走读网络协议栈 tcp 的内核源码(Linux - 5.0.1 下载)。通过 Linux 内核源码理解 tcp 三次握手状态变化。
因为我走读的是 Linux 5.0.1 源码,与旧版的 Linux 3.x 系列比较,新版的三次握手的状态已经发生改变,这个需要注意一下。
1. 概述
tcp 通信,客户端和服务端通过三次握手进行连接;握手流程,查看下图。

图片来源:TCP 三次握手(内核)
2. 源码
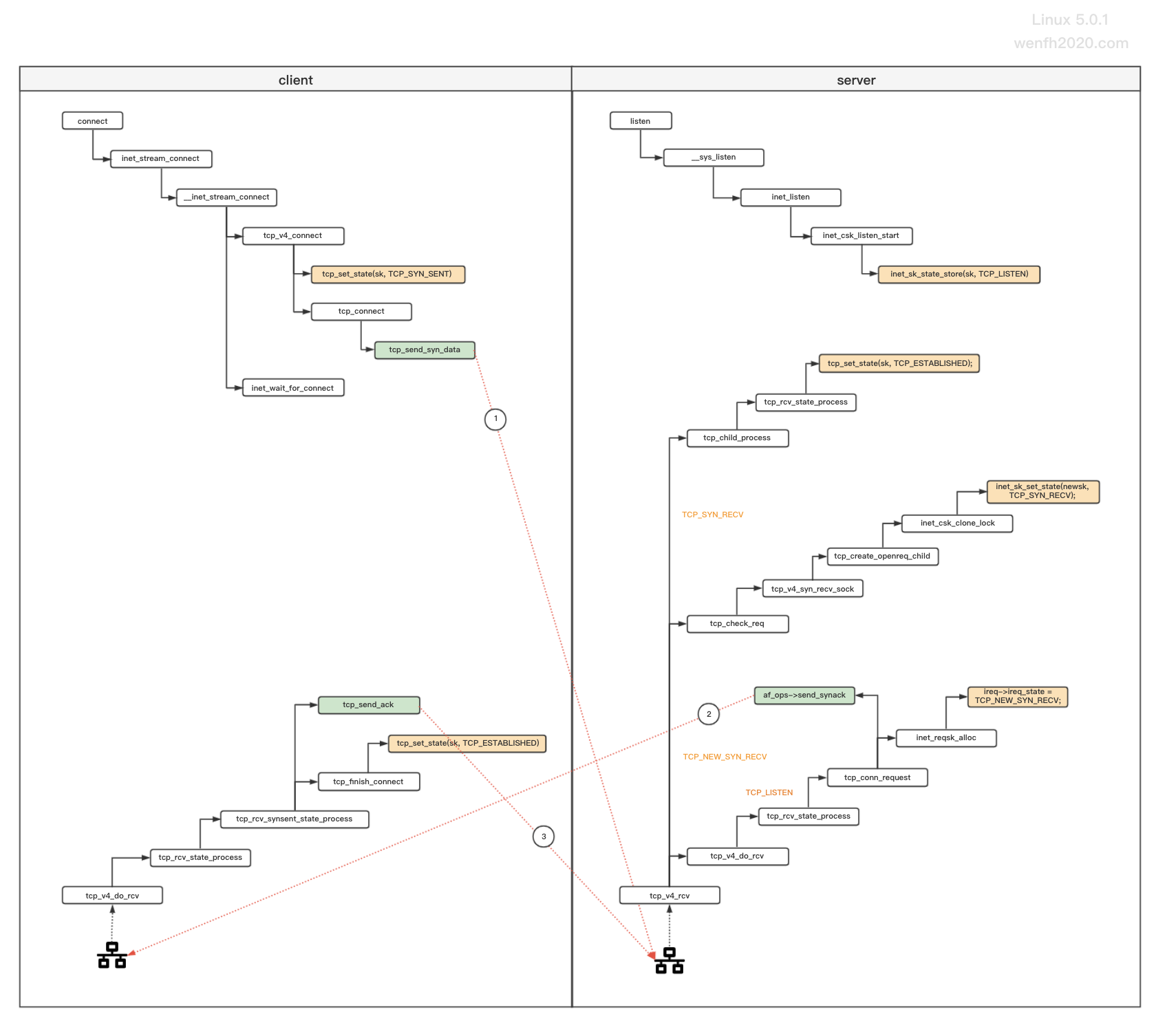
图片来源:TCP 三次握手(内核)
2.1. 客户端 - TCP_SYN_SENT
第一次握手,客户端向服务端发送 SYN 报文包。
- 函数堆栈。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
tcp_v4_connect(struct sock * sk, struct sockaddr * uaddr, int addr_len) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c:203)
__inet_stream_connect(struct socket * sock, struct sockaddr * uaddr, int addr_len, int flags, int is_sendmsg) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/af_inet.c:655)
inet_stream_connect(struct socket * sock, struct sockaddr * uaddr, int addr_len, int flags) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/af_inet.c:719)
__sys_connect(int fd, struct sockaddr * uservaddr, int addrlen) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:1663)
__do_sys_connect() (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:1674)
__se_sys_connect() (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:1671)
__x64_sys_connect(const struct pt_regs * regs) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:1671)
do_syscall_64(unsigned long nr, struct pt_regs * regs) (/root/linux-5.0.1/arch/x86/entry/common.c:290)
entry_SYSCALL_64() (/root/linux-5.0.1/arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:175)
- 内核源码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
/* /net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c */
int tcp_v4_connect(struct sock *sk, struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len) {
...
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_SYN_SENT);
...
}
2.2. 服务端 - TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV
服务端收到客户端发送的 SYN 包后,将状态修改为 TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV,为了节省资源,并没有为 struct sock 分配空间,而是创建轻量级的连接请求 struct request_sock。
