redis 可能存在大量过期数据,一次性遍历检查不太现实。
redis 有丰富的数据结构,key-value, value 数据结构对象(redisObj)可能存储大量数据,key 过期了,value 也不建议在进程中实时回收。
为了保证系统高性能,每次处理一点点,逐渐完成大任务,“分而治之” 这是 redis 处理大任务的一贯作风。
1. 流程
主服务检查过期/删除过期逻辑 -> 删除过期键值 -> 异步/同步删除数据 -> 主从同步。
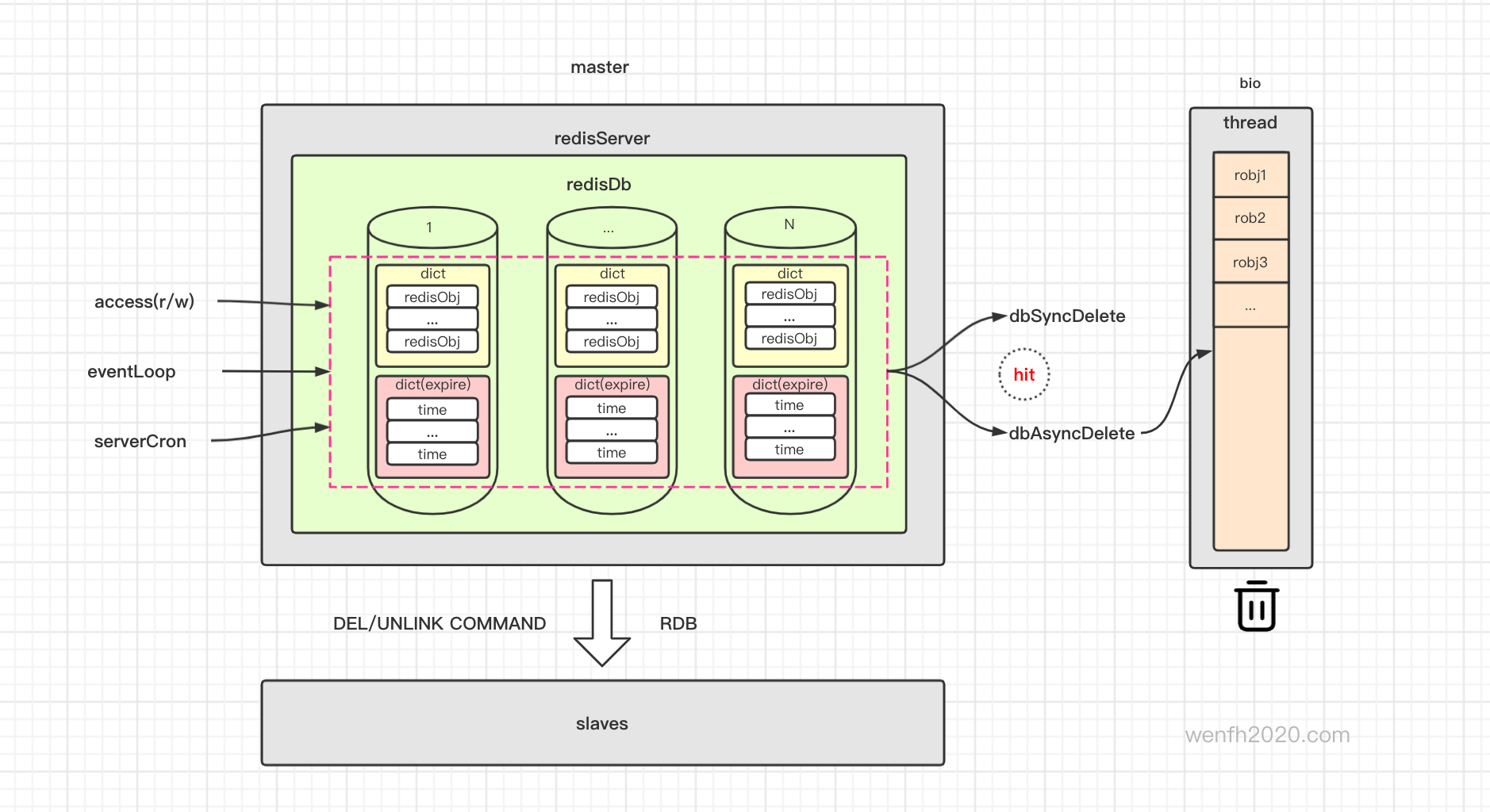
设计图来源:《redis 过期数据淘汰流程》
redis 数据库,数据内容和过期时间是分开保存。expires 保存了键值对应的过期时间。
1
2
3
4
5
typedef struct redisDb {
dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */
dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */
...
