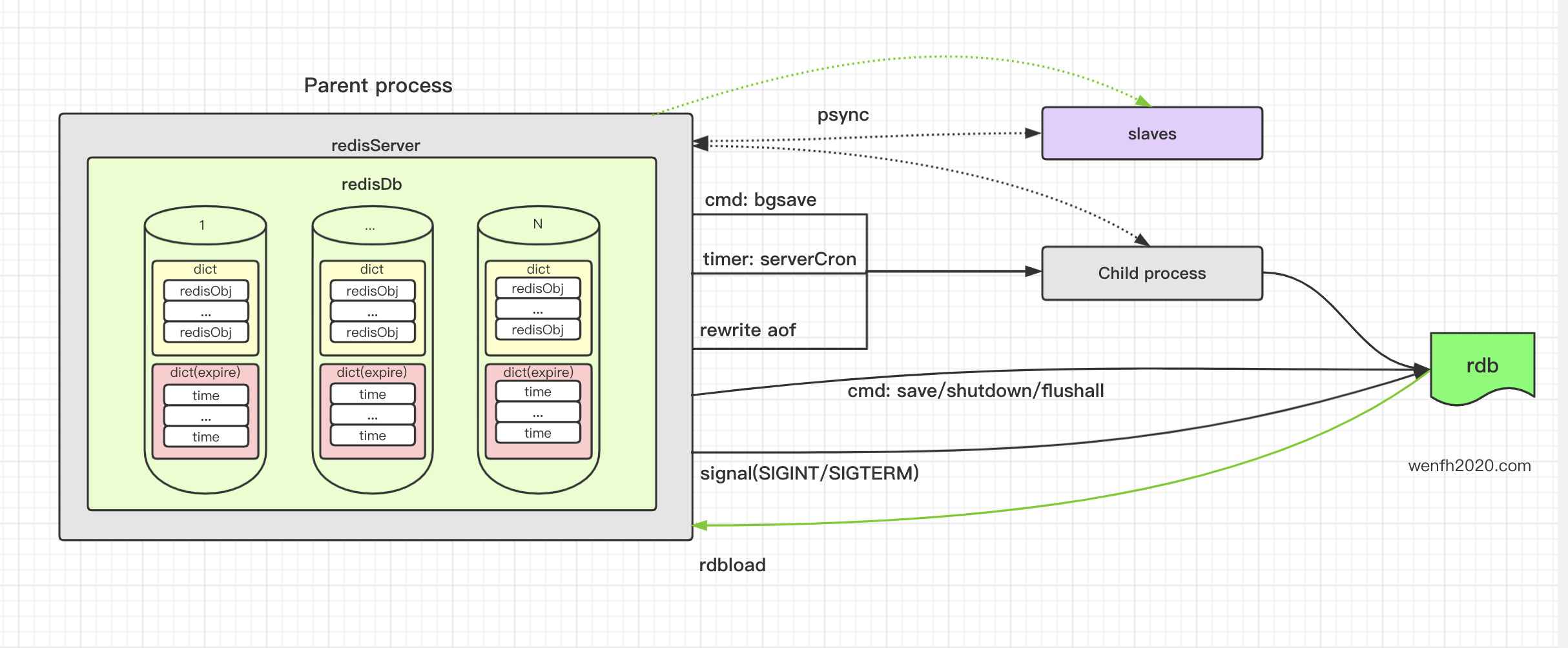
3.1. 服务启动加载数据
redis 程序启动,从磁盘 rdb 文件加载数据到内存。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| int main(int argc, char **argv) {
...
if (!server.sentinel_mode) {
loadDataFromDisk();
}
}
/* flags on the purpose of rdb save or load */
#define RDBFLAGS_NONE 0
#define RDBFLAGS_AOF_PREAMBLE (1<<0)
#define RDBFLAGS_REPLICATION (1<<1)
/* Function called at startup to load RDB or AOF file in memory. */
void loadDataFromDisk(void) {
long long start = ustime();
if (server.aof_state == AOF_ON) {
if (loadAppendOnlyFile(server.aof_filename) == C_OK)
...
