走读网络协议栈 listen (tcp) 的(Linux - 5.0.1 下载)内核源码。
要了解 listen 工作原理,须要搞清楚两个部分:
- listen socket 数据在内核里是如何存储的。
- listen socket 半连接和全连接逻辑。
1. 概述
listen 主要做两件事:
- 将 socket 设置为监听 socket,作为服务端被动等待客户端连接。
- backlog 限制全连接队列的大小,还有限制半连接个数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
#include <sys/socket.h>
/* sockfd:socket's fd。
* backlog:全连接队列和半连接队列限制大小。
* return:正确返回 0,否则返回 -1。
*/
int listen(int sockfd, int backlog);
参考:《UNIX 网络编程_卷1》
2. 系统调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
SYSCALL_DEFINE2(listen, int, fd, int, backlog) {
return __sys_listen(fd, backlog);
}
/* net/socket.c */
int __sys_listen(int fd, int backlog) {
struct socket *sock;
int err, fput_needed;
int somaxconn;
/* 通过 fd 查找 socket. */
sock = sockfd_lookup_light(fd, &err, &fput_needed);
if (sock) {
/* backlog 配置默认最大值。 */
somaxconn = sock_net(sock->sk)->core.sysctl_somaxconn;
/* 如果 backlog 超过了配置值,就采用配置的值。 */
if ((unsigned int)backlog > somaxconn)
backlog = somaxconn;
...
if (!err)
/* inet_listen */
err = sock->ops->listen(sock, backlog);
...
}
...
}
/* net/ipv4/af_inet.c */
int inet_listen(struct socket *sock, int backlog) {
struct sock *sk = sock->sk;
unsigned char old_state;
int err, tcp_fastopen;
lock_sock(sk);
err = -EINVAL;
/* 只有 tcp 才允许 listen,作为服务端的 socket,不能主动连接其它服务。 */
if (sock->state != SS_UNCONNECTED || sock->type != SOCK_STREAM)
goto out;
/* 只有处于 TCP_CLOSE 或者 TCP_LISTEN 状态的 socket 才能调用 listen。*/
old_state = sk->sk_state;
if (!((1 << old_state) & (TCPF_CLOSE | TCPF_LISTEN)))
goto out;
sk->sk_max_ack_backlog = backlog;
/* listen 可以重复调用,重复调用 listen 可修改 backlog,参考 nginx。*/
if (old_state != TCP_LISTEN) {
...
/* 开始 listen 主逻辑。 */
err = inet_csk_listen_start(sk, backlog);
if (err)
goto out;
...
}
err = 0;
...
}
int inet_csk_listen_start(struct sock *sk, int backlog) {
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
int err = -EADDRINUSE;
reqsk_queue_alloc(&icsk->icsk_accept_queue);
sk->sk_ack_backlog = 0;
inet_csk_delack_init(sk);
/* There is race window here: we announce ourselves listening,
* but this transition is still not validated by get_port().
* It is OK, because this socket enters to hash table only
* after validation is complete.
*/
/* 经过验证后,设置 socket 的状态为 TCP_LISTEN。*/
inet_sk_state_store(sk, TCP_LISTEN);
/* 重新验证端口,虽然在这之前 bind 绑定了端口,但是 bind 和 listen 这是两个独立的操作,
* 这两个操作之间时间段,整个系统,可能执行了一些影响端口的操作,
* 所以 listen 要重新验证一下端口是否已经成功绑定了。 */
if (!sk->sk_prot->get_port(sk, inet->inet_num)) {
inet->inet_sport = htons(inet->inet_num);
sk_dst_reset(sk);
/* inet_hash */
err = sk->sk_prot->hash(sk);
...
}
...
