本文基于 tcp,走读 socket 的(Linux - 5.0.1 下载)内核源码实现。
socket 是管理网络通信的对象,适合本地或网络环境的进程间通信,它主要分两部分:与文件系统关系密切的部分,与通信关系密切的部分。
1. 应用层
应用层创建 socket 对象返回整型的文件描述符。详细参考(文档 - 可能要翻墙)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
/* family:被称为协议族,或者协议域。
* type:套接字类型。
* protocol:某个协议的类型常值,可以设置为 0。
* return:返回整型的文件描述符,如果返回 -1 就失败。
*/
#include <sys/socket.h>
int socket(int domain/family, int type, int protocol);
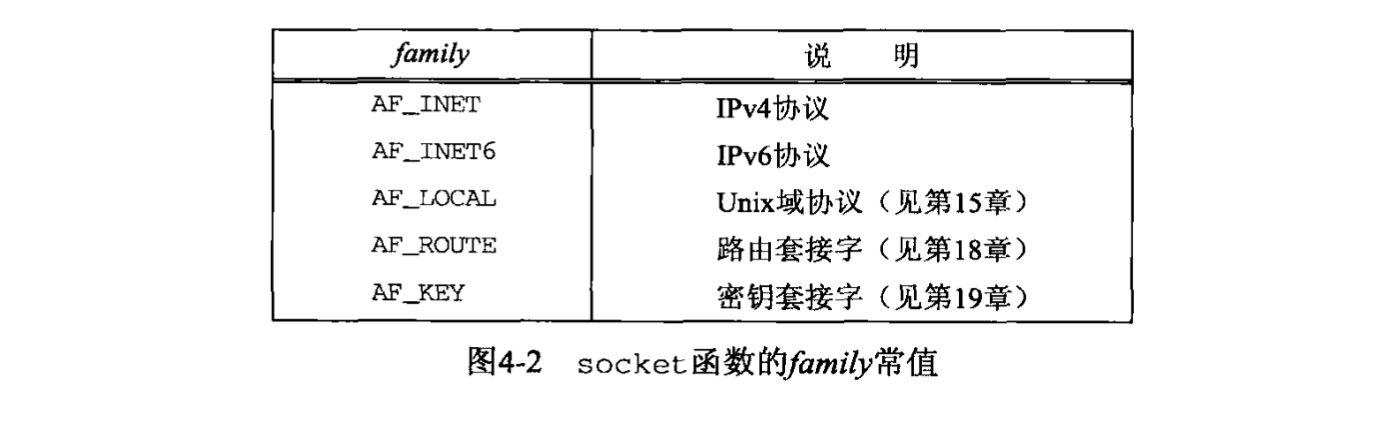

图片来源:《UNIX 网络编程_卷1》
2. 系统调用
从用户层到内核系统调用流程:user(socket()) –> glibc –> kernel。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# System.map
ffffffff81792870 T __x64_sys_socket
# socket
__do_sys_socket() (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:1355)
__se_sys_socket() (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:1353)
__x64_sys_socket(const struct pt_regs * regs) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:1353)
do_syscall_64(unsigned long nr, struct pt_regs * regs) (/root/linux-5.0.1/arch/x86/entry/common.c:290)
entry_SYSCALL_64() (/root/linux-5.0.1/arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:175)
3. socket 结构
socket 结构主要分两部分:与文件系统关系密切的部分,与通信关系密切的部分。

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
/** include/linux/net.h
* struct socket - general BSD socket
* @state: socket state (%SS_CONNECTED, etc)
* @type: socket type (%SOCK_STREAM, etc)
* @flags: socket flags (%SOCK_NOSPACE, etc)
* @ops: protocol specific socket operations
* @file: File back pointer for gc
* @sk: internal networking protocol agnostic socket representation
* @wq: wait queue for several uses
*/
struct socket {
socket_state state;
short type;
unsigned long flags;
struct socket_wq *wq;
struct file *file;
struct sock *sk;
const struct proto_ops *ops;
};
/* include/linux/net.h */
struct proto_ops {
...
}
/* include/net/sock.h */
struct tcp_sock {
/* inet_connection_sock has to be the first member of tcp_sock */
struct inet_connection_sock inet_conn;
...
}
struct inet_connection_sock {
struct inet_sock icsk_inet;
...