} else {
rdbSaveInfo rsi = RDB_SAVE_INFO_INIT;
if (rdbLoad(server.rdb_filename,&rsi,RDBFLAGS_NONE) == C_OK) {
...
}
}
...
}
|
3.2. 命令
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| void saveCommand(client *c) {
...
if (rdbSave(server.rdb_filename,rsiptr) == C_OK) {
addReply(c,shared.ok);
} else {
addReply(c,shared.err);
}
}
|
BGSAVE 命令,主进程通过 fork 子进程进行异步存盘。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| void bgsaveCommand(client *c) {
...
if (server.rdb_child_pid != -1) {
addReplyError(c,"Background save already in progress");
} else if (hasActiveChildProcess()) {
if (schedule) {
server.rdb_bgsave_scheduled = 1;
addReplyStatus(c,"Background saving scheduled");
} else {
...
}
} else if (rdbSaveBackground(server.rdb_filename,rsiptr) == C_OK) {
addReplyStatus(c,"Background saving started");
}
...
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| void flushallCommand(client *c) {
...
flushAllDataAndResetRDB(flags);
...
}
/* Flushes the whole server data set. */
void flushAllDataAndResetRDB(int flags) {
server.dirty += emptyDb(-1,flags,NULL);
if (server.rdb_child_pid != -1) killRDBChild();
if (server.saveparamslen > 0) {
/* Normally rdbSave() will reset dirty, but we don't want this here
* as otherwise FLUSHALL will not be replicated nor put into the AOF. */
int saved_dirty = server.dirty;
rdbSaveInfo rsi, *rsiptr;
rsiptr = rdbPopulateSaveInfo(&rsi);
rdbSave(server.rdb_filename,rsiptr);
server.dirty = saved_dirty;
}
server.dirty++;
...
}
|
SHUTDOWN 命令关闭服务。
服务运行过程中,一般情况是通过定期策略对内存数据进行持久化,内存数据和持久化文件数据不同步的,所以当服务正常退出或者重启,需要将内存数据进行持久化。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| void shutdownCommand(client *c) {
...
if (prepareForShutdown(flags) == C_OK) exit(0);
...
}
int prepareForShutdown(int flags) {
...
/* Create a new RDB file before exiting. */
if ((server.saveparamslen > 0 && !nosave) || save) {
...
rdbSaveInfo rsi, *rsiptr;
rsiptr = rdbPopulateSaveInfo(&rsi);
if (rdbSave(server.rdb_filename,rsiptr) != C_OK) {
...
}
}
...
}
|
3.3. 数据定期持久化
rdb 持久化是有条件限制的:
- 数据修改个数。
- 存盘时间间隔。
- 默认配置
从默认配置看,rdb 持久化不是实时的。时间间隔,最大 900 秒(15 分钟),最小 60 秒(1分钟),所以用 rdb 做持久化丢失数据风险比较大。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| # redis.conf
################################ SNAPSHOTTING ################################
#
# Save the DB on disk:
#
# save <seconds> <changes>
#
# Will save the DB if both the given number of seconds and the given
# number of write operations against the DB occurred.
#
# In the example below the behaviour will be to save:
# after 900 sec (15 min) if at least 1 key changed
# after 300 sec (5 min) if at least 10 keys changed
# after 60 sec if at least 10000 keys changed
#
# Note: you can disable saving completely by commenting out all "save" lines.
#
# It is also possible to remove all the previously configured save
# points by adding a save directive with a single empty string argument
# like in the following example:
#
# save ""
save 900 1
save 300 10
save 60 10000
|
1
2
3
4
5
| // rdb 定期存盘参数
struct saveparam {
time_t seconds; // 时间间隔
int changes; // 修改次数
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| #define CONFIG_BGSAVE_RETRY_DELAY 5 /* Wait a few secs before trying again. */
struct redisServer {
...
long long dirty; /* Changes to DB from the last save */
time_t lastsave; /* Unix time of last successful save */
time_t lastbgsave_try; /* Unix time of last attempted bgsave */
...
