本文将通过测试,重现 nginx(1.20.1) 的惊群现象,并深入 Linux (5.0.1) 内核源码,剖析惊群原因。
- 探索惊群 ①
- 探索惊群 ② - accept
- 探索惊群 ③ - nginx 惊群现象(★)
- 探索惊群 ④ - nginx - accept_mutex
- 探索惊群 ⑤ - nginx - NGX_EXCLUSIVE_EVENT
- 探索惊群 ⑥ - nginx - reuseport
- 探索惊群 ⑦ - 文件描述符透传
1. nginx 惊群现象
在不配置 nginx 处理惊群特性的情况下,通过 strace 命令观察 nginx 的系统调用日志。
在 ubuntu 14.04 系统,由简单的 telnet 测试可见:有的进程被唤醒后获取资源失败——惊群现象发生了!
先不配置 accept_mutex,reuseport 等特性。
- telnet 测试命令。
1
telnet 127.0.0.1 80
- nginx 工作流程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
# strace -f -s 512 -o /tmp/nginx.log /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
# 1. pid 2. syscall
...
# 主进程。
# 79979 进程启动加载 nginx。nginx 主进程 socket -> bind -> listen。
79979 socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_IP) = 6
79979 bind(6, {sa_family=AF_INET, sin_port=htons(80), sin_addr=inet_addr("0.0.0.0")}, 16) = 0
79979 listen(6, 511) = 0
# (79979)进程 clone 子进程(79980) 作为 nginx 的主进程。
79979 clone(child_stack=0, flags=CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID|CLONE_CHILD_SETTID|SIGCHLD, child_tidptr=0x7f9e6f67fa10) = 79980
# nginx 主进程 fork 两个子进程作为工作进程:79981,79982。
79980 clone(child_stack=0, flags=CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID|CLONE_CHILD_SETTID|SIGCHLD, child_tidptr=0x7f9e6f67fa10) = 79981
79980 clone( <unfinished ...>
79980 <... clone resumed> child_stack=0, flags=CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID|CLONE_CHILD_SETTID|SIGCHLD, child_tidptr=0x7f9e6f67fa10) = 79982
...
# 子进程 79981
79980 clone(child_stack=0, flags=CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID|CLONE_CHILD_SETTID|SIGCHLD, child_tidptr=0x7f9e6f67fa10) = 79981
79981 epoll_create(512 <unfinished ...>
79981 <... epoll_create resumed> ) = 8
# 子进程 epoll 监控共享的 listen socket ---> 6。
79981 epoll_ctl(8, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, 6, {EPOLLIN|EPOLLRDHUP, {u32=1868849168, u64=140318450409488}} <unfinished ...>
# 子进程 79981 被唤醒。
79981 epoll_wait(8, {EPOLLIN, {u32=1868849392, u64=140318450409712}}, 512, -1) = 1
79981 epoll_wait(8, <unfinished ...>
79981 accept4(6, <unfinished ...>
# accept4 成功获取一个链接资源。
79981 <... accept4 resumed> {sa_family=AF_INET, sin_port=htons(58960), sin_addr=inet_addr("127.0.0.1")}, [16], SOCK_NONBLOCK) = 10
79981 epoll_ctl(8, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, 10, {EPOLLIN|EPOLLRDHUP|EPOLLET, {u32=1868849616, u64=140318450409936}}) = 0
79981 epoll_wait(8, {EPOLLIN|EPOLLRDHUP, {u32=1868849616, u64=140318450409936}}, 512, 60000) = 1
79981 recvfrom(10, "", 1024, 0, NULL, NULL) = 0
79981 close(10) = 0
...
# 子进程 79982
79980 <... clone resumed> child_stack=0, flags=CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID|CLONE_CHILD_SETTID|SIGCHLD, child_tidptr=0x7f9e6f67fa10) = 79982
79982 epoll_create(512 <unfinished ...>
79982 <... epoll_create resumed> ) = 10
79982 epoll_wait(10, <unfinished ...>
# 子进程 epoll 监控共享的 listen socket ---> 6。
79982 epoll_ctl(10, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, 6, {EPOLLIN|EPOLLRDHUP, {u32=1868849168, u64=140318450409488}}) = 0
79982 epoll_wait(10, <unfinished ...>
# 子进程被唤醒后,accept4 获取链接资源失败,返回 EAGAIN。
79982 accept4(6, <unfinished ...>
79982 <... accept4 resumed> 0x7ffe70c17e40, [112], SOCK_NONBLOCK) = -1 EAGAIN (Resource temporarily unavailable)
79982 epoll_wait(10, <unfinished ...>
...
