rdb 文件是一个经过压缩的二进制文件,上一章讲了 rdb 持久化 - 应用场景,本章主要讲述 rdb 文件的结构组成包含了哪些数据。
1. rdb 临时文件
redis 内存数据异步落地到临时 rdb 文件,成功存储后,临时文件覆盖原有文件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
/* flags on the purpose of rdb save or load */
#define RDBFLAGS_NONE 0
#define RDBFLAGS_AOF_PREAMBLE (1<<0)
#define RDBFLAGS_REPLICATION (1<<1)
#define REDIS_AUTOSYNC_BYTES (1024*1024*32) /* fdatasync every 32MB */
// 主进程 fork 子进程存盘
int rdbSaveBackground(char *filename, rdbSaveInfo *rsi) {
...
if ((childpid = redisFork()) == 0) {
...
/* Child */
retval = rdbSave(filename,rsi);
...
}
...
}
// 内存数据 -> 临时 rdb 文件 -> 覆盖原 rdb 文件
int rdbSave(char *filename, rdbSaveInfo *rsi) {
...
// 初始化 rdb 文件结构
rioInitWithFile(&rdb,fp);
startSaving(RDBFLAGS_NONE);
// 写文件缓存,缓存满 REDIS_AUTOSYNC_BYTES,缓存刷新到磁盘。
if (server.rdb_save_incremental_fsync)
rioSetAutoSync(&rdb,REDIS_AUTOSYNC_BYTES);
// 将内存数据写入 rio 文件
if (rdbSaveRio(&rdb,&error,RDBFLAGS_NONE,rsi) == C_ERR) {
errno = error;
goto werr;
}
/* fflush 是 libc 提供的方法,调用 write 函数写到磁盘[其实是写到内核的缓冲区]。
* fsync 是系统提供的系统调用,把内核缓冲刷到磁盘上。*/
if (fflush(fp) == EOF) goto werr;
if (fsync(fileno(fp)) == -1) goto werr;
if (fclose(fp) == EOF) goto werr;
if (rename(tmpfile,filename) == -1) {...}
...
}
2. 逐步持久化