} redisDb;
2. 策略概述
2.1. 过期检查
过期数据检查有三个策略:
- 访问键值触发检查。访问包括外部读写命令,内部逻辑调用。
不可能每个过期键都能实时被访问触发,所以要结合其它策略。
- 事件驱动处理事件前触发快速检查。
将过期检查负载一点点分摊到每个事件处理中。
- 时钟定期慢速检查。
2.2. 数据回收
数据回收有同步和异步两种方式,配置文件可以设置,一般默认异步回收数据。
异步数据回收有两个策略:
- 小数据实时回收。
- 大数据放到任务队列,后台线程处理任务队列异步回收内存。
可以看看
bio.c的实现。
2.2.1. 同步
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
int dbSyncDelete(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
/* Deleting an entry from the expires dict will not free the sds of
* the key, because it is shared with the main dictionary. */
if (dictSize(db->expires) > 0)
dictDelete(db->expires, key->ptr);
if (dictDelete(db->dict, key->ptr) == DICT_OK) {
if (server.cluster_enabled)
slotToKeyDel(key);
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
2.2.2. 异步
unlink 逻辑删除 key,数据放在 bio 线程异步删除。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
#define LAZYFREE_THRESHOLD 64
int dbAsyncDelete(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
if (dictSize(db->expires) > 0) dictDelete(db->expires,key->ptr);
dictEntry *de = dictUnlink(db->dict,key->ptr);
if (de) {
robj *val = dictGetVal(de);
size_t free_effort = lazyfreeGetFreeEffort(val);
if (free_effort > LAZYFREE_THRESHOLD && val->refcount == 1) {
atomicIncr(lazyfree_objects,1);
// 删除数据对象,要注意对象计数,decrRefCount 删除。
bioCreateBackgroundJob(BIO_LAZY_FREE,val,NULL,NULL);
dictSetVal(db->dict,de,NULL);
}
}
if (de) {
dictFreeUnlinkedEntry(db->dict,de);
if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyDel(key);
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
3. 检查具体策略
3.1. 访问检查
3.1.1. expireIfNeeded
外部读写命令/内部逻辑调用,基本所有的键值读写操作都会触发 expireIfNeeded 过期检查。
db.c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
int expireIfNeeded(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
if (!keyIsExpired(db,key)) return 0;
if (server.masterhost != NULL) return 1;
server.stat_expiredkeys++;
// 传播数据更新,传播到集群中去,如果数据库是 `aof` 格式存储,更新落地 `aof` 文件。
propagateExpire(db,key,server.lazyfree_lazy_expire);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED, "expired",key,db->id);
return server.lazyfree_lazy_expire ? dbAsyncDelete(db,key) :
dbSyncDelete(db,key);
}
void propagateExpire(redisDb *db, robj *key, int lazy) {
robj *argv[2];
argv[0] = lazy ? shared.unlink : shared.del;
argv[1] = key;
incrRefCount(argv[0]);
incrRefCount(argv[1]);
// aof 存储,del/unlink 命令入库
if (server.aof_state != AOF_OFF)
feedAppendOnlyFile(server.delCommand, db->id, argv, 2);
// 同步 del/unlink 命令到从库