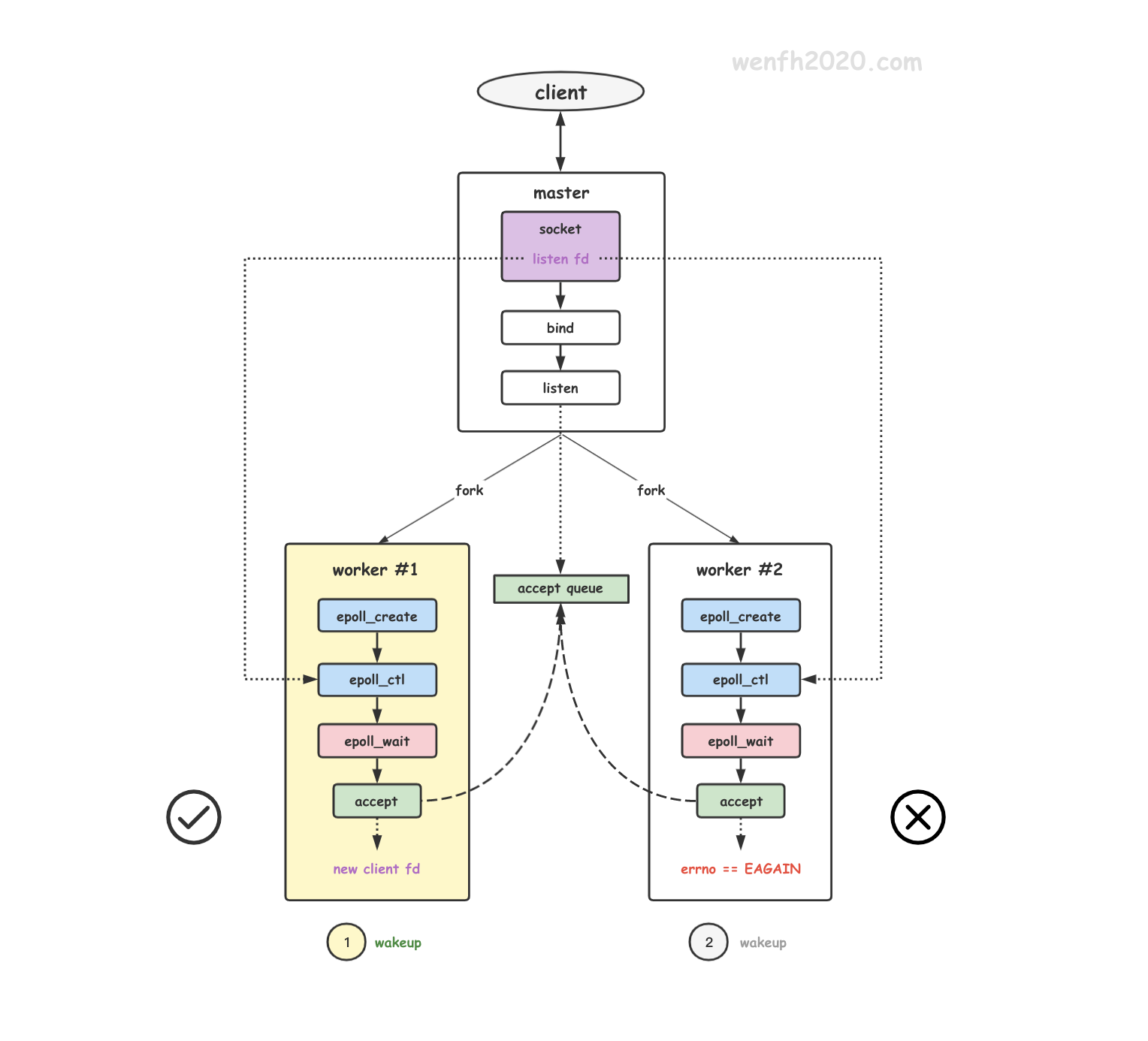
- 惊群现象。
1
2
3
4
79982 epoll_wait(10, <unfinished ...>
# 子进程被唤醒后,accept4 获取链接资源失败,返回 EAGAIN。
79982 accept4(6, <unfinished ...>
79982 <... accept4 resumed> 0x7ffe70c17e40, [112], SOCK_NONBLOCK) = -1 EAGAIN (Resource temporarily unavailable)
2. 原因
惊群现象出现,有的子进程被唤醒但是并没有 accept 到链接资源。原因:
两个子进程通过 epoll_ctl 添加关注了主进程创建的 socket,当该 listen socket 没有资源时,子进程都通过 epoll_wait 进入了阻塞睡眠状态。也就是子进程分别往 socket.wq 等待队列添加了各自的等待事件。
因为添加的方式是 add_wait_queue,而不是 add_wait_queue_exclusive,add_wait_queue 并没有设置 WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE 排它唤醒标识,所以当 listen socket 的资源到来时,内核通过 __wake_up_common 去唤醒两个子进程去 accept 获取资源。
如果只有一个链接资源,那么 nginx 的两个子进程被唤醒,当然只有一个子进程能成功,另外一个则无功而返。
- socket 结构。
1
2
3
4
5
6
/* include/linux/net.h*/
struct socket {
...
struct socket_wq *wq; /* socket 等待队列。 */
...
};
- 进程在 epoll_ctl 关注 listen socket 时,添加了当前进程的等待事件到 socket.wq 等待队列,进程的 epoll 唤醒回调函数 ep_poll_callback 与 socket 关联起来了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
/* fs/eventpoll.c */
static void ep_ptable_queue_proc(struct file *file, wait_queue_head_t *whead, poll_table *pt) {
struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_epqueue(pt);
struct eppoll_entry *pwq;
if (epi->nwait >= 0 && (pwq = kmem_cache_alloc(pwq_cache, GFP_KERNEL)) {
init_waitqueue_func_entry(&pwq->wait, ep_poll_callback);
pwq->whead = whead;
pwq->base = epi;
if (epi->event.events & EPOLLEXCLUSIVE)
add_wait_queue_exclusive(whead, &pwq->wait);
else
/* 因为 nginx 默认情况下在 Linux 4.5 版本以下内核是没有开启 EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 特性的,
* 所以调用的是没有设置排它性属性的函数 add_wait_queue。 */
add_wait_queue(whead, &pwq->wait);
...
}
...
}
- 当 listen socket 的资源到来,唤醒等待的进程。因为 add_wait_queue 没有添加 WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE 标识,所以两个子进程被唤醒。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
/* kernel/sched/wait.c
* This is the callback that is passed to the wait queue wakeup
* mechanism. It is called by the stored file descriptors when they
* have events to report. */
static int __wake_up_common(struct wait_queue_head *wq_head, unsigned int mode,
int nr_exclusive, int wake_flags, void *key,
wait_queue_entry_t *bookmark) {
wait_queue_entry_t *curr, *next;
int cnt = 0;
...
/* 遍历等待队列,调用唤醒函数去唤醒进程。 */
list_for_each_entry_safe_from(curr, next, &wq_head->head, entry) {
unsigned flags = curr->flags;
int ret;
...
/* 调用进程唤醒回调函数:ep_poll_callback。*/
ret = curr->func(curr, mode, wake_flags, key);
if (ret < 0)
break;
/* 检测 WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE 属性,是否只唤醒一个进。*/
if (ret && (flags & WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE) && !--nr_exclusive)
break;
...
}
...