内存可以逐步持久化到磁盘,缓存满 REDIS_AUTOSYNC_BYTES (32MB),缓存刷新到磁盘。这样将大数据分散开来,减少系统压力,避免一次写盘带来的问题。
1
2
# redis.conf
rdb-save-incremental-fsync yes
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
void rioSetAutoSync(rio *r, off_t bytes) {
if (r->write != rioFileIO.write) return;
r->io.file.autosync = bytes;
}
static size_t rioFileWrite(rio *r, const void *buf, size_t len) {
size_t retval;
retval = fwrite(buf,len,1,r->io.file.fp);
r->io.file.buffered += len;
if (r->io.file.autosync &&
r->io.file.buffered >= r->io.file.autosync)
{
fflush(r->io.file.fp);
redis_fsync(fileno(r->io.file.fp));
r->io.file.buffered = 0;
}
return retval;
}
3. 结构
粗略将 rdb 文件的结构元素添加到图表,可以看作是“伪代码”吧,有些元素是建立在一定条件下才会添加进去。
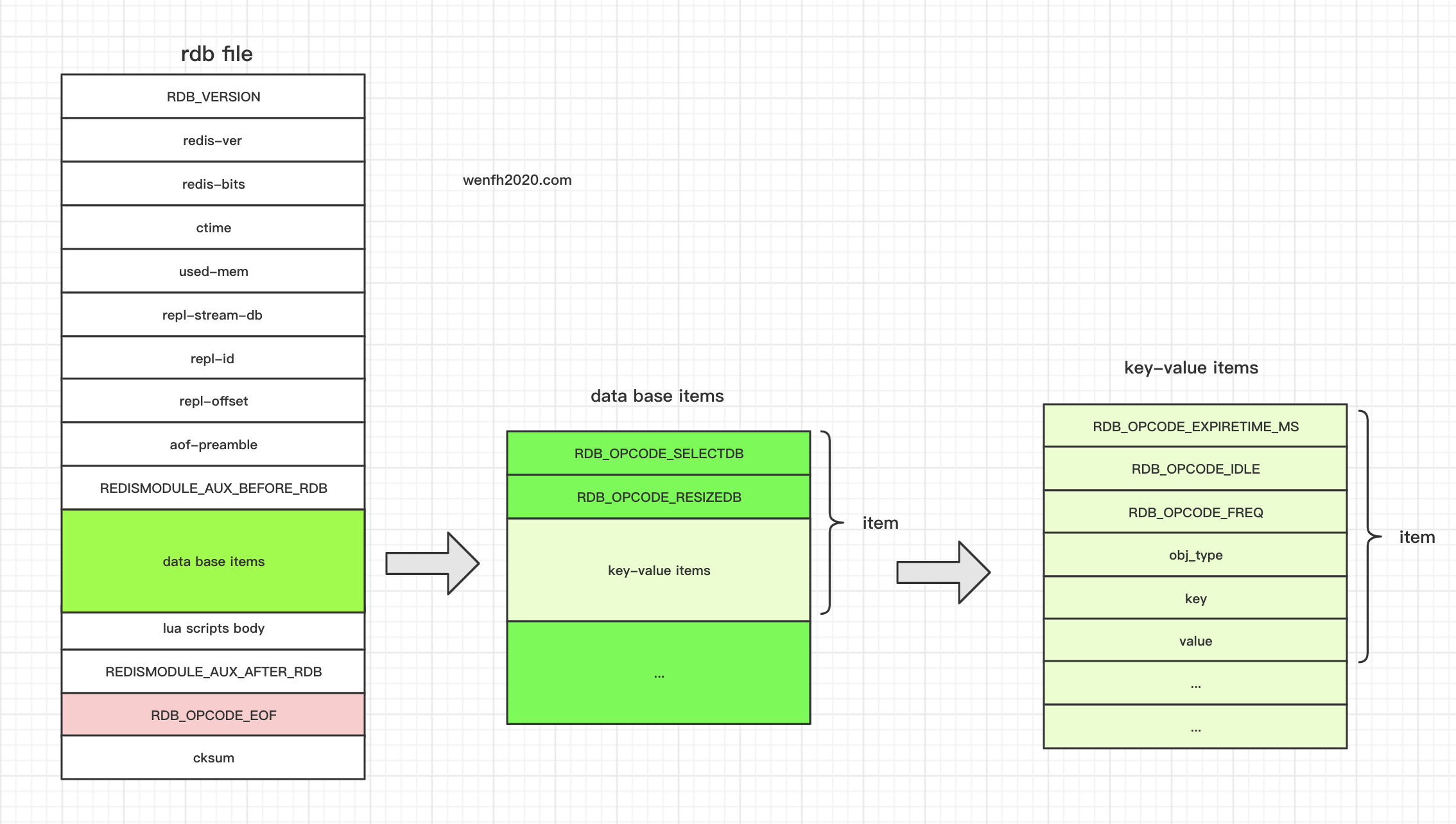
有兴趣的朋友,可以参考我的帖子:用 gdb 调试 redis,下个断点,走一下 redis 保存和加载 rdb 文件的工作流程。
3.1. 数据保存时序
从上图我们可以看到 rdb 文件的结构。整个文件是由不同类型的数据单元组成的(type + value) 。内存持久化为 rdb 文件,我们可以参考 rdbSaveRio。
redis 加载 rdb 文件时(
rdbLoadRio),也是先读出数据类型 (type),再根据数据类型,加载对应的数据——这样顺序将 rdb 文件数据加载到内存。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
/* Produces a dump of the database in RDB format sending it to the specified
* Redis I/O channel. */
int rdbSaveRio(rio *rdb, int *error, int rdbflags, rdbSaveInfo *rsi) {
...
