这个函数,在多线程场景与锁结合使用。如果某些线程没事干,就把它阻塞,等待唤醒,这样可以避免线程空跑,浪费系统资源。
1. pthread_cond_wait
The pthread_cond_wait() function atomically blocks the current thread waiting on the condition variable specified by cond, and releases the mutex specified by mutex. The waiting thread unblocks only after another thread calls pthread_cond_signal(3), or pthread_cond_broadcast(3) with the same condition variable, and the current thread reac- quires the lock on mutex.
2. 使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
bool Bio::bio_init() {
...
/* 创建线程。 */
pthread_create(&thread, &attr, bio_process_tasks, this);
...
}
/* 添加数据。 */
bool Bio::add_req_task(...) {
...
pthread_mutex_lock(&m_mutex);
m_req_tasks.push_back(task);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_mutex);
/* 发“信号”唤醒正在睡眠的一个线程。*/
pthread_cond_signal(&m_cond);
...
}
/* 线程处理函数。 */
void* Bio::bio_process_tasks(void* arg) {
...
while (!bio->m_stop_thread) {
...
pthread_mutex_lock(&bio->m_mutex);
while (bio->m_req_tasks.size() == 0) {
/* 没有数据就睡眠阻塞,等待唤醒。 */
pthread_cond_wait(&bio->m_cond, &bio->m_mutex);
}
/* 处理数据。*/
task = *bio->m_req_tasks.begin();
bio->m_req_tasks.erase(bio->m_req_tasks.begin());
pthread_mutex_unlock(&bio->m_mutex);
...
}
return nullptr;
}
3. 流程
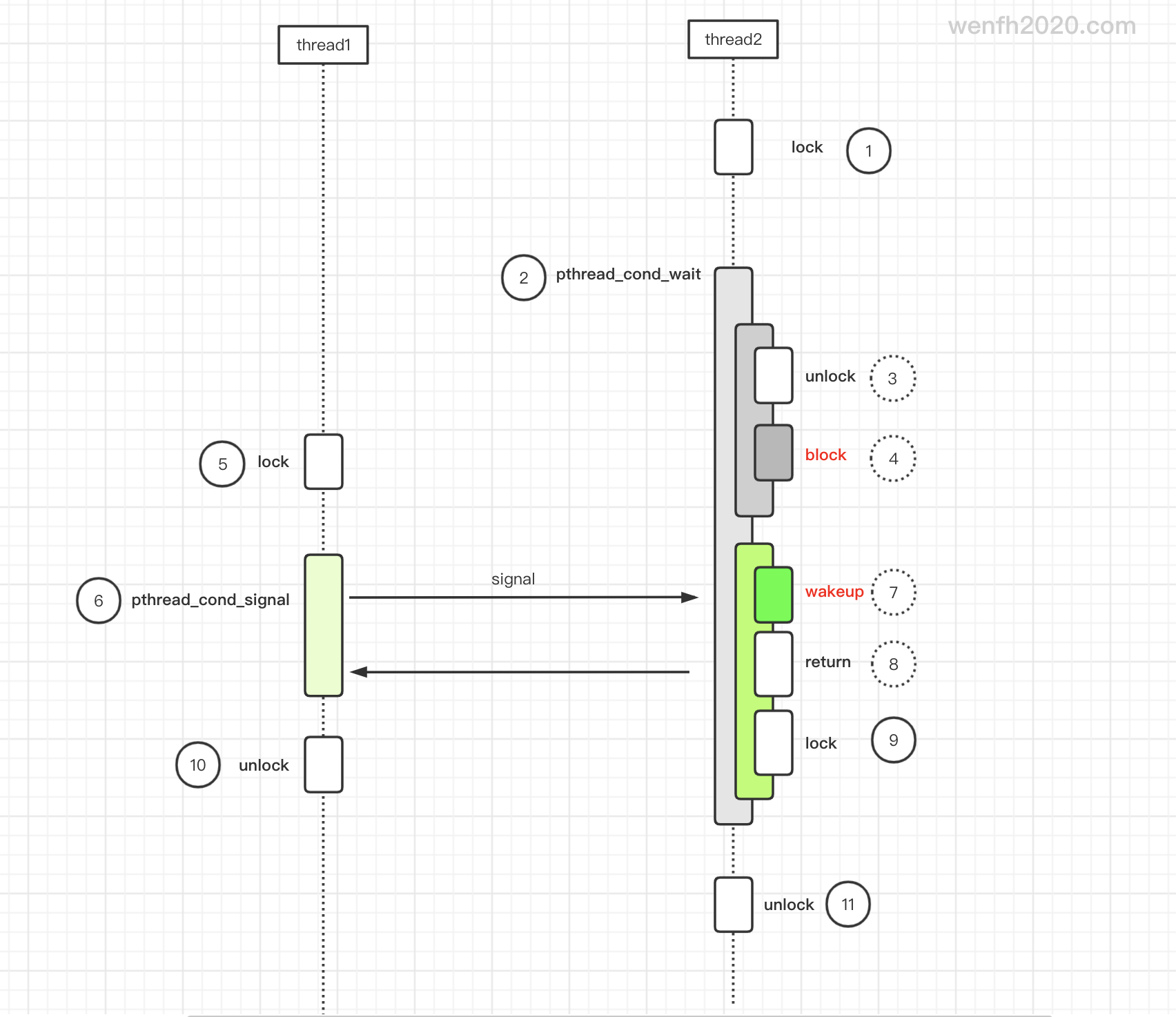
pthread_cond_wait 主要做这几件事。
- 解锁。
- 阻塞等待唤醒。
- 被唤醒(pthread_cond_signal / pthread_cond_broadcast)。
- “回复”唤醒者。
- 重新上锁。
4. glibc 源码
pthread_cond_wait 实现在 glibc 的 pthread_cond_wait.c 文件。个人不熟悉内核源码,理解可能有偏差 ^_^!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
/* pthread_cond_wait.c */
versioned_symbol (libpthread, __pthread_cond_wait, pthread_cond_wait, GLIBC_2_3_2);
int
__pthread_cond_wait (pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mutex) {
return __pthread_cond_wait_common (cond, mutex, NULL);
}
static __always_inline int
__pthread_cond_wait_common(pthread_cond_t* cond, pthread_mutex_t* mutex,
const struct timespec* abstime) {
...
/* 解锁。 */
err = __pthread_mutex_unlock_usercnt(mutex, 0);
...
unsigned int signals = atomic_load_acquire(cond->__data.__g_signals + g);
do {
while (1) {
...
/* If our group will be closed as indicated by the flag on signals,
don't bother grabbing a signal. */
if (signals & 1)
goto done;
/* If there is an available signal, don't block. */
if (signals != 0)
break;
...
if (abstime == NULL) {
/* 睡眠阻塞等待。 */
err = futex_wait_cancelable(
cond->__data.__g_signals + g, 0, private);
} else {
...
/* 限时阻塞等待。 */
err = futex_reltimed_wait_cancelable(...);
...
}
...
if (__glibc_unlikely(err == ETIMEDOUT)) {
__condvar_dec_grefs(cond, g, private);
/* 超时唤醒。 */
__condvar_cancel_waiting(cond, seq, g, private);
result = ETIMEDOUT;
goto done;
}
...
}
}
...
/* “回复”唤醒者。 */
futex_wake(cond->__data.__g_signals + g, 1, private);
...
done:
/* 确认唤醒。 */
__condvar_confirm_wakeup(cond, private);
/* 上锁。*/
err = __pthread_mutex_cond_lock(mutex);
/* XXX Abort on errors that are disallowed by POSIX? */
return (err != 0) ? err : result;
}