}
3. 原理
3.1. 基本原理
先捋一捋这个通知唤醒的工作流程:tcp 产生链接资源后唤醒阻塞等待的子进程去 accept 获取。
-
tcp 协议的链接是通过三次握手实现的,而完整的链接资源是服务端在第三次握手中产生的,服务端会将新的链接资源存储在 listen socket 的完全队列中。
-
nginx 作为高性能服务程序,在 Linux 系统,它处理网络事件时,一般会采用 epoll 事件驱动。它通过
epoll_wait等待事件,当通过 epoll_ctl 关注的 tcp listen socket 产生事件时,阻塞等待的 epoll_wait 被唤醒去 accept 链接资源。
3.2. 等待唤醒流程
- 进程通过 epoll_ctl 监控 listen socket 的 EPOLLIN 事件。
- 进程通过 epoll_wait 阻塞等待监控的 listen socket 事件触发,然后返回。
- tcp 第三次握手,服务端产生新的链接资源。
- 内核将链接资源保存到 listen socket 的完全队列中。
- 内核唤醒步骤2的进程去 accept 获取 listen socket 完全队列中的链接资源。
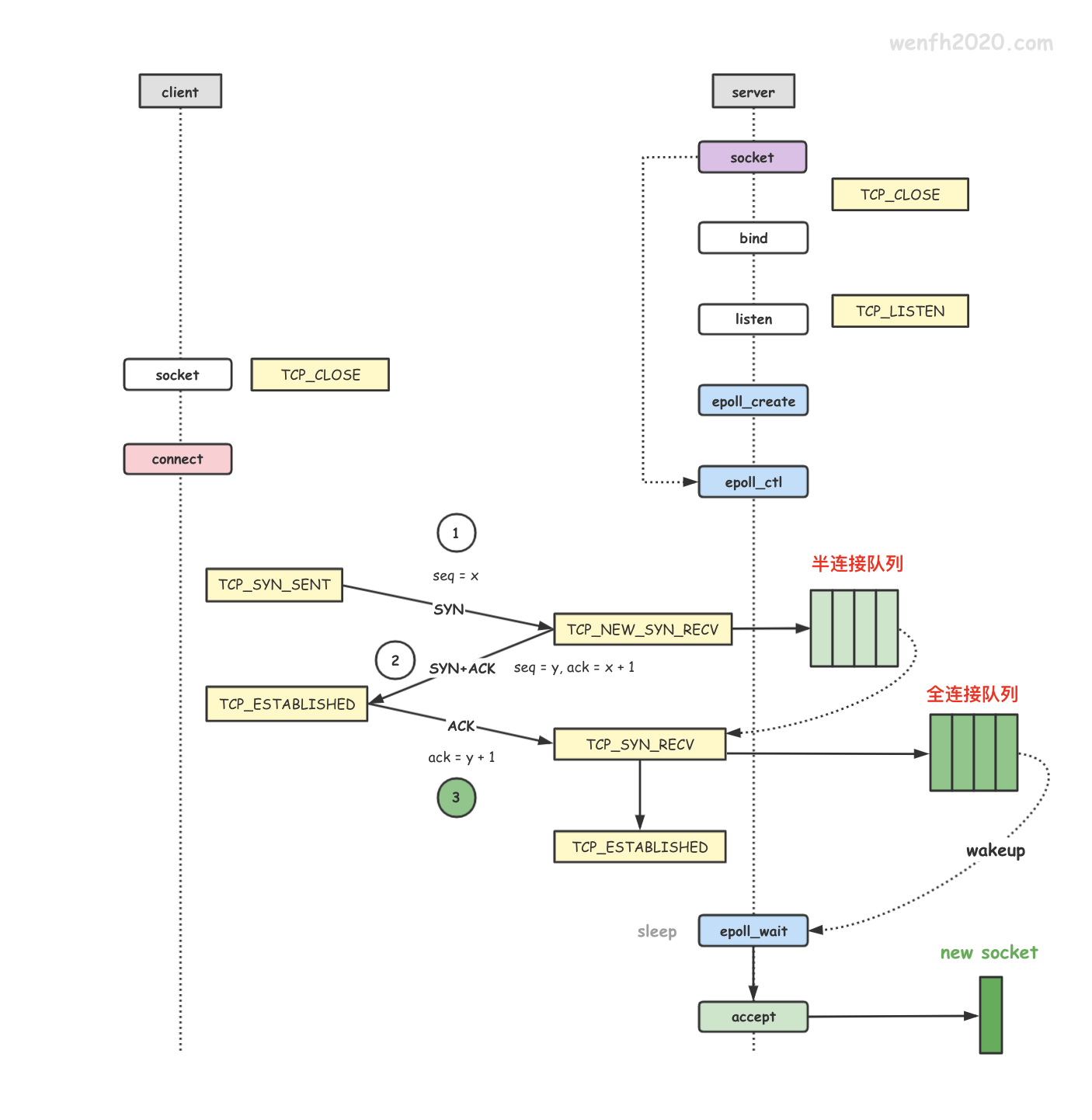
3.3. 内核原理
通过下图,了解一下服务端 tcp 的第三次握手和 epoll 内核的等待唤醒工作流程。
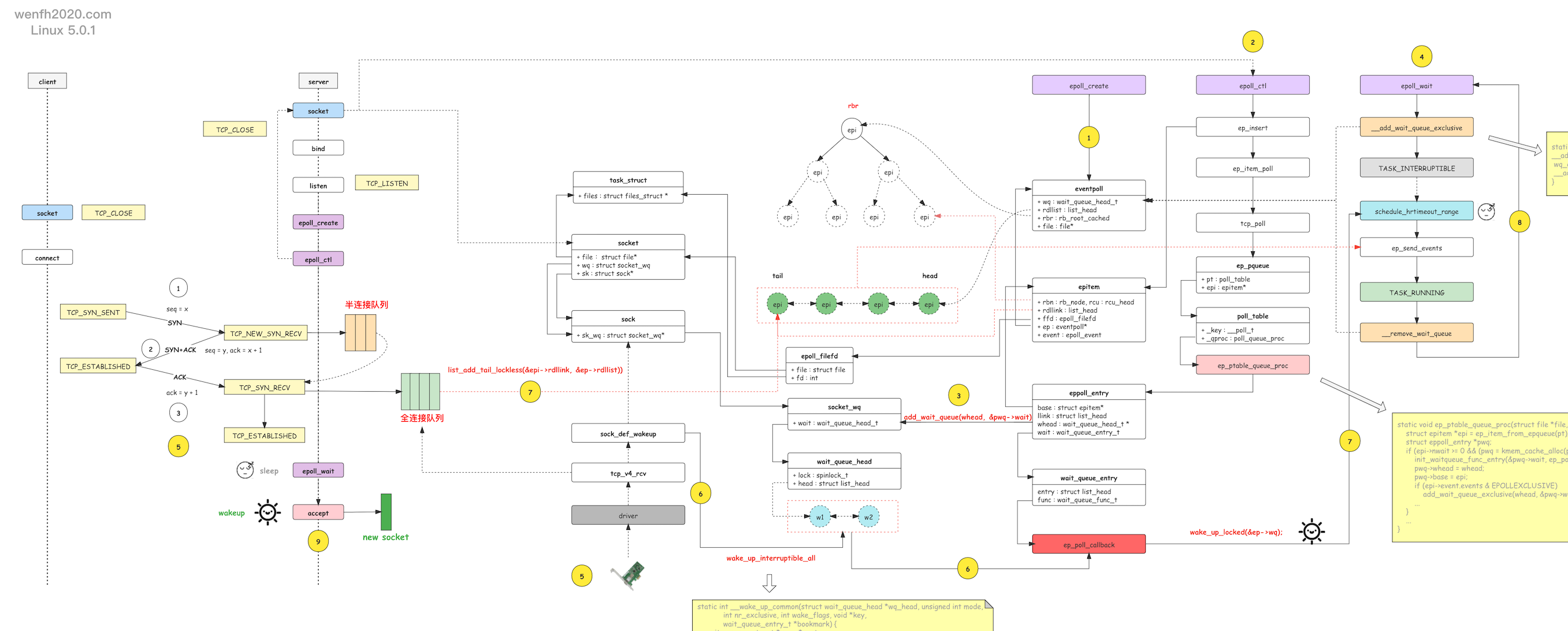
- 进程通过 epoll_create 创建 eventpoll 对象。
- 进程通过 epoll_ctl 添加关注 listen socket 的 EPOLLIN 可读事件。
- 接步骤 2,epoll_ctl 还将 epoll 的 socket 唤醒等待事件(唤醒函数:ep_poll_callback)通过 add_wait_queue 函数添加到 socket.wq 等待队列。
当 listen socket 有链接资源时,内核通过 __wake_up_common 调用 epoll 的 ep_poll_callback 唤醒函数,唤醒进程。
- 进程通过 epoll_wait 等待就绪事件,往 eventpoll.wq 等待队列中添加当前进程的等待事件,当 epoll_ctl 监控的 socket 产生对应的事件时,被唤醒返回。
- 客户端通过 tcp connect 链接服务端,三次握手成功,第三次握手在服务端进程产生新的链接资源。
- 服务端进程根据 socket.wq 等待队列,唤醒正在等待资源的进程处理。例如 nginx 的惊群现象,__wake_up_common 唤醒等待队列上的两个等待进程,调用 ep_poll_callback 去唤醒 epoll_wait 阻塞等待的进程。
- ep_poll_callback 唤醒回调会检查 listen socket 的完全队列是否为空,如果不为空,那么就将 epoll_ctl 监控的 listen socket 的节点 epi 添加到
就绪队列:eventpoll.rdllist,然后唤醒 eventpoll.wq 里通过 epoll_wait 等待的进程,处理 eventpoll.rdllist 上的事件数据。 - 睡眠在内核的 epoll_wait 被唤醒后,内核通过 ep_send_events 将就绪事件数据,从内核空间拷贝到用户空间,然后进程从内核空间返回到用户空间。
- epoll_wait 被唤醒,返回用户空间,读取 listen socket 返回的 EPOLLIN 事件,然后 accept listen socket 完全队列上的链接资源。
【注意】 有了 socket.wq 为啥还要有 eventpoll.wq 啊?因为 listen socket 能被多个进程共享,epoll 实例也能被多个进程共享!
-
添加等待事件流程:
epoll_ctl -> listen socket -> add_wait_queue <+ep_poll_callback+> -> socket.wq ==> epoll_wait -> eventpoll.wq
-
唤醒流程:
tcp_v4_rcv -> socket.wq -> __wake_up_common -> ep_poll_callback -> eventpoll.wq -> wake_up_locked -> epoll_wait -> accept
4. 内核源码分析
4.1. TCP 三次握手
客户端主动链接服务端,TCP 三次握手成功后,服务端产生新的 tcp 链接资源,内核将唤醒 socket.wq 上的等待进程,通过 accept 从 listen socket 上的 全链接队列 中获取 TCP 链接资源。

参考:《[内核源码] 网络协议栈 - tcp 三次握手状态》 《[内核源码] 网络协议栈 - listen (tcp)》