snprintf(magic,sizeof(magic),"REDIS%04d",RDB_VERSION);
// 写入 rdb 版本号
if (rdbWriteRaw(rdb,magic,9) == -1) goto werr;
// 写入 redis 属性信息
if (rdbSaveInfoAuxFields(rdb,rdbflags,rsi) == -1) goto werr;
// 写入扩展插件‘before’数据
if (rdbSaveModulesAux(rdb, REDISMODULE_AUX_BEFORE_RDB) == -1) goto werr;
// 遍历数据库,落地数据。
for (j = 0; j < server.dbnum; j++) {
redisDb *db = server.db+j;
dict *d = db->dict;
if (dictSize(d) == 0) continue;
di = dictGetSafeIterator(d);
// 保存数据库 id
if (rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_OPCODE_SELECTDB) == -1) goto werr;
if (rdbSaveLen(rdb,j) == -1) goto werr;
// 保存数据库字典大小(db->dict),过期字典大小(db->expires)。
uint64_t db_size, expires_size;
db_size = dictSize(db->dict);
expires_size = dictSize(db->expires);
if (rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_OPCODE_RESIZEDB) == -1) goto werr;
if (rdbSaveLen(rdb,db_size) == -1) goto werr;
if (rdbSaveLen(rdb,expires_size) == -1) goto werr;
// 遍历数据库数据。
while((de = dictNext(di)) != NULL) {
sds keystr = dictGetKey(de);
robj key, *o = dictGetVal(de);
long long expire;
initStaticStringObject(key,keystr);
expire = getExpire(db,&key);
// 保存 key,value,expire。
if (rdbSaveKeyValuePair(rdb,&key,o,expire) == -1) goto werr;
/* When this RDB is produced as part of an AOF rewrite, move
* accumulated diff from parent to child while rewriting in
* order to have a smaller final write. */
if (rdbflags & RDBFLAGS_AOF_PREAMBLE &&
rdb->processed_bytes > processed+AOF_READ_DIFF_INTERVAL_BYTES)
{
processed = rdb->processed_bytes;
aofReadDiffFromParent();
}
}
dictReleaseIterator(di);
di = NULL; /* So that we don't release it again on error. */
}
/* If we are storing the replication information on disk, persist
* the script cache as well: on successful PSYNC after a restart, we need
* to be able to process any EVALSHA inside the replication backlog the
* master will send us. */
if (rsi && dictSize(server.lua_scripts)) {
di = dictGetIterator(server.lua_scripts);
while((de = dictNext(di)) != NULL) {
robj *body = dictGetVal(de);
if (rdbSaveAuxField(rdb,"lua",3,body->ptr,sdslen(body->ptr)) == -1)
goto werr;
}
dictReleaseIterator(di);
di = NULL; /* So that we don't release it again on error. */
}
// 写入扩展插件‘after’数据。
if (rdbSaveModulesAux(rdb, REDISMODULE_AUX_AFTER_RDB) == -1) goto werr;
// 保存 rdb 文件结束符。
if (rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_OPCODE_EOF) == -1) goto werr;
// 写入 crc64 检验码。
cksum = rdb->cksum;
memrev64ifbe(&cksum);
if (rioWrite(rdb,&cksum,8) == 0) goto werr;
return C_OK;
...
}
3.2. 保存集群复制信息
rdb 实现附加功能,保存服务数据复制的相关信息。当服务在某些数据复制场景下,需要 redis 进程的内存复制 id,复制位置,可以直接保存在 rdb 中,即便redis 服务重启或者服务角色发生转移(由主服务变成从服务),也可以从 rdb 文件中,获得相应的复制数据信息,不至于什么信息都没有,需要重新全量同步。
可以参考 redis 这两个源码改动:
- PSYNC2: Save replication ID/offset on RDB file.
- PSYNC2: different improvements to Redis replication.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
/* This structure can be optionally passed to RDB save/load functions in
* order to implement additional functionalities, by storing and loading
* metadata to the RDB file.
*
* Currently the only use is to select a DB at load time, useful in
* replication in order to make sure that chained slaves (slaves of slaves)
* select the correct DB and are able to accept the stream coming from the
* top-level master. */
typedef struct rdbSaveInfo {
/* Used saving and loading. */
int repl_stream_db; /* DB to select in server.master client. */
/* Used only loading. */
int repl_id_is_set; /* True if repl_id field is set. */
char repl_id[CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE+1]; /* Replication ID. */
long long repl_offset; /* Replication offset. */
} rdbSaveInfo;
// 保存复制副本相关信息。
int rdbSaveInfoAuxFields(rio *rdb, int rdbflags, rdbSaveInfo *rsi) {
...
if (rsi) {
if (rdbSaveAuxFieldStrInt(rdb,"repl-stream-db",rsi->repl_stream_db)
== -1) return -1;
if (rdbSaveAuxFieldStrStr(rdb,"repl-id",server.replid)
== -1) return -1;
if (rdbSaveAuxFieldStrInt(rdb,"repl-offset",server.master_repl_offset)
== -1) return -1;
}
...