}
int inet_hash(struct sock *sk) {
int err = 0;
if (sk->sk_state != TCP_CLOSE) {
local_bh_disable();
/* hash 保存 sk 值,参考下文剖析。 */
err = __inet_hash(sk, NULL);
local_bh_enable();
}
return err;
}
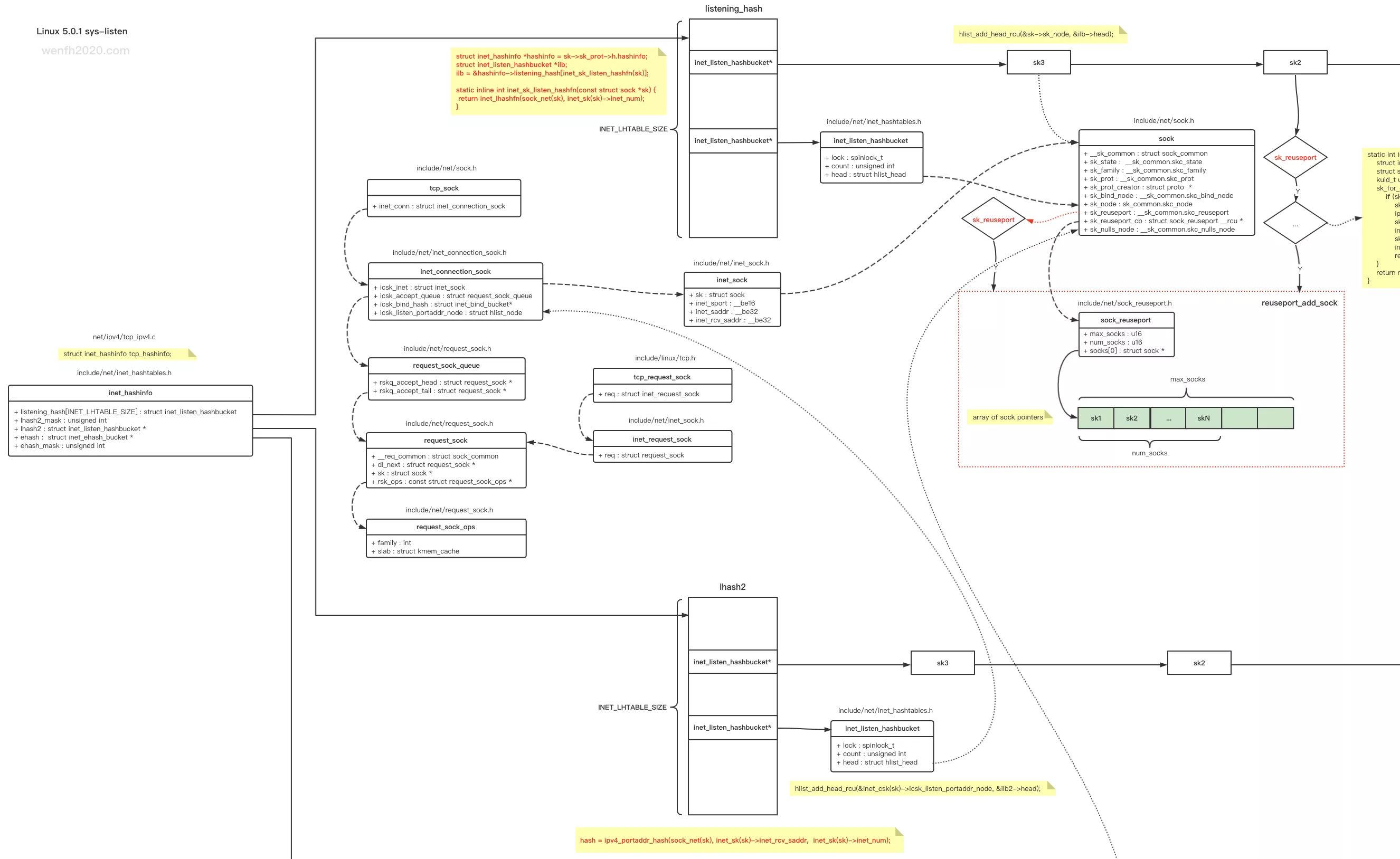
3. 哈希表
listen 成功,socket.sock 指针被保存于哈希表中,因为添加了 reuseport 端口重用功能(负载均衡),逻辑变得复杂起来。reuseport 逻辑,可以看看 linux 这几个补丁的修改:
因为墙,github 链接不一定能正常打开~
- (2013 年) soreuseport: TCP/IPv4 implementation
- (2016 年) soreuseport: define reuseport groups
- (2017 年) inet: Add a 2nd listener hashtable (port+addr)
3.1. 数据结构
- 源码结构。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
/* net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c */
struct inet_hashinfo tcp_hashinfo;
/* include/net/inet_hashtables.h
* Sockets can be hashed in established or listening table
*/
struct inet_listen_hashbucket {
spinlock_t lock;
unsigned int count;
struct hlist_head head;
};
#define INET_LHTABLE_SIZE 32 /* Yes, really, this is all you need. */
/* include/net/inet_hashtables.h
* hash 结构,保存了端口对应的 socket 信息。 */
struct inet_hashinfo {
/* always be without wildcards and will have the following invariant:
*
* TCP_ESTABLISHED <= sk->sk_state < TCP_CLOSE
*
*/
struct inet_ehash_bucket *ehash; /* 保存了 TCP_ESTABLISHED <= sk->sk_state < TCP_CLOSE 状态的连接。 */
spinlock_t *ehash_locks;
unsigned int ehash_mask;
unsigned int ehash_locks_mask;
/* The 2nd listener table hashed by local port and address */
unsigned int lhash2_mask;
struct inet_listen_hashbucket *lhash2;
/* All the above members are written once at bootup and
* never written again _or_ are predominantly read-access.
*
* Now align to a new cache line as all the following members
* might be often dirty.
*/
/* All sockets in TCP_LISTEN state will be in listening_hash.
* This is the only table where wildcard'd TCP sockets can
* exist. listening_hash is only hashed by local port number.
* If lhash2 is initialized, the same socket will also be hashed
* to lhash2 by port and address.