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
/* include/net/sock.h */
struct sock {
...
void (*sk_data_ready)(struct sock *sk);
...
}
static int inet_create(struct net *net, struct socket *sock, int protocol, int kern) {
struct sock *sk;
...
sock_init_data(sock, sk);
...
}
/* net/core/sock.c */
void sock_init_data(struct socket *sock, struct sock *sk) {
sk_init_common(sk);
...
sk->sk_data_ready = sock_def_readable;
...
}
/* 三次握手,服务端第三次握手。 */
int tcp_v4_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb) {
process:
...
if (sk->sk_state == TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV) {
...
else if (tcp_child_process(sk, nsk, skb)) {
...
}
...
}
}
/* parent 参数是 listen socket 的网络对象指针。 */
int tcp_child_process(struct sock *parent, struct sock *child,
struct sk_buff *skb) {
int ret = 0;
int state = child->sk_state;
...
tcp_segs_in(tcp_sk(child), skb);
if (!sock_owned_by_user(child)) {
ret = tcp_rcv_state_process(child, skb);
/* Wakeup parent, send SIGIO */
if (state == TCP_SYN_RECV && child->sk_state != state)
/* 唤醒 */
parent->sk_data_ready(parent);
}
...
}
/* sk_data_ready */
static void sock_def_wakeup(struct sock *sk) {
struct socket_wq *wq;
rcu_read_lock();
wq = rcu_dereference(sk->sk_wq);
if (skwq_has_sleeper(wq))
wake_up_interruptible_all(&wq->wait);
rcu_read_unlock();
}
/* 调用 __wake_up_sync_key 函数,将 nr_exclusive 唤醒进程/线程的个数设置为 1. */
#define wake_up_interruptible_sync_poll(x, m) \
__wake_up_sync_key((x), TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, 1, poll_to_key(m))
void __wake_up_sync_key(struct wait_queue_head *wq_head, unsigned int mode,
int nr_exclusive, void *key) {
__wake_up_common_lock(wq_head, mode, nr_exclusive, wake_flags, key);
}
static void __wake_up_common_lock(struct wait_queue_head *wq_head, unsigned int mode,
int nr_exclusive, int wake_flags, void *key) {
...
nr_exclusive = __wake_up_common(wq_head, mode, nr_exclusive, wake_flags, key, &bookmark);
...
}
static int __wake_up_common(struct wait_queue_head *wq_head, unsigned int mode,
int nr_exclusive, int wake_flags, void *key,
wait_queue_entry_t *bookmark) {
wait_queue_entry_t *curr, *next;
int cnt = 0;
...