- 函数堆栈。
1
2
3
4
5
6
inet_reqsk_alloc(const struct request_sock_ops * ops, struct sock * sk_listener, bool attach_listener) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_input.c:6355)
tcp_conn_request(struct request_sock_ops * rsk_ops, const struct tcp_request_sock_ops * af_ops, struct sock * sk, struct sk_buff * skb) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_input.c:6442)
tcp_rcv_state_process(struct sock * sk, struct sk_buff * skb) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_input.c:6032)
tcp_v4_do_rcv(struct sock * sk, struct sk_buff * skb) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c:1563)
tcp_v4_rcv(struct sk_buff * skb) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c:1905)
...
- 内核源码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
/* net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c */
int tcp_v4_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb) {
...
if (sk->sk_state == TCP_LISTEN) {
ret = tcp_v4_do_rcv(sk, skb);
goto put_and_return;
}
...
}
/* net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c */
int tcp_v4_do_rcv(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) {
...
if (tcp_rcv_state_process(sk, skb)) {
...
}
...
}
/* net/ipv4/tcp_input.c */
int tcp_rcv_state_process(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) {
...
switch (sk->sk_state) {
...
case TCP_LISTEN:
...
if (th->syn) {
...
acceptable = icsk->icsk_af_ops->conn_request(sk, skb) >= 0;
...
}
...
}
...
}
/* net/ipv4/tcp_input.c */
int tcp_conn_request(struct request_sock_ops *rsk_ops,
const struct tcp_request_sock_ops *af_ops,
struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) {
...
req = inet_reqsk_alloc(rsk_ops, sk, !want_cookie);
...
if (fastopen_sk) {
...
} else {
...
/* 服务端给客户端发送 SYN + ACK 包。 */
af_ops->send_synack(sk, dst, &fl, req, &foc,
!want_cookie ? TCP_SYNACK_NORMAL :
TCP_SYNACK_COOKIE);
...