}
/* include/net/inet_sock.h */
struct inet_sock {
/* sk and pinet6 has to be the first two members of inet_sock */
struct sock sk;
...
}
struct sock {
struct sock_common __sk_common;
...
};
4. 创建 socket
函数调用关系。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
#------------------- *用户态* ---------------------------
socket
#------------------- *内核态* ---------------------------
__x64_sys_socket # 内核系统调用。
__sys_socket # net/socket.c
|-- sock_create # net/socket.c
|-- __sock_create # net/socket.c
#------------------- 文件部分 ---------------------------
|-- sock_alloc # net/socket.c
|-- new_inode_pseudo # fs/inode.c
|-- alloc_inode # fs/inode.c
|-- sock_alloc_inode # net/socket.c
|-- kmem_cache_alloc
#------------------- 网络部分 ---------------------------
|-- inet_create # pf->create -- af_inet.c
|-- sk_alloc # net/core/sock.c
|-- sk_prot_alloc # net/core/sock.c
|-- kmem_cache_alloc
|-- inet_sk
|-- sock_init_data # net/core/sock.c
|-- sk_init_common # net/core/sock.c
|-- timer_setup
|-- sk->sk_prot->init(sk) # tcp_v4_init_sock -- net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c
|-- tcp_init_sock
#------------------- 文件+网络+关联进程 ------------------------
|-- sock_map_fd # net/socket.c
|-- get_unused_fd_flags # fs/file.c -- 进程分配空闲 fd。
|-- sock_alloc_file # net/socket.c
|-- alloc_file_pseudo # fs/file_table.c
|-- fd_install # fs/file.c
|-- __fd_install # fs/file.c
|-- fdt = rcu_dereference_sched(files->fdt);
|-- rcu_assign_pointer(fdt->fd[fd], file); # file 关联到进程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
int __sys_socket(int family, int type, int protocol) {
struct socket *sock;
...
retval = sock_create(family, type, protocol, &sock);
if (retval < 0)
return retval;
return sock_map_fd(sock, flags & (O_CLOEXEC | O_NONBLOCK));
}
int sock_create(int family, int type, int protocol, struct socket **res) {
return __sock_create(current->nsproxy->net_ns, family, type, protocol, res, 0);
}
int __sock_create(struct net *net, int family, int type, int protocol,
struct socket **res, int kern) {
int err;
struct socket *sock;
const struct net_proto_family *pf;
...
sock = sock_alloc();
...
pf = rcu_dereference(net_families[family]);
...
err = pf->create(net, sock, protocol, kern);
...
*res = sock;
return 0;
...
}
4.1. 文件部分
Linux 系统一切皆文件,Linux 通过 vfs(虚拟文件系统)管理文件,内核为 socket 定义了一种特殊的文件类型,形成了一种特殊的文件系统:sockfs,系统初始化时,进行安装。
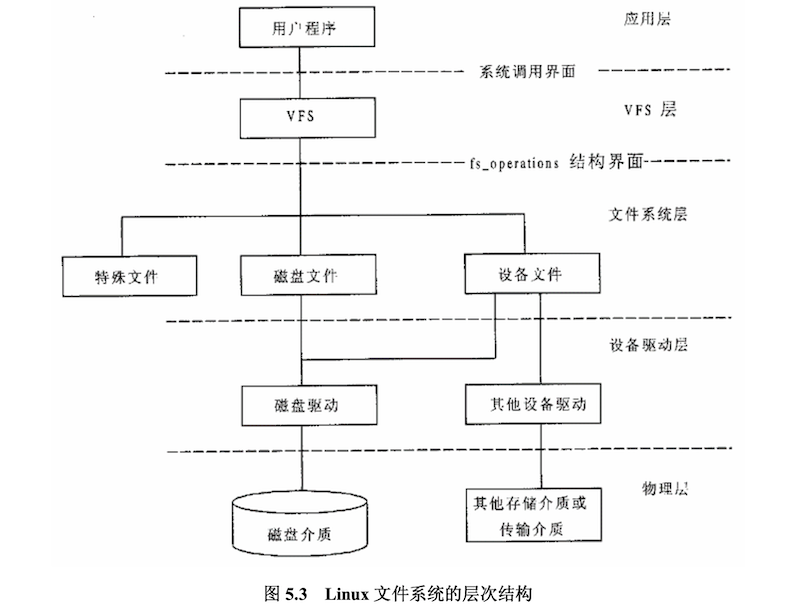
图片来源:《Linux 内核源代码情景分析》- 第五章 - 文件系统
创建一个 socket,要把 socket 关联到一个已打开文件,方便进程进行管理。
- 相关结构。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
/* include/linux/mount.h */
struct vfsmount {
struct dentry *mnt_root; /* root of the mounted tree */
struct super_block *mnt_sb; /* pointer to superblock */
int mnt_flags;
} __randomize_layout;
/* net/socket.c */
static struct vfsmount *sock_mnt __read_mostly;
/* sock 文件类型。 */
static struct file_system_type sock_fs_type = {
.name = "sockfs",
.mount = sockfs_mount,
.kill_sb = kill_anon_super,
};
/* sock 文件操作。 */
static const struct super_operations sockfs_ops = {
.alloc_inode = sock_alloc_inode,
.destroy_inode = sock_destroy_inode,