/* 遍历唤醒等待队列。 */
list_for_each_entry_safe_from(curr, next, &wq_head->head, entry) {
unsigned flags = curr->flags;
int ret;
...
/* 将睡眠的进程唤醒: ep_poll_callback。 */
ret = curr->func(curr, mode, wake_flags, key);
if (ret < 0)
break;
if (ret && (flags & WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE) && !--nr_exclusive)
break;
...
}
return nr_exclusive;
}
4.2. epoll
4.2.1. epoll_wait 逻辑
epoll_wait 它的核心实现逻辑并不复杂,先添加进程的等待事件,然后检查就绪队列是否有就绪事件,如果没有就绪事件就睡眠等待,如果有事件就唤醒,将就绪事件从内核空间拷贝到用户空间,然后删除进程的等待事件。
1
2
3
4
5
#------------------- *用户空间* ---------------------------
epoll_wait
#------------------- *内核空间* ---------------------------
|-- do_epoll_wait
|-- ep_poll
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
/* fs/eventpoll.c */
static int ep_poll(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event __user *events,
int maxevents, long timeout) {
...
fetch_events:
...
/* 检查 epoll 是否有就绪事件。 */
eavail = ep_events_available(ep);
if (eavail)
/* 如果有就绪事件,直接将事件从内核空间拷贝到用户空间,不需要睡眠等待。 */
goto send_events;
...
/* 如果没有就绪事件,进程将进入睡眠等待状态,添加等待事件到等待队列。
* 当 epoll 关注的文件有对应的事件发生,会触发 ep_poll_callback 函数(epoll_ctl 里绑定的),
* 唤醒等待队列里的对应进程。 */
if (!waiter) {
waiter = true;
init_waitqueue_entry(&wait, current);
spin_lock_irq(&ep->wq.lock);
/* epoll 往等待队列中,添加当前进程的等待事件,等待唤醒。 */
__add_wait_queue_exclusive(&ep->wq, &wait);
spin_unlock_irq(&ep->wq.lock);
}
for (;;) {
/* 将进程设置为可被中断唤醒的睡眠状态。 */
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
...
/* 再检查是否有就绪事件发生,如果有就不睡了。 */
eavail = ep_events_available(ep);
if (eavail)
break;
...
/* 进入超时等待睡眠状态。 */
if (!schedule_hrtimeout_range(to, slack, HRTIMER_MODE_ABS)) {
timed_out = 1;
break;
}
}
/* 上面循环退出,进程恢复运行状态。 */
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
send_events:
/* 如果检测到有就绪事件发生,内核空间向用户空间拷贝就绪事件。 */
if (!res && eavail &&
!(res = ep_send_events(ep, events, maxevents)) && !timed_out)
goto fetch_events;
if (waiter) {
spin_lock_irq(&ep->wq.lock);
/* epoll 从等待队列中,删除当前进程的等待事件。 */
__remove_wait_queue(&ep->wq, &wait);
spin_unlock_irq(&ep->wq.lock);
}
}
4.2.2. epoll_wait 睡眠等待逻辑
epoll_wait 通过 __add_wait_queue_exclusive 函数添加 WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE 排它性唤醒属性的等待事件到等待队列,表明当 ep_poll_callback 回调函数被调用时(请看下面 ep_poll 源码的英文注释),拥有 epoll fd 的进程只能有一个被唤醒处理资源(有可能有多个进程共享 epoll,而 nginx 每个子进程都有自己独立的 epoll 实例,不共享)。通过__remove_wait_queue 函数删除对应的等待事件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
/* include/linux/wait.h */
static inline void
__add_wait_queue_exclusive(struct wait_queue_head *wq_head, struct wait_queue_entry *wq_entry) {
/* 唤醒事件,增加了 WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE 排它性唤醒属性。*/
wq_entry->flags |= WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE;
__add_wait_queue(wq_head, wq_entry);
}
/* fs/eventpoll.c */
static int ep_poll(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event __user *events,
int maxevents, long timeout) {
...
/*
* We don't have any available event to return to the caller. We need
* to sleep here, and we will be woken by ep_poll_callback() when events
* become available.
*/
if (!waiter) {
waiter = true;
init_waitqueue_entry(&wait, current);
spin_lock_irq(&ep->wq.lock);
/* 添加排它性唤醒标识,将等待事件添加到 epoll 的等待队列。 */
__add_wait_queue_exclusive(&ep->wq, &wait);
spin_unlock_irq(&ep->wq.lock);
}
...
}
4.2.3. epoll_wait 唤醒流程
4.2.3.1. socket 注册唤醒函数
epoll_ctl -> listen socket -> add_wait_queue <+ep_poll_callback+> -> socket.wq
-
函数调用堆栈。
通过函数堆栈,可以发现:epoll 里的进程睡眠唤醒函数 ep_poll_callback,与 tcp socket 关联起来了,睡眠事件添加到 socket 的睡眠队列里,当 socket 有对应的就绪事件,就会触发对应的函数,在这里就会触发 ep_poll_callback。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
init_waitqueue_func_entry() (/root/linux-5.0.1/include/linux/wait.h:89)
ep_ptable_queue_proc(struct file * file, wait_queue_head_t * whead, poll_table * pt) (/root/linux-5.0.1/fs/eventpoll.c:1245)
poll_wait() (/root/linux-5.0.1/include/linux/poll.h:47)
sock_poll_wait() (/root/linux-5.0.1/include/net/sock.h:2091)
tcp_poll(struct file * file, struct socket * sock, poll_table * wait) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp.c:510)
sock_poll(struct file * file, poll_table * wait) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:1128)
vfs_poll() (/root/linux-5.0.1/include/linux/poll.h:86)
ep_item_poll(poll_table * pt, int depth) (/root/linux-5.0.1/fs/eventpoll.c:892)
ep_insert(struct eventpoll * ep, const struct epoll_event * event, struct file * tfile, int fd, int full_check) (/root/linux-5.0.1/fs/eventpoll.c:1463)
__do_sys_epoll_ctl() (/root/linux-5.0.1/fs/eventpoll.c:2139)
__se_sys_epoll_ctl() (/root/linux-5.0.1/fs/eventpoll.c:2025)
__x64_sys_epoll_ctl(const struct pt_regs * regs) (/root/linux-5.0.1/fs/eventpoll.c:2025)
do_syscall_64(unsigned long nr, struct pt_regs * regs) (/root/linux-5.0.1/arch/x86/entry/common.c:290)
entry_SYSCALL_64() (/root/linux-5.0.1/arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:175)
[Unknown/Just-In-Time compiled code] (Unknown Source:0)
- 内核源码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
/* epoll 结构对象。*/
struct eventpoll {
...