}
int hasActiveChildProcess() {
return server.rdb_child_pid != -1 ||
server.aof_child_pid != -1 ||
server.module_child_pid != -1;
}
int serverCron(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData) {
...
if (hasActiveChildProcess() || ldbPendingChildren()) {
// 如果后台有子进程正在进行活动,检查进程是否已经终止。
checkChildrenDone();
} else {
for (j = 0; j < server.saveparamslen; j++) {
struct saveparam *sp = server.saveparams+j;
// 需要满足默认数据保存频率条件。
// 如果上次存盘失败后,需要延时 CONFIG_BGSAVE_RETRY_DELAY 再进行操作。
if (server.dirty >= sp->changes &&
server.unixtime-server.lastsave > sp->seconds &&
(server.unixtime-server.lastbgsave_try >
CONFIG_BGSAVE_RETRY_DELAY ||
server.lastbgsave_status == C_OK))
{
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"%d changes in %d seconds. Saving...",
sp->changes, (int)sp->seconds);
rdbSaveInfo rsi, *rsiptr;
rsiptr = rdbPopulateSaveInfo(&rsi);
rdbSaveBackground(server.rdb_filename,rsiptr);
break;
}
}
...
}
...
// 我们在执行 BGSAVE 命令时,当时有其它子进程正在进行工作,所以该命令被安排延后处理。
if (!hasActiveChildProcess() &&
server.rdb_bgsave_scheduled &&
(server.unixtime-server.lastbgsave_try > CONFIG_BGSAVE_RETRY_DELAY ||
server.lastbgsave_status == C_OK))
{
rdbSaveInfo rsi, *rsiptr;
rsiptr = rdbPopulateSaveInfo(&rsi);
if (rdbSaveBackground(server.rdb_filename,rsiptr) == C_OK)
server.rdb_bgsave_scheduled = 0;
}
...
}
|
3.4. 重写 aof 文件
aof 文件在重写过程中,为了快速将数据落地,也会将文件保存成 rdb 文件,rdb 文件里会保存 aof 标识进行识别。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| # redis.conf
#
# When rewriting the AOF file, Redis is able to use an RDB preamble in the
# AOF file for faster rewrites and recoveries. When this option is turned
# on the rewritten AOF file is composed of two different stanzas:
#
# [RDB file][AOF tail]
#
# When loading Redis recognizes that the AOF file starts with the "REDIS"
# string and loads the prefixed RDB file, and continues loading the AOF
# tail.
aof-use-rdb-preamble yes
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| // 重写 aof 文件
int rewriteAppendOnlyFile(char *filename) {
...
startSaving(RDBFLAGS_AOF_PREAMBLE);
if (server.aof_use_rdb_preamble) {
int error;
if (rdbSaveRio(&aof,&error,RDBFLAGS_AOF_PREAMBLE,NULL) == C_ERR) {
errno = error;
goto werr;
}
}
...
}
// 加载 aof 文件
int loadAppendOnlyFile(char *filename) {
...
char sig[5]; /* "REDIS" */
if (fread(sig,1,5,fp) != 5 || memcmp(sig,"REDIS",5) != 0) {
/* No RDB preamble, seek back at 0 offset. */
if (fseek(fp,0,SEEK_SET) == -1) goto readerr;
} else {
...
// 从 rdb 文件加载 aof 需要的数据。
if (rdbLoadRio(&rdb,RDBFLAGS_AOF_PREAMBLE,NULL) != C_OK) {
...
}
...
}
...
}
|
3.5. 信号终止进程
服务运行过程中,一般情况是通过定期策略对内存数据进行持久化,内存数据和持久化文件数据不同步的,所以当服务正常退出或者重启,需要将内存数据进行持久化。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| void initServer(void) {
...
setupSignalHandlers();
...