replicationFeedSlaves(server.slaves, db->id, argv, 2);
decrRefCount(argv[0]);
decrRefCount(argv[1]);
}
3.1.2. 修改/删除过期 key
部分命令会修改或删除过期时间。
| 命令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| del | 删除指定 key 。 |
| unlink | 逻辑删除指定 key,数据在线程异步删除。 |
| set | 设置一个键的值,ex 选项可以设置过期时间 |
| persist | 移除 key 的过期时间 |
| rename | 重命名 key,会删除原来 key 的过期时间。 |
| flushdb | 清空当前数据库。 |
| flushall | 清空所有数据。 |
| expire | 设置 key 的过期时间秒数。 |
| expireat | 设置一个 UNIX 时间戳的过期时间。 |
| pexpireat | 设置key到期 UNIX 时间戳,以毫秒为单位。 |
3.1.3. maxmemory 淘汰
超出最大内存 maxmemory,触发数据淘汰。淘汰合适的数据,可以参考《[redis 源码走读] maxmemory 数据淘汰策略
》。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
typedef struct redisObject {
...
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or
* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency
* and most significant 16 bits access time). */
...
} robj;
int processCommand(client *c) {
...
if (server.maxmemory && !server.lua_timedout) {
int out_of_memory = freeMemoryIfNeededAndSafe() == C_ERR;
...
}
...
}
int freeMemoryIfNeededAndSafe(void) {
if (server.lua_timedout || server.loading) return C_OK;
return freeMemoryIfNeeded();
}
3.2. 事件触发
在事件模型中,处理事件前,触发快速检查。将过期检查负载分散到各个事件中去。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
...
aeSetBeforeSleepProc(server.el,beforeSleep);
...
aeMain(server.el);
...
}
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
eventLoop->stop = 0;
while (!eventLoop->stop) {
if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL)
eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop);
aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS|AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP);
}
}
void beforeSleep(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
...
if (server.active_expire_enabled && server.masterhost == NULL)
activeExpireCycle(ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST);
...
}
3.3. 定期检查
通过时钟实现,定期检查过期键值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
void initServer(void) {
...
// 创建时钟事件
if (aeCreateTimeEvent(server.el, 1, serverCron, NULL, NULL) == AE_ERR) {
serverPanic("Can't create event loop timers.");
exit(1);
}
...
}
int serverCron(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData) {
...
databasesCron();
...
}
// 主库中检查即可,主库会同步结果到从库。
void databasesCron(void) {
if (server.active_expire_enabled) {
if (server.masterhost == NULL) {
// 主库慢速检查
activeExpireCycle(ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW);
} else {
// 从库如果设置了可写功能。
expireSlaveKeys();
}
}
...