.statfs = simple_statfs,
};
/* include/sock.h
* sock 与 inode 文件节点关联结构。*/
struct socket_alloc {
struct socket socket;
struct inode vfs_inode;
};
/* include/net/sock.h
* 从文件节点结构获得 socket 成员。*/
static inline struct socket *SOCKET_I(struct inode *inode) {
return &container_of(inode, struct socket_alloc, vfs_inode)->socket;
}
/* include/linux/fs.h */
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
...
} __randomize_layout;
/* net/socket.c
* Socket files have a set of 'special' operations as well as the generic file ones. These don't appear
* in the operation structures but are done directly via the socketcall() multiplexor.
*/
static const struct file_operations socket_file_ops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.read_iter = sock_read_iter,
.write_iter = sock_write_iter,
.poll = sock_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = sock_ioctl,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_ioctl = compat_sock_ioctl,
#endif
.mmap = sock_mmap,
.release = sock_close,
.fasync = sock_fasync,
.sendpage = sock_sendpage,
.splice_write = generic_splice_sendpage,
.splice_read = sock_splice_read,
};
- 函数调用堆栈
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
sockfs_mount(struct file_system_type * fs_type, int flags, const char * dev_name, void * data) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:357)
mount_fs(struct file_system_type * type, int flags, const char * name, void * data) (/root/linux-5.0.1/fs/super.c:1258)
vfs_kern_mount(struct file_system_type * type, int flags, const char * name, void * data) (/root/linux-5.0.1/fs/namespace.c:959)
kern_mount_data(struct file_system_type * type, void * data) (/root/linux-5.0.1/fs/namespace.c:3301)
sock_init() (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:2737)
...
kernel_init(void * unused) (/root/linux-5.0.1/init/main.c:1054)
...
- 系统初始化,安装 sockfs。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
/* ./net/socket.c */
static int __init sock_init(void) {
...
sock_mnt = kern_mount(&sock_fs_type);
...
}
core_initcall(sock_init); /* early initcall */
/* 初始化的时候绑定 socket 的信息。*/
static struct dentry *sockfs_mount(struct file_system_type *fs_type,
int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data) {
return mount_pseudo_xattr(fs_type, "socket:", &sockfs_ops,
sockfs_xattr_handlers,
&sockfs_dentry_operations, SOCKFS_MAGIC);
}
- 创建 socket_alloc 对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
struct socket *sock_alloc(void) {
struct inode *inode;
struct socket *sock;
/* 创建文件节点。 */
inode = new_inode_pseudo(sock_mnt->mnt_sb);
if (!inode)
return NULL;
sock = SOCKET_I(inode);
inode->i_ino = get_next_ino();
inode->i_mode = S_IFSOCK | S_IRWXUGO;
inode->i_uid = current_fsuid();
inode->i_gid = current_fsgid();
inode->i_op = &sockfs_inode_ops;
return sock;
}
struct inode *new_inode_pseudo(struct super_block *sb) {
struct inode *inode = alloc_inode(sb);
...
return inode;
}
static struct inode *alloc_inode(struct super_block *sb) {
struct inode *inode;
if (sb->s_op->alloc_inode)
/* socket 调用这个。 */
inode = sb->s_op->alloc_inode(sb);
...