}
}
/* net/ipv4/tcp_input.c */
struct request_sock *inet_reqsk_alloc(const struct request_sock_ops *ops,
struct sock *sk_listener,
bool attach_listener) {
struct request_sock *req = reqsk_alloc(ops, sk_listener,
attach_listener);
if (req) {
struct inet_request_sock *ireq = inet_rsk(req);
...
/* 设置 TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV 状态。*/
ireq->ireq_state = TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV;
...
}
return req;
}
2.3. 客户端 - TCP_ESTABLISHED
客户端向服务端发送 SYN 报文后,收到服务端的 SYN(服务端自己的 SYN 包)+ ACK 回复包(对应客户端发的 SYN 包),默认阻塞(inet_wait_for_connect)的进程被唤醒处理 ACK。
握手正常的情况下,客户端将当前 TCP 状态改变为 TCP_ESTABLISHED,并给服务端返回的 SYN 包,发送对应的 ACK。
- 函数调用堆栈。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
tcp_finish_connect(struct sock * sk, struct sk_buff * skb) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_input.c:5676)
tcp_rcv_synsent_state_process() (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_input.c:5879)
tcp_rcv_state_process(struct sock * sk, struct sk_buff * skb) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_input.c:6046)
tcp_v4_do_rcv(struct sock * sk, struct sk_buff * skb) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c:1563)
sk_backlog_rcv() (/root/linux-5.0.1/include/net/sock.h:936)
__release_sock(struct sock * sk) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/core/sock.c:2284)
release_sock(struct sock * sk) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/core/sock.c:2800)
inet_wait_for_connect() (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/af_inet.c:588)
__inet_stream_connect(struct socket * sock, struct sockaddr * uaddr, int addr_len, int flags, int is_sendmsg) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/af_inet.c:680)
inet_stream_connect(struct socket * sock, struct sockaddr * uaddr, int addr_len, int flags) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/af_inet.c:719)
__sys_connect(int fd, struct sockaddr * uservaddr, int addrlen) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:1663)
__do_sys_connect() (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:1674)
__se_sys_connect() (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/socket.c:1671)
...
- 内核源码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
/* net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c */
int tcp_v4_do_rcv(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) {
...
if (tcp_rcv_state_process(sk, skb)) {
...
}
...
}
/* net/ipv4/tcp_input.c */
int tcp_rcv_state_process(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) {
...
switch (sk->sk_state) {
...
case TCP_SYN_SENT:
...
queued = tcp_rcv_synsent_state_process(sk, skb, th);
...
}
...
}
/* net/ipv4/tcp_input.c */
static int tcp_rcv_synsent_state_process(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct tcphdr *th) {
...
if (th->ack) {
...
/* 将 TCP 状态改变为 TCP_ESTABLISHED。 */
tcp_finish_connect(sk, skb);
...
if (sk->sk_write_pending ||
icsk->icsk_accept_queue.rskq_defer_accept ||
icsk->icsk_ack.pingpong) {
...
} else {
/* 向服务发送 ack. */
tcp_send_ack(sk);
}
}
}
/* net/ipv4/tcp_input.c */
void tcp_finish_connect(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) {
...
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_ESTABLISHED);
...
}
2.4. 服务端 - TCP_SYN_RECV
服务端收到客户端第三次握手发过来的 ACK 包,服务端将 TCP 状态从 TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV 修改为 TCP_SYN_RECV,然后为连接结构(struct sock)分配空间,这样可以提高资源的分配效率。
【注意】 旧版的 Linux 内核,在第二次握手时,TCP 状态已经是 TCP_SYN_RECV,但是新版已经修改逻辑,第二次握手 TCP 状态是 TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV,第三次握手后,TCP 状态才是 TCP_SYN_RECV。
详细参考 2015 年 Linux 4.1 的补丁:inet: add TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV state
- 函数堆栈。
1
2
3
4
5
6
inet_csk_clone_lock(const struct sock * sk, const struct request_sock * req, const gfp_t priority) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/inet_connection_sock.c:799)
tcp_create_openreq_child(const struct sock * sk, struct request_sock * req, struct sk_buff * skb) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_minisocks.c:452)
tcp_v4_syn_recv_sock(const struct sock * sk, struct sk_buff * skb, struct request_sock * req, struct dst_entry * dst, struct request_sock * req_unhash, bool * own_req) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c:1423)
tcp_check_req(struct sock * sk, struct sk_buff * skb, struct request_sock * req, bool fastopen, bool * req_stolen) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_minisocks.c:786)
tcp_v4_rcv(struct sk_buff * skb) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c:1856)
...