}
redis 主逻辑在单进程主线程中实现,要保证不能影响主业务前提下,检查过期数据,不能太影响系统性能。主要三方面进行限制:
- 检查时间限制。
- 过期数据检查数量限制。
- 过期数据是否达到可接受比例。
被检查的数据到期了,系统会把该键值从字典中逻辑删除,切断数据与主逻辑联系。键值对应的数据,放到线程队列,后台线程进行异步回收(如果配置设置了异步回收)。
activeExpireCycle 检查有“快速”和“慢速”两种,时钟定期检查属于慢速类型。慢速检查被分配更多的检查时间。在一个时间范围内,到期数据最好不要太密集,因为系统发现到期数据很多,会迫切希望尽快处理掉这些过期数据,所以每次检查都要耗尽分配的时间片,直到到期数据到达一个可接受的密度比例。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
#define CRON_DBS_PER_CALL 16 /* 每次检查的数据库个数 */
#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_KEYS_PER_LOOP 20 /* Keys for each DB loop. */
#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION 1000 /* Microseconds. */
#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC 25 /* Max % of CPU to use. */
#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_ACCEPTABLE_STALE 10 /* % of stale keys after which
we do extra efforts. */
void activeExpireCycle(int type) {
/* Adjust the running parameters according to the configured expire
* effort. The default effort is 1, and the maximum configurable effort
* is 10. */
unsigned long
// 努力力度,默认 1,也就是遍历过期字典的力度,力度越大,遍历数量越多,但是性能损耗更多。
effort = server.active_expire_effort-1, /* Rescale from 0 to 9. */
// 每次循环遍历键值个数。力度越大,遍历个数越多。
config_keys_per_loop = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_KEYS_PER_LOOP +
ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_KEYS_PER_LOOP/4*effort,
// 快速遍历时间范围,力度越大,给予遍历时间越多。
config_cycle_fast_duration = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION +
ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION/4*effort,
// 慢速遍历检查时间片
config_cycle_slow_time_perc = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC +
2*effort,
// 已经到期数据 / 检查数据 比例。达到可以接受的比例。
config_cycle_acceptable_stale = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_ACCEPTABLE_STALE-
effort;
static unsigned int current_db = 0; /* Last DB tested. */
// 检查是否已经超时。
static int timelimit_exit = 0; /* Time limit hit in previous call? */
// 上一次快速检查数据起始时间。
static long long last_fast_cycle = 0; /* When last fast cycle ran. */
// iteration 迭代检查个数,每 16 次循环遍历,确认一下是否检查超时。
int j, iteration = 0;
// 每次周期检查的数据库个数。redis 默认有 16 个库。
int dbs_per_call = CRON_DBS_PER_CALL;
long long start = ustime(), timelimit, elapsed;
/* 如果链接已经停止了,那么要保留现场,不允许修改数据,也不允许到期淘汰数据。
* 使用命令 ‘pause’ 暂停 redis 工作或者主服务正在进行从服务的故障转移。*/
if (clientsArePaused()) return;
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST) {
/* 检查还没超时,但是到期数据密集度已经达到了可以接受的范围,不要快速检查了,
毕竟它是快速的,留给其它方式的检查。*/
if (!timelimit_exit &&
server.stat_expired_stale_perc < config_cycle_acceptable_stale)
return;
/* 限制快速检查频次,在两个 config_cycle_fast_duration 内,只能执行一次快速检查。 */
if (start < last_fast_cycle + (long long)config_cycle_fast_duration*2)
return;
last_fast_cycle = start;
}
if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum || timelimit_exit)
dbs_per_call = server.dbnum;
/* 检查过期数据,但是不能太损耗资源,得有个限制。server.hz 默认为 10
hz 是执行后台任务的频率,越大表明执行的次数越频繁,一般用默认值 10 */
timelimit = config_cycle_slow_time_perc*1000000/server.hz/100;
timelimit_exit = 0;
if (timelimit <= 0) timelimit = 1;
// 如果是快速模式,更改检查周期时间。
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST)
timelimit = config_cycle_fast_duration; /* in microseconds. */
/* 过期数据一般是异步方式,检查到过期数据,都是从字典中移除键值信息,
* 避免再次使用,但是数据回收放在后台回收,不是实时的,有数据有可能还存在数据库里。*/
// 检查数据个数。
long total_sampled = 0;
// 检查数据,数据已经过期的个数。
long total_expired = 0;
for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call && timelimit_exit == 0; j++) {