}
#define SIGINT 2 /* interrupt */
#define SIGTERM 15 /* software termination signal from kill */
void setupSignalHandlers(void) {
struct sigaction act;
/* When the SA_SIGINFO flag is set in sa_flags then sa_sigaction is used.
* Otherwise, sa_handler is used. */
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
act.sa_flags = 0;
act.sa_handler = sigShutdownHandler;
sigaction(SIGTERM, &act, NULL);
sigaction(SIGINT, &act, NULL);
...
}
static void sigShutdownHandler(int sig) {
...
server.shutdown_asap = 1;
}
int serverCron(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData) {
...
/* We received a SIGTERM, shutting down here in a safe way, as it is
* not ok doing so inside the signal handler. */
if (server.shutdown_asap) {
if (prepareForShutdown(SHUTDOWN_NOFLAGS) == C_OK) exit(0);
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"SIGTERM received but errors trying to shut down the server, check the logs for more information");
server.shutdown_asap = 0;
}
...
}
|
3.6. 主从复制
主从复制,全量同步数据,可以通过 rdb 文件传输。rdb 文件可以采用硬盘备份方式;也可以无盘备份,数据不存盘,直接通过 socket 发送给其它服务。
从服务刚启动或因网络原因,与主服务长时间断开,重连后发现主从数据已经严重不匹配了,主服务需要将内存数据保存成 rdb 二进制压缩文件,传送给这些重新链接的服务。
一主多从架构,如果出现网络问题,极端情况,主服务要给多个从服务发送 rdb 文件数据,数据量大的话,可能会造成网络拥堵,所以从服务尽量少吧。如果应用场景确实需要,可以启用多级从服务(chained slaves (slaves of slaves)),避免主服务出现过载问题。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| /* State of slaves from the POV of the master. Used in client->replstate.
* In SEND_BULK and ONLINE state the slave receives new updates
* in its output queue. In the WAIT_BGSAVE states instead the server is waiting
* to start the next background saving in order to send updates to it. */
#define SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_START 6 /* We need to produce a new RDB file. */
#define SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_END 7 /* Waiting RDB file creation to finish. */
#define SLAVE_STATE_SEND_BULK 8 /* Sending RDB file to slave. */
#define SLAVE_STATE_ONLINE 9 /* RDB file transmitted, sending just updates. */
void syncCommand(client *c) {
...
/* Setup the slave as one waiting for BGSAVE to start. The following code
* paths will change the state if we handle the slave differently. */
c->replstate = SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_START;
...
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| void replicationCron(void) {
...
/* 如果使用无硬盘备份,主服务会在开始传送前等待一段时间(repl_diskless_sync_delay),
这过程中可能有多个服务链接上来需要全量同步数据的,那么一起同步。*/
if (!hasActiveChildProcess()) {
time_t idle, max_idle = 0;
int slaves_waiting = 0;
int mincapa = -1;
listNode *ln;
listIter li;
// 遍历从服务,确认是否需要主从复制。
listRewind(server.slaves,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *slave = ln->value;
if (slave->replstate == SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_START) {
idle = server.unixtime - slave->lastinteraction;
if (idle > max_idle) max_idle = idle;
slaves_waiting++;
mincapa = (mincapa == -1) ? slave->slave_capa :
(mincapa & slave->slave_capa);
}
}
if (slaves_waiting &&
(!server.repl_diskless_sync ||
max_idle > server.repl_diskless_sync_delay)) {
startBgsaveForReplication(mincapa);
}
}
...
}
int startBgsaveForReplication(int mincapa) {
...
if (rsiptr) {
if (socket_target)
retval = rdbSaveToSlavesSockets(rsiptr);
else
retval = rdbSaveBackground(server.rdb_filename,rsiptr);
}
...
}
|
4. 总结
rdb 作为持久化方式的一种,它是一种经过压缩的二进制数据。
rdb 这一块内容挺多的,一章节太长了,所以分开了两章,本章主要讲应用场景,文件结构请参考下一章 rdb 持久化 - 文件结构
5. 参考