/* 使用当前 epoll 的进程等待队列。 */
wait_queue_head_t wq;
...
/* 就绪队列。关注事件已发生,将对应的 fd 节点 epi 添加到就绪队列。 */
struct list_head rdllist;
...
};
/* socket 结构。 */
struct socket {
...
struct socket_wq *wq; /* socket 等待队列。 */
struct file *file;
struct sock *sk;
...
};
/* fs/eventpoll.c */
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_ctl, int, epfd, int, op, int, fd,
struct epoll_event __user *, event) {
...
struct epitem *epi;
...
epi = ep_find(ep, tf.file, fd);
error = -EINVAL;
switch (op) {
case EPOLL_CTL_ADD:
if (!epi) {
epds.events |= EPOLLERR | EPOLLHUP;
error = ep_insert(ep, &epds, tf.file, fd, full_check);
}
...
}
...
}
/* fs/eventpoll.c */
static int ep_insert(struct eventpoll *ep, const struct epoll_event *event,
struct file *tfile, int fd, int full_check) {
...
struct epitem *epi;
struct ep_pqueue epq;
...
if (!(epi = kmem_cache_alloc(epi_cache, GFP_KERNEL)))
return -ENOMEM;
...
/* Initialize the poll table using the queue callback */
epq.epi = epi;
init_poll_funcptr(&epq.pt, ep_ptable_queue_proc);
...
/* ep_item_poll 通过 ep_ptable_queue_proc 函数的调用,
* 将 ep_poll_callback 回调函数与对应的 socket 进行绑定。
* 同时检查并返回对应的 socket 已发生的就绪事件。 */
revents = ep_item_poll(epi, &epq.pt, 1);
...
}
/* include/linux/poll.h */
static inline void init_poll_funcptr(poll_table *pt, poll_queue_proc qproc) {
pt->_qproc = qproc;
pt->_key = ~(__poll_t)0; /* all events enabled */
}
/* fs/eventpoll.c */
static __poll_t ep_item_poll(const struct epitem *epi, poll_table *pt, int depth) {
struct eventpoll *ep;
bool locked;
pt->_key = epi->event.events;
if (!is_file_epoll(epi->ffd.file))
return vfs_poll(epi->ffd.file, pt) & epi->event.events;
...
}
/* include/linux/poll.h */
static inline __poll_t vfs_poll(struct file *file, struct poll_table_struct *pt) {
...
/* sock_poll */
return file->f_op->poll(file, pt);
}
/* net/socket.c */
static __poll_t sock_poll(struct file *file, poll_table *wait) {
struct socket *sock = file->private_data;
...
/* tcp_poll */
return sock->ops->poll(file, sock, wait) | flag;
}
/* net/ipv4/tcp.c */
__poll_t tcp_poll(struct file *file, struct socket *sock, poll_table *wait) {
__poll_t mask;
struct sock *sk = sock->sk;
const struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
int state;
sock_poll_wait(file, sock, wait);
state = inet_sk_state_load(sk);
if (state == TCP_LISTEN)
/* 要检查完全队列是否有准备就绪的链接提供 accept。 */
return inet_csk_listen_poll(sk);
...
}
/* include/net/sock.h */
static inline void sock_poll_wait(struct file *filp, struct socket *sock, poll_table *p) {
if (!poll_does_not_wait(p)) {
/* 当前进程添加等待事件到 socket. */
poll_wait(filp, &sock->wq->wait, p);
...
}
}
/* include/net/inet_connection_sock.h */
static inline __poll_t inet_csk_listen_poll(const struct sock *sk) {
/* 根据 listen socket 的完全队列是否为空返回对应的事件。 */
return !reqsk_queue_empty(&inet_csk(sk)->icsk_accept_queue) ?
(EPOLLIN | EPOLLRDNORM) : 0;
}
/* include/linux/poll.h */
static inline void poll_wait(struct file * filp, wait_queue_head_t * wait_address, poll_table *p) {
if (p && p->_qproc && wait_address)
/* ep_ptable_queue_proc */
p->_qproc(filp, wait_address, p);
}
/* 进程添加等待事件到 socket.wq 等待队列,
* 进程的 epoll 唤醒函数 ep_poll_callback 与 socket 关联起来了。*/
static void ep_ptable_queue_proc(struct file *file, wait_queue_head_t *whead, poll_table *pt) {
struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_epqueue(pt);
struct eppoll_entry *pwq;
if (epi->nwait >= 0 && (pwq = kmem_cache_alloc(pwq_cache, GFP_KERNEL)) {
init_waitqueue_func_entry(&pwq->wait, ep_poll_callback);
pwq->whead = whead;
pwq->base = epi;
if (epi->event.events & EPOLLEXCLUSIVE)
add_wait_queue_exclusive(whead, &pwq->wait);
else
/* 因为 nginx 默认情况下在 Linux 4.5 版本以下内核是没有开启 EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 特性的,
* 所以调用的是没有设置排它性属性的函数 add_wait_queue。 */
add_wait_queue(whead, &pwq->wait);
...
}
...
}
4.2.3.2. epoll_wait 唤醒
tcp_v4_rcv -> socket.wq -> __wake_up_common -> ep_poll_callback -> eventpoll.wq -> wake_up_locked -> epoll_wait
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
/*
* This is the callback that is passed to the wait queue wakeup
* mechanism. It is called by the stored file descriptors when they
* have events to report.
*/
static int ep_poll_callback(wait_queue_entry_t *wait, unsigned mode, int sync, void *key) {
int pwake = 0;
unsigned long flags;
struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_wait(wait);
struct eventpoll *ep = epi->ep;
__poll_t pollflags = key_to_poll(key);
int ewake = 0;
...
/* 检查已经发生的就绪事件 pollflags,是否是用户关注(epoll_ctl)的就绪事件,
* 如果不是就返回。*/
if (pollflags && !(pollflags & epi->event.events))
goto out_unlock;
...
/* 如果发生的事件是用户关注的事件,而且就绪列表上还没有添加这个 fd 节点 epi,
* 那么将 epi 添加到就绪队列尾部。 */
if (!ep_is_linked(epi)) {
list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
ep_pm_stay_awake_rcu(epi);
}
/*
* Wake up ( if active ) both the eventpoll wait list and the ->poll()
* wait list.
*/
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq)) {
...