unsigned long expired, sampled;
redisDb *db = server.db+(current_db % server.dbnum);
current_db++;
// 遍历数据库检查过期数据,直到超出检查周期时间,或者过期数据比例已经很少了。
do {
// num 数据量,slots 哈希表大小(字典数据如果正在迁移,双表大小)
unsigned long num, slots;
long long now, ttl_sum;
int ttl_samples;
iteration++;
if ((num = dictSize(db->expires)) == 0) {
db->avg_ttl = 0;
break;
}
slots = dictSlots(db->expires);
now = mstime();
/* 过期存储数据结构是字典,数据经过处理后,字典存储的数据可能已经很少,
* 但是字典还是大字典,这样遍历数据有效命中率会很低,处理起来会浪费资源,
* 后面的访问会很快触发字典的缩容,缩容后再进行处理效率更高。*/
if (num && slots > DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE &&
(num*100/slots < 1)) break;
// 过期的数据个数。
expired = 0;
// 检查的数据个数。
sampled = 0;
// 没有过期的数据时间差之和。
ttl_sum = 0;
// 没有过期的数据个数。
ttl_samples = 0;
// 每次检查的数据限制。
if (num > config_keys_per_loop)
num = config_keys_per_loop;
/* 哈希表本质上是一个数组,可能有键值碰撞的数据,用链表将碰撞数据串联起来,
* 放在一个数组下标下,也就是放在哈希表的一个桶里。max_buckets 是最大能检查的桶个数。
* 跳过空桶,不处理。*/
long max_buckets = num*20;
// 当前已经检查哈希表桶的个数。
long checked_buckets = 0;
// 一个桶上有可能有多个数据。所以检查从两方面限制:一个是数据量,一个是桶的数量。
while (sampled < num && checked_buckets < max_buckets) {
for (int table = 0; table < 2; table++) {
// 如果 dict 没有正在进行扩容,不需要检查它的第二张表了。
if (table == 1 && !dictIsRehashing(db->expires)) break;
unsigned long idx = db->expires_cursor;
idx &= db->expires->ht[table].sizemask;
dictEntry *de = db->expires->ht[table].table[idx];
long long ttl;
checked_buckets++;
while(de) {
dictEntry *e = de;
de = de->next;
// 检查数据是否已经超时。
ttl = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(e)-now;
// 如果数据过期了,进行回收处理。
if (activeExpireCycleTryExpire(db,e,now)) expired++;
if (ttl > 0) {
/* We want the average TTL of keys yet
* not expired. */
ttl_sum += ttl;
ttl_samples++;
}
sampled++;
}
}
db->expires_cursor++;
}
total_expired += expired;
total_sampled += sampled;
if (ttl_samples) {
long long avg_ttl = ttl_sum/ttl_samples;
/* Do a simple running average with a few samples.
* We just use the current estimate with a weight of 2%
* and the previous estimate with a weight of 98%. */
if (db->avg_ttl == 0) db->avg_ttl = avg_ttl;
// 对没过期的数据,平均过期时间进行采样,上一次统计的平均时间占 98 %,本次占 2%。
db->avg_ttl = (db->avg_ttl/50)*49 + (avg_ttl/50);
}
/* 避免检查周期太长,当前数据库每 16 次循环迭代检查,检查是否超时,超时退出。*/
if ((iteration & 0xf) == 0) { /* check once every 16 iterations. */
elapsed = ustime()-start;
if (elapsed > timelimit) {
timelimit_exit = 1;
server.stat_expired_time_cap_reached_count++;
break;
}
}
/* 当前数据库,如果没有检查到数据,或者过期数据已经达到可接受比例
* 就退出该数据库检查,进入到下一个数据库检查。*/
} while (sampled == 0 ||
(expired*100/sampled) > config_cycle_acceptable_stale);
}
// 添加统计信息
elapsed = ustime()-start;
server.stat_expire_cycle_time_used += elapsed;
latencyAddSampleIfNeeded("expire-cycle",elapsed/1000);
double current_perc;
if (total_sampled) {
current_perc = (double)total_expired/total_sampled;
} else
current_perc = 0;
// 通过累加每次检查的过期概率影响,保存过期数据占数据比例。
server.stat_expired_stale_perc = (current_perc*0.05)+
(server.stat_expired_stale_perc*0.95);
}
- 删除过期数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
int activeExpireCycleTryExpire(redisDb *db, dictEntry *de, long long now) {
long long t = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de);
if (now > t) {
sds key = dictGetKey(de);
robj *keyobj = createStringObject(key,sdslen(key));
propagateExpire(db,keyobj,server.lazyfree_lazy_expire);
if (server.lazyfree_lazy_expire)
dbAsyncDelete(db,keyobj);
else
dbSyncDelete(db,keyobj);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED, "expired", keyobj, db->id);