}
3.3. 保存属性信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// 写入 redis 属性信息
int rdbSaveInfoAuxFields(rio *rdb, int rdbflags, rdbSaveInfo *rsi) {
int redis_bits = (sizeof(void*) == 8) ? 64 : 32;
int aof_preamble = (rdbflags & RDBFLAGS_AOF_PREAMBLE) != 0;
/* Add a few fields about the state when the RDB was created. */
// 写入 redis 版本号
if (rdbSaveAuxFieldStrStr(rdb,"redis-ver",REDIS_VERSION) == -1) return -1;
// 写入redis 工作的机器多少位。
if (rdbSaveAuxFieldStrInt(rdb,"redis-bits",redis_bits) == -1) return -1;
// rdb 写入数据时间
if (rdbSaveAuxFieldStrInt(rdb,"ctime",time(NULL)) == -1) return -1;
// 当前使用内存大小
if (rdbSaveAuxFieldStrInt(rdb,"used-mem",zmalloc_used_memory()) == -1) return -1;
// 存储从库信息,方便 (slaves of slaves) 数据同步
if (rsi) {
if (rdbSaveAuxFieldStrInt(rdb,"repl-stream-db",rsi->repl_stream_db)
== -1) return -1;
if (rdbSaveAuxFieldStrStr(rdb,"repl-id",server.replid)
== -1) return -1;
if (rdbSaveAuxFieldStrInt(rdb,"repl-offset",server.master_repl_offset)
== -1) return -1;
}
if (rdbSaveAuxFieldStrInt(rdb,"aof-preamble",aof_preamble) == -1) return -1;
return 1;
}
3.4. 保存 key-value
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
#define RDB_OPCODE_IDLE 248 /* LRU idle time. */
#define RDB_OPCODE_FREQ 249 /* LFU frequency. */
#define RDB_OPCODE_AUX 250 /* RDB aux field. */
#define RDB_OPCODE_EXPIRETIME_MS 252 /* Expire time in milliseconds. */
/* Save a key-value pair, with expire time, type, key, value.
* On error -1 is returned.
* On success if the key was actually saved 1 is returned, otherwise 0
* is returned (the key was already expired). */
int rdbSaveKeyValuePair(rio *rdb, robj *key, robj *val, long long expiretime) {
int savelru = server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LRU;
int savelfu = server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU;
// 保存数据到期时间。
if (expiretime != -1) {
if (rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_OPCODE_EXPIRETIME_MS) == -1) return -1;
if (rdbSaveMillisecondTime(rdb,expiretime) == -1) return -1;
}
// 保存数据 lru 时间,精度是秒,这样可以减少存储的空间。
if (savelru) {
uint64_t idletime = estimateObjectIdleTime(val);
idletime /= 1000; /* Using seconds is enough and requires less space.*/
if (rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_OPCODE_IDLE) == -1) return -1;
if (rdbSaveLen(rdb,idletime) == -1) return -1;
}
// 保存数据使用频率信息。
if (savelfu) {
uint8_t buf[1];
buf[0] = LFUDecrAndReturn(val);
// 使用频率是一个 0 - 255 的计数,只用一个字节保存即可。
if (rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_OPCODE_FREQ) == -1) return -1;
if (rdbWriteRaw(rdb,buf,1) == -1) return -1;
}
// 保存数据类型。
if (rdbSaveObjectType(rdb,val) == -1) return -1;
// 保存键数据。
if (rdbSaveStringObject(rdb,key) == -1) return -1;
// 保存键对应数据信息。
if (rdbSaveObject(rdb,val,key) == -1) return -1;
...
return 1;
}
// 数据对象,根据不同的结构类型,进行保存。
ssize_t rdbSaveObject(rio *rdb, robj *o, robj *key) {
...
if (o->type == OBJ_STRING) {
...
} else if (o->type == OBJ_LIST) {
...
} else if (o->type == OBJ_SET) {
...
} else if (o->type == OBJ_ZSET) {
...
} else if (o->type == OBJ_HASH) {
...
} else if (o->type == OBJ_STREAM) {
...
} else if (o->type == OBJ_MODULE) {
...
}
...
}