/* 唤醒通过 epoll_wait 睡眠的进程。 */
wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);
}
...
}
/* include/linux/wait.h */
#define wake_up_locked(x) __wake_up_locked((x), TASK_NORMAL, 1)
/* kernel/sched/wait.c */
void __wake_up_locked(struct wait_queue_head *wq_head, unsigned int mode, int nr) {
__wake_up_common(wq_head, mode, nr, 0, NULL, NULL);
}
/* kernel/sched/wait.c */
static int __wake_up_common(struct wait_queue_head *wq_head, unsigned int mode,
int nr_exclusive, int wake_flags, void *key,
wait_queue_entry_t *bookmark) {
wait_queue_entry_t *curr, *next;
int cnt = 0;
...
list_for_each_entry_safe_from(curr, next, &wq_head->head, entry) {
unsigned flags = curr->flags;
int ret;
if (flags & WQ_FLAG_BOOKMARK)
continue;
/* 唤醒进程。 */
ret = curr->func(curr, mode, wake_flags, key);
if (ret < 0)
break;
/* 排它性唤醒属性,而且 nr_exclusive == 1,所以循环只执行一次就退出,
* 也就是只唤醒了一个进程。 */
if (ret && (flags & WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE) && !--nr_exclusive)
break;
...
}
...
}
5. 压测
httpclient <–> nginx <–> httpserver
nginx 作为代理,httpclient 模拟多个短链接发包,测试 nginx 的惊群问题。

5.1. 测试环境
| cpu 核心 | 内存 | 系统 | nginx 版本 | nginx 子进程个数 | 测试并发数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 4g | ubuntu(14.04) | 1.20.1 | 2 | 10000 |
5.2. 测试源码
用 golang 实现的简单的测试 demo,源码详见:github。
- 测试服务:httpserver,简单的接收数据和回复数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
package main
import (
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/hello", hello)
log.Println("start http server, port: 1210.")
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":1210", nil))
}
func hello(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.Write([]byte("hello world!"))
}
- 测试客户端:httpclient,通过 golang 多协程,模拟多个客户端进行简单的数据发送和接收。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
package main
import (
"bytes"
"flag"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"sync"
"sync/atomic"
"time"
)
const (
timeFmt = "2006-01-02 15:04:05.000"
connCnt = 10
host = "172.16.230.15"
)
var cnt int
var failed int32
var wait sync.WaitGroup
func main() {
flag.IntVar(&cnt, "cnt", connCnt, "connect count")
flag.Parse()
wait.Add(cnt)
begin := time.Now()
url := fmt.Sprintf("http://%s/hello", host)
for i := 0; i < cnt; i++ {
go func(index int) {
jsonStr := []byte(`{"title":"Buy cheese and bread for breakfast."}`)
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", url, bytes.NewBuffer(jsonStr))
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=UTF-8")
client := &http.Client{}
res, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
atomic.AddInt32(&failed, 1)
fmt.Printf("%d, connect failed!, err: %v\n", index, err)
} else {
defer res.Body.Close()
}
wait.Done()
}(i)
}
wait.Wait()
spend := time.Now().Sub(begin).Seconds()
fmt.Printf("cnt: %d, failed: %d, spend: %v\n", cnt, failed, spend)
}
- 运行测试客户端 httpclient,并发 1w 个短链接。
1
2
./httpclient --cnt 10000
cnt: 10000, failed: 0, spend: 8.080221123
5.3. nginx
- nginx 转发配置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
worker_processes 2;
events {
worker_connections 50240;
}
...
http {
...
server {
listen 80;
...
# 将 hello 协议转发到 httpserver 服务。
location /hello {
proxy_pass http://172.16.230.16:1210/hello;
}
...
}
...
}
- nginx 启动后,主进程和子进程的运行情况。
1
2
3
root 79980 1 0 22:28 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nobody 79981 79980 0 22:28 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 79982 79980 0 22:28 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