return inode;
}
/* 初始化 socket 结构成员。 */
static struct inode *sock_alloc_inode(struct super_block *sb) {
struct socket_alloc *ei;
struct socket_wq *wq;
ei = kmem_cache_alloc(sock_inode_cachep, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!ei)
return NULL;
wq = kmalloc(sizeof(*wq), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!wq) {
kmem_cache_free(sock_inode_cachep, ei);
return NULL;
}
init_waitqueue_head(&wq->wait);
wq->fasync_list = NULL;
wq->flags = 0;
ei->socket.wq = wq;
ei->socket.state = SS_UNCONNECTED;
ei->socket.flags = 0;
ei->socket.ops = NULL;
ei->socket.sk = NULL;
ei->socket.file = NULL;
return &ei->vfs_inode;
}
- sock 与进程(task_struct)关联。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
static int sock_map_fd(struct socket *sock, int flags) {
struct file *newfile;
/* 进程分配空闲 fd。 */
int fd = get_unused_fd_flags(flags);
if (unlikely(fd < 0)) {
sock_release(sock);
return fd;
}
/* 进程为 sock 分配新的文件。 */
newfile = sock_alloc_file(sock, flags, NULL);
if (likely(!IS_ERR(newfile))) {
/* fd 与 file 进行关联。 */
fd_install(fd, newfile);
return fd;
}
...
}
struct file *sock_alloc_file(struct socket *sock, int flags, const char *dname) {
...
file = alloc_file_pseudo(SOCK_INODE(sock), sock_mnt, dname,
O_RDWR | (flags & O_NONBLOCK),
&socket_file_ops);
...
sock->file = file;
file->private_data = sock;
return file;
}
void fd_install(unsigned int fd, struct file *file) {
__fd_install(current->files, fd, file);
}
void __fd_install(struct files_struct *files, unsigned int fd,
struct file *file) {
struct fdtable *fdt;
...
fdt = rcu_dereference_sched(files->fdt);
...
rcu_assign_pointer(fdt->fd[fd], file);
..
}
4.2. 网络部分
协议:socket –> 传输层 –> 网络层。
- net_proto_family:网域(PF_INET/AF_INET)数据结构。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
/* ./include/linux/net.h */
struct net_proto_family {
int family;
int (*create)(struct net *net, struct socket *sock, int protocol, int kern);
struct module *owner;
};
/* ./net/ipv4/af_inet.c */
static const struct net_proto_family inet_family_ops = {
.family = PF_INET,
.create = inet_create,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
# 保存网域数据结构指针到 net_families[] 数组。
sock_register(const struct net_proto_family * ops) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:2661)
inet_init() (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/af_inet.c:1927)
...
kernel_init(void * unused) (/root/linux-5.0.1/init/main.c:1054)
...
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
/**
* sock_register - add a socket protocol handler
* @ops: description of protocol
*
* This function is called by a protocol handler that wants to
* advertise its address family, and have it linked into the
* socket interface. The value ops->family corresponds to the
* socket system call protocol family.
*/
int sock_register(const struct net_proto_family *ops) {
...
rcu_assign_pointer(net_families[ops->family], ops);
...
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(sock_register);
- inet_protosw。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
/* ./include/net/protocol.h
* This is used to register socket interfaces for IP protocols. */
struct inet_protosw {
struct list_head list;
/* These two fields form the lookup key. */
unsigned short type; /* This is the 2nd argument to socket(2). */
unsigned short protocol; /* This is the L4 protocol number. */
struct proto *prot;
const struct proto_ops *ops;
unsigned char flags; /* See INET_PROTOSW_* below. */
};
/* af_inet.c
* Upon startup we insert all the elements in inetsw_array[] into
* the linked list inetsw.
*/
static struct inet_protosw inetsw_array[] = {
{
.type = SOCK_STREAM,
.protocol = IPPROTO_TCP,
.prot = &tcp_prot,
.ops = &inet_stream_ops,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT | INET_PROTOSW_ICSK,
},
...
};
- proto_ops。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
/* net/ipv4/af_inet.c */
const struct proto_ops inet_stream_ops = {
.family = PF_INET,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.release = inet_release,
.bind = inet_bind,
.connect = inet_stream_connect,
.socketpair = sock_no_socketpair,
.accept = inet_accept,
...