trackingInvalidateKey(keyobj);
decrRefCount(keyobj);
server.stat_expiredkeys++;
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
4. 总结
- 要熟悉字典 dict 的实现原理,
dict是 redis 常用的几个基础数据结构之一。 - 看了几天源码,大致理解了键值过期处理策略。很多细节,感觉理解还是不够深刻,以后还是要结合实战多思考。
- redis 为了保证系统的高性能,采取了很多巧妙的“分治策略”,例如键值过期检查。过期数据检查和处理流程看,它不是一个实时的操作,有一定的延时,这样系统不能很好地保证数据一致性。有得必有失。
- 从定期回收策略的慢速检查中,我们可以看到,redis 处理到期数据,通过采样,判断到期数据的密集度。到期数据越密集,处理时间越多。我们在使用过程中,不应该把大量数据设置在同一个时间段到期。
redis.conf配置里面有比较详细的过期键处理策略描述。很多细节,可以参考源码注释和文档。文档极其详细,redis 作者的耐心,在开源项目中,是比较少见的 👍。例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
############################# LAZY FREEING ####################################
# Redis has two primitives to delete keys. One is called DEL and is a blocking
# deletion of the object. It means that the server stops processing new commands
# in order to reclaim all the memory associated with an object in a synchronous
# way. If the key deleted is associated with a small object, the time needed
# in order to execute the DEL command is very small and comparable to most other
# O(1) or O(log_N) commands in Redis. However if the key is associated with an
# aggregated value containing millions of elements, the server can block for
# a long time (even seconds) in order to complete the operation.
#
# For the above reasons Redis also offers non blocking deletion primitives
# such as UNLINK (non blocking DEL) and the ASYNC option of FLUSHALL and
# FLUSHDB commands, in order to reclaim memory in background. Those commands
# are executed in constant time. Another thread will incrementally free the
# object in the background as fast as possible.
#
# DEL, UNLINK and ASYNC option of FLUSHALL and FLUSHDB are user-controlled.
# It's up to the design of the application to understand when it is a good
# idea to use one or the other. However the Redis server sometimes has to
# delete keys or flush the whole database as a side effect of other operations.
# Specifically Redis deletes objects independently of a user call in the
# following scenarios:
#
# 1) On eviction, because of the maxmemory and maxmemory policy configurations,
# in order to make room for new data, without going over the specified
# memory limit.
# 2) Because of expire: when a key with an associated time to live (see the
# EXPIRE command) must be deleted from memory.
# 3) Because of a side effect of a command that stores data on a key that may
# already exist. For example the RENAME command may delete the old key
# content when it is replaced with another one. Similarly SUNIONSTORE
# or SORT with STORE option may delete existing keys. The SET command
# itself removes any old content of the specified key in order to replace
# it with the specified string.
# 4) During replication, when a replica performs a full resynchronization with
# its master, the content of the whole database is removed in order to
# load the RDB file just transferred.
#
# In all the above cases the default is to delete objects in a blocking way,
# like if DEL was called. However you can configure each case specifically
# in order to instead release memory in a non-blocking way like if UNLINK
# was called, using the following configuration directives:
lazyfree-lazy-eviction no
lazyfree-lazy-expire no
lazyfree-lazy-server-del no
replica-lazy-flush no
5. 参考
- [redis 源码走读] 字典(dict)
- 《redis 设计与实现》
- redis 过期策略及内存回收机制
- redis3.2配置文件redis.conf详细说明