-
nginx 测试结果。
从 strace 统计的系统调用数据可见:79982 子进程的 accept4 系统调用有 195 个错误,因为进程被唤醒后,异步调用 accept4 去获取资源,有时它获取资源失败了,返回
EAGAIN错误,也就是说进程被唤醒后做了无用功。因为 strace 监控进程,还要写日志,处理速度应该会比正常的慢,所以测试客户端并发 1w 个,但是监控的进程只调用了 accept4 处理了 1356 个,失败了 195 个。
1356 - 195 = 1161,刚好是 nginx accept 成功了新的连接,然后转发数据到目标服务 connect 的系统调用次数。
因为 connect 也是异步的,所以调用后马上会返回错误,这是正常的;在 connect 前,accept 的新 socket 已经被 epoll_ctl 关注了,所以 connect 的结果会通过 epoll_wait 返回。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# strace -C -T -ttt -p 79982 -o strace.log
# tail strace.log -n 18
% time seconds usecs/call calls errors syscall
------ ----------- ----------- --------- --------- ----------------
33.80 0.030308 13 2322 writev
28.47 0.025531 11 2322 close
# connect 是 nginx 转发到目标服务的连接次数。
14.58 0.013073 11 1161 1161 connect
11.83 0.010610 5 2269 epoll_wait
# accept4 有 195 个错误。
9.15 0.008203 6 1356 195 accept4
0.73 0.000656 0 3483 recvfrom
0.38 0.000339 0 1161 setsockopt
0.35 0.000311 19 16 brk
0.30 0.000267 0 1161 socket
0.21 0.000185 0 1161 write
0.14 0.000126 0 1161 ioctl
0.04 0.000034 0 3483 epoll_ctl
0.02 0.000020 0 1098 readv
0.01 0.000010 0 1161 getsockopt
------ ----------- ----------- --------- --------- ----------------
100.00 0.089673 23315 1356 total
5.4. 惊群影响
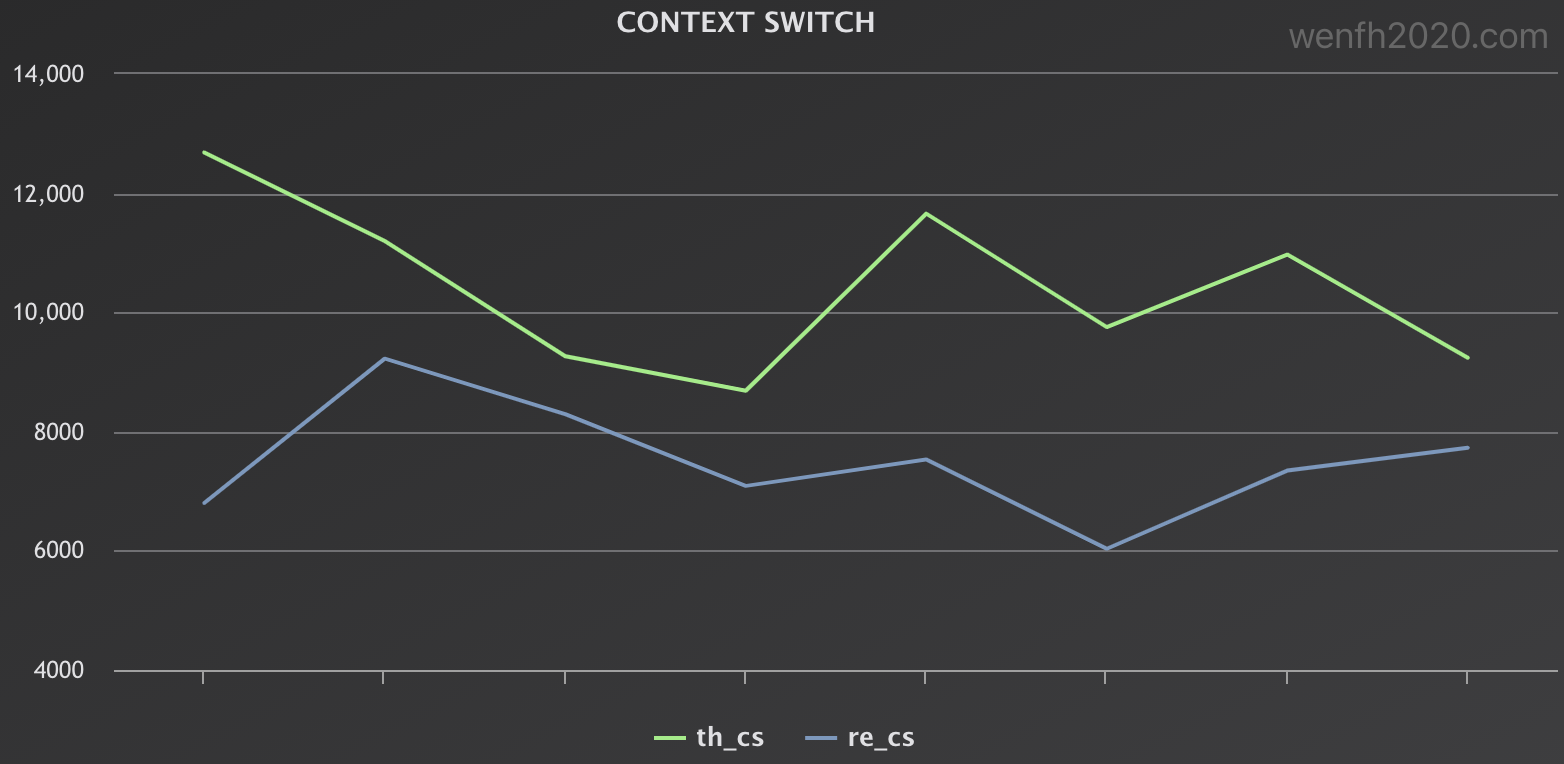
惊群使得部分进程唤醒做了无用功,我们对比一下惊群与非惊群两个场景的数据。
惊群的系统资源损耗总体上要比非惊群的高,参考两个场景的 vmstat 虚拟内存统计数据:in 中断数据和 cs 上下文切换数据。
开启了 4 个 nginx 子进程,进行压力测试。
这里压测比较简单,只查看了部分数据,也不太严谨,至于系统负载和CPU使用率,有兴趣的朋友可以在实际应用场景中再观察对比。
- 压测脚本。用 shell 脚本简单调用了上面的 httpclient 测试客户端进行测试。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
#!/bin/bash
test() {
sleep 1
./httpclient --cnt $1
}
array=(1000 3000 5000 8000 10000 15000 20000 25000)
for x in ${array[*]}; do
test $x
done
- nginx 惊群数据,主要看 in 中断次数,cs 上下文切换次数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# vmstat 1
procs -----------memory---------- ---swap-- -----io---- -system-- ------cpu-----
r b swpd free buff cache si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa st
3 0 4191228 453076 78140 488652 0 0 0 160 8296 12684 6 43 51 0 0
8 0 4191228 450404 78140 488848 0 0 0 0 6251 11197 6 51 44 0 0
3 0 4191228 451812 78140 489032 0 0 0 0 5007 9264 7 54 39 0 0
2 0 4191228 453368 78140 489220 0 0 0 0 5166 8686 6 51 42 0 0
5 0 4191228 456108 78140 489380 0 0 0 0 6634 11658 6 50 44 0 0
3 0 4191228 452932 78144 489532 0 0 0 44 5344 9753 8 55 37 0 0
6 0 4191228 443464 78144 489700 0 0 0 0 5944 10971 7 54 39 0 0
5 0 4191228 440380 78144 489844 0 0 0 0 5031 9240 5 54 41 0 0
- 开启 reuseport 避免惊群的特性,nginx 数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
procs -----------memory---------- ---swap-- -----io---- -system-- ------cpu-----
r b swpd free buff cache si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa st
5 0 4191228 444228 78316 497104 0 0 0 0 5735 6802 6 45 48 0 0
3 0 4191228 443664 78320 497296 0 0 0 12 6010 9224 6 44 50 0 0
2 0 4191228 443384 78320 497468 0 0 0 0 5828 8294 7 45 48 0 0
5 0 4191228 436444 78320 497644 0 0 0 4 4943 7089 9 48 43 0 0
2 0 4191228 436820 78320 497824 0 0 0 12 4757 7532 5 50 45 0 0
3 0 4191228 437720 78320 497980 0 0 0 0 3871 6035 7 54 39 0 0
5 0 4191228 439788 78320 498140 0 0 0 72 4576 7346 6 53 42 0 0
2 0 4191228 443580 78320 498324 0 0 0 0 4718 7729 8 50 42 0 0
- 对比两个场景的中断数据。(th_in:惊群,re_in:非惊群。)

- 对比两个场景的上下文切换数据。(th_cs:惊群,re_cs:非惊群。)
6. 小结
- 惊群本质是进程睡眠和唤醒问题,重点理解 tcp 结合 epoll 睡眠和唤醒的时机以及工作流程。
- 避免惊群,内核源码需要重点理解
WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE标识的作用。