- 内核源码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
int tcp_v4_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb) {
...
if (sk->sk_state == TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV) {
...
if (!tcp_filter(sk, skb)) {
...
nsk = tcp_check_req(sk, skb, req, false, &req_stolen);
}
...
}
...
}
struct sock *tcp_check_req(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb,
struct request_sock *req,
bool fastopen, bool *req_stolen)
{
...
/* OK, ACK is valid, create big socket and
* feed this segment to it. It will repeat all
* the tests. THIS SEGMENT MUST MOVE SOCKET TO
* ESTABLISHED STATE. If it will be dropped after
* socket is created, wait for troubles.
*/
child = inet_csk(sk)->icsk_af_ops->syn_recv_sock(sk, skb, req, NULL,
req, &own_req);
...
}
struct sock *tcp_v4_syn_recv_sock(const struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb,
struct request_sock *req,
struct dst_entry *dst,
struct request_sock *req_unhash,
bool *own_req) {
...
if (sk_acceptq_is_full(sk))
goto exit_overflow;
newsk = tcp_create_openreq_child(sk, req, skb);
if (!newsk)
goto exit_nonewsk;
...
}
struct sock *tcp_create_openreq_child(const struct sock *sk,
struct request_sock *req,
struct sk_buff *skb) {
struct sock *newsk = inet_csk_clone_lock(sk, req, GFP_ATOMIC);
...
}
struct sock *inet_csk_clone_lock(const struct sock *sk,
const struct request_sock *req,
const gfp_t priority) {
struct sock *newsk = sk_clone_lock(sk, priority);
if (newsk) {
struct inet_connection_sock *newicsk = inet_csk(newsk);
/* 为新连接分配 sock 空间,tcp 改变为 TCP_SYN_RECV。 */
inet_sk_set_state(newsk, TCP_SYN_RECV);
...
}
return newsk;
}
2.5. 服务端 - TCP_ESTABLISHED
第三次握手,将 TCP 状态修改为 TCP_SYN_RECV,处理完逻辑后,随后将修改为 TCP_ESTABLISHED。
1
TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV --> TCP_SYN_RECV --> TCP_ESTABLISHED
- 函数堆栈。
1
2
3
4
tcp_rcv_state_process(struct sock * sk, struct sk_buff * skb) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_input.c:6113)
tcp_child_process(struct sock * parent, struct sock * child, struct sk_buff * skb) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_minisocks.c:845)
tcp_v4_rcv(struct sk_buff * skb) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c:1875)
...
- 内核源码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
int tcp_v4_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb) {
...
if (sk->sk_state == TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV) {
...
if (!tcp_filter(sk, skb)) {
...
/* 修改 TCP 状态为:TCP_SYN_RECV */
nsk = tcp_check_req(sk, skb, req, false, &req_stolen);
}
...
if (nsk == sk) {
...
} else if (tcp_child_process(sk, nsk, skb)) {
...
}
...
}
...
}
int tcp_child_process(struct sock *parent, struct sock *child,
struct sk_buff *skb) {
...
if (!sock_owned_by_user(child)) {
ret = tcp_rcv_state_process(child, skb);
/* Wakeup parent, send SIGIO */
if (state == TCP_SYN_RECV && child->sk_state != state)
parent->sk_data_ready(parent);
}
...
}
int tcp_rcv_state_process(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) {
...
switch (sk->sk_state) {
case TCP_SYN_RECV:
...
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_ESTABLISHED);
...
}
}