};
EXPORT_SYMBOL(inet_stream_ops);
- proto。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
/* include/net/sock.h
* Networking protocol blocks we attach to sockets.
* socket layer -> transport layer interface
*/
struct proto {
void (*close)(struct sock *sk, long timeout);
int (*pre_connect)(struct sock *sk, struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len);
int (*connect)(struct sock *sk, struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len);
int (*disconnect)(struct sock *sk, int flags);
struct sock * (*accept)(struct sock *sk, int flags, int *err, bool kern);
...
} __randomize_layout;
/* net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c */
struct proto tcp_prot = {
.name = "TCP",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.close = tcp_close,
.pre_connect = tcp_v4_pre_connect,
.connect = tcp_v4_connect,
.disconnect = tcp_disconnect,
.accept = inet_csk_accept,
...
.obj_size = sizeof(struct tcp_sock),
...
};
EXPORT_SYMBOL(tcp_prot);
1
2
3
4
5
# 初始化 tcp 协议。
proto_register(struct proto * prot, int alloc_slab) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/core/sock.c:3209)
inet_init() (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/af_inet.c:1907)
...
kernel_init(void * unused) (/root/linux-5.0.1/init/main.c:1054)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
static int __init inet_init(void) {
...
rc = proto_register(&tcp_prot, 1);
...
}
/* 为 tcp 协议分配空间。*/
int proto_register(struct proto *prot, int alloc_slab) {
if (alloc_slab) {
prot->slab = kmem_cache_create_usercopy(prot->name,
prot->obj_size, 0,
SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN | SLAB_ACCOUNT |
prot->slab_flags,
prot->useroffset, prot->usersize,
NULL);
...
}
/* 分配的空间其实是 tcp_sock,struct proto --> struct proto tcp_prot.obj_size */
static struct sock *sk_prot_alloc(struct proto *prot, gfp_t priority, int family) {
struct sock *sk;
struct kmem_cache *slab;
slab = prot->slab;
if (slab != NULL) {
sk = kmem_cache_alloc(slab, priority & ~__GFP_ZERO);
if (!sk)
return sk;
if (priority & __GFP_ZERO)
sk_prot_clear_nulls(sk, prot->obj_size);
}
...
}
- 详细源码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
static int inet_create(struct net *net, struct socket *sock, int protocol, int kern) {
struct sock *sk;
struct inet_protosw *answer;
struct inet_sock *inet;
struct proto *answer_prot;
...
sock->state = SS_UNCONNECTED;
/* Look for the requested type/protocol pair. */
lookup_protocol:
...
/* 查找对应的协议。 */
list_for_each_entry_rcu(answer, &inetsw[sock->type], list) {
...
}
...
sock->ops = answer->ops;
answer_prot = answer->prot;
answer_flags = answer->flags;
...
/* 为 sock 分配空间。 */
sk = sk_alloc(net, PF_INET, GFP_KERNEL, answer_prot, kern);
...
sock_init_data(sock, sk);
...
if (sk->sk_prot->init) {
/* tcp_v4_init_sock */
err = sk->sk_prot->init(sk);
...
}
...
out:
return err;
...
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
/*
* sk_alloc - All socket objects are allocated here
* @net: the applicable net namespace
* @family: protocol family
* @priority: for allocation (%GFP_KERNEL, %GFP_ATOMIC, etc)
* @prot: struct proto associated with this new sock instance
* @kern: is this to be a kernel socket?
*/
struct sock *sk_alloc(struct net *net, int family, gfp_t priority,
struct proto *prot, int kern)
{
struct sock *sk;
sk = sk_prot_alloc(prot, priority | __GFP_ZERO, family);
if (sk) {
sk->sk_family = family;
/*
* See comment in struct sock definition to understand
* why we need sk_prot_creator -acme
*/
sk->sk_prot = sk->sk_prot_creator = prot;
sk->sk_kern_sock = kern;
sock_lock_init(sk);
...
sock_net_set(sk, net);
...
}
return sk;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
void sock_init_data(struct socket *sock, struct sock *sk) {
sk_init_common(sk);
sk->sk_send_head = NULL;
timer_setup(&sk->sk_timer, NULL, 0);
sk->sk_allocation = GFP_KERNEL;
sk->sk_rcvbuf = sysctl_rmem_default;
sk->sk_sndbuf = sysctl_wmem_default;
sk->sk_state = TCP_CLOSE;
sk_set_socket(sk, sock);
sock_set_flag(sk, SOCK_ZAPPED);
if (sock) {
sk->sk_type = sock->type;
sk->sk_wq = sock->wq;
sock->sk = sk;
sk->sk_uid = SOCK_INODE(sock)->i_uid;
} else {
sk->sk_wq = NULL;
sk->sk_uid = make_kuid(sock_net(sk)->user_ns, 0);
}
...
sk->sk_state_change = sock_def_wakeup;
sk->sk_data_ready = sock_def_readable;
sk->sk_write_space = sock_def_write_space;
sk->sk_error_report = sock_def_error_report;
sk->sk_destruct = sock_def_destruct;
sk->sk_frag.page = NULL;
sk->sk_frag.offset = 0;
sk->sk_peek_off = -1;
sk->sk_peer_pid = NULL;
sk->sk_peer_cred = NULL;
sk->sk_write_pending = 0;
sk->sk_rcvlowat = 1;
sk->sk_rcvtimeo = MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT;
sk->sk_sndtimeo = MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT;
sk->sk_stamp = SK_DEFAULT_STAMP;
#if BITS_PER_LONG==32
seqlock_init(&sk->sk_stamp_seq);
#endif
atomic_set(&sk->sk_zckey, 0);
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLL
sk->sk_napi_id = 0;
sk->sk_ll_usec = sysctl_net_busy_read;
#endif
sk->sk_max_pacing_rate = ~0UL;
sk->sk_pacing_rate = ~0UL;
sk->sk_pacing_shift = 10;
sk->sk_incoming_cpu = -1;
...
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(sock_init_data);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
static void sk_init_common(struct sock *sk) {
/* 传输层的接收和发送数据缓冲区。 */
skb_queue_head_init(&sk->sk_receive_queue);
skb_queue_head_init(&sk->sk_write_queue);
...
}
static int tcp_v4_init_sock(struct sock *sk) {
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
tcp_init_sock(sk);
...
}
/* Address-family independent initialization for a tcp_sock.
*
* NOTE: A lot of things set to zero explicitly by call to
* sk_alloc() so need not be done here.
*/
void tcp_init_sock(struct sock *sk) {
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
tp->out_of_order_queue = RB_ROOT;
sk->tcp_rtx_queue = RB_ROOT;
tcp_init_xmit_timers(sk);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&tp->tsq_node);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&tp->tsorted_sent_queue);
icsk->icsk_rto = TCP_TIMEOUT_INIT;
tp->mdev_us = jiffies_to_usecs(TCP_TIMEOUT_INIT);
minmax_reset(&tp->rtt_min, tcp_jiffies32, ~0U);
/* So many TCP implementations out there (incorrectly) count the
* initial SYN frame in their delayed-ACK and congestion control
* algorithms that we must have the following bandaid to talk
* efficiently to them. -DaveM
*/
tp->snd_cwnd = TCP_INIT_CWND;
/* There's a bubble in the pipe until at least the first ACK. */
tp->app_limited = ~0U;
/* See draft-stevens-tcpca-spec-01 for discussion of the
* initialization of these values.
*/
tp->snd_ssthresh = TCP_INFINITE_SSTHRESH;
tp->snd_cwnd_clamp = ~0;
tp->mss_cache = TCP_MSS_DEFAULT;
tp->reordering = sock_net(sk)->ipv4.sysctl_tcp_reordering;
tcp_assign_congestion_control(sk);
tp->tsoffset = 0;
tp->rack.reo_wnd_steps = 1;
sk->sk_state = TCP_CLOSE;
sk->sk_write_space = sk_stream_write_space;
sock_set_flag(sk, SOCK_USE_WRITE_QUEUE);
icsk->icsk_sync_mss = tcp_sync_mss;
/* 发送缓冲区大小。 */
sk->sk_sndbuf = sock_net(sk)->ipv4.sysctl_tcp_wmem[1];
/* 接收缓冲区大小。 */
sk->sk_rcvbuf = sock_net(sk)->ipv4.sysctl_tcp_rmem[1];
sk_sockets_allocated_inc(sk);
sk->sk_route_forced_caps = NETIF_F_GSO;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(tcp_init_sock);