*/
struct inet_listen_hashbucket listening_hash[INET_LHTABLE_SIZE]
____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
};
- 哈希表与 socket 的结构关系:
- 逻辑。
-
一开始监听的 socket,根据端口值哈希,保存在 inet_hashinfo.listening_hash 哈希表里。后面因为引入 reuseport 功能,多个 socket 可以 bind/listen 相同的 ip/port,这样导致根据端口哈希值保存的数据,哈希链冲突严重,查询性能下降。
-
后面引入了 (sock_reuseport) 数组,保存符合 reuseport 条件的 socket,当要从 reuseport 场景中,找出一个 socket,先根据端口哈希值,从 inet_hashinfo.listening_hash 中找出第一个符合条件的 socket,因为每个 socket.sock.sk_reuseport_cb 指针都指向了 (sock_reuseport) 数组,然后再从该数组中再哈希查找一个 socket,这样 reuseport 选项的每个 socket 查询的概率相对平衡。
-
但是上述操作还是无法解决相同端口 sk 过多会导致哈希链冲突的问题,所以后面又引入了 inet_hashinfo.lhash2 哈希表,哈希因子再也不只是端口值,而是 ip/port 两个数值(ipv4_portaddr_hash()),这样查找哈希链的冲突减少了。(参考下文:查找 listen socket)
详细查看补丁:(2017 年) inet: Add a 2nd listener hashtable (port+addr)
3.2. 哈希存储逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
/* 本函数主要有两个逻辑:inet_reuseport_add_sock 和 inet_hash2。 */
int __inet_hash(struct sock *sk, struct sock *osk) {
struct inet_hashinfo *hashinfo = sk->sk_prot->h.hashinfo;
struct inet_listen_hashbucket *ilb;
int err = 0;
...
/* 根据 sk 端口哈希值保存 sk。 */
ilb = &hashinfo->listening_hash[inet_sk_listen_hashfn(sk)];
spin_lock(&ilb->lock);
if (sk->sk_reuseport) {
/* 如果 sk_reuseport 选项,那么将 sk 也保存于 sock_reuseport.socks 数组里。 */
err = inet_reuseport_add_sock(sk, ilb);
if (err)
goto unlock;
}
/* 保存 sk 于 inet_hashinfo.listening_hash 哈希表。 */
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IPV6) && sk->sk_reuseport &&
sk->sk_family == AF_INET6)
hlist_add_tail_rcu(&sk->sk_node, &ilb->head);
else
hlist_add_head_rcu(&sk->sk_node, &ilb->head);
/* 将 sk 保存于 inet_hashinfo.lhash2 哈希表中(根据 ip/port 哈希值保存)。 */
inet_hash2(hashinfo, sk);
ilb->count++;
...
}
/* 添加 sk 到 sock_reuseport.socks 数组。 */
static int inet_reuseport_add_sock(struct sock *sk,
struct inet_listen_hashbucket *ilb) {
struct inet_bind_bucket *tb = inet_csk(sk)->icsk_bind_hash;
struct sock *sk2;
kuid_t uid = sock_i_uid(sk);
sk_for_each_rcu(sk2, &ilb->head) {
if (sk2 != sk &&
sk2->sk_family == sk->sk_family &&
ipv6_only_sock(sk2) == ipv6_only_sock(sk) &&
sk2->sk_bound_dev_if == sk->sk_bound_dev_if &&
inet_csk(sk2)->icsk_bind_hash == tb &&
sk2->sk_reuseport && uid_eq(uid, sock_i_uid(sk2)) &&
inet_rcv_saddr_equal(sk, sk2, false))
/* 将符合 reuseport 条件的 sk 保存于 sock_reuseport.socks 数组。 */
return reuseport_add_sock(sk, sk2, inet_rcv_saddr_any(sk));
}
/* 第一次将符合 reuseport 条件的 sk 保存于 sock_reuseport.socks 数组。
* 因为第一次数组等信息需要初始化。 */
return reuseport_alloc(sk, inet_rcv_saddr_any(sk));
}
/* 将 sk 保存于 inet_hashinfo.lhash2 哈希表。 */
static void inet_hash2(struct inet_hashinfo *h, struct sock *sk) {
struct inet_listen_hashbucket *ilb2;
if (!h->lhash2)
return;
ilb2 = inet_lhash2_bucket_sk(h, sk);
spin_lock(&ilb2->lock);
if (sk->sk_reuseport && sk->sk_family == AF_INET6)
hlist_add_tail_rcu(&inet_csk(sk)->icsk_listen_portaddr_node,
&ilb2->head);
else
hlist_add_head_rcu(&inet_csk(sk)->icsk_listen_portaddr_node,
&ilb2->head);
ilb2->count++;
spin_unlock(&ilb2->lock);
}
/* 根据 ip/port 找到哈希表对应的 slot。 */
static struct inet_listen_hashbucket *
inet_lhash2_bucket_sk(struct inet_hashinfo *h, struct sock *sk) {
u32 hash;
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IPV6)
if (sk->sk_family == AF_INET6)
hash = ipv6_portaddr_hash(sock_net(sk),
&sk->sk_v6_rcv_saddr,
inet_sk(sk)->inet_num);
else
#endif
hash = ipv4_portaddr_hash(sock_net(sk),
inet_sk(sk)->inet_rcv_saddr,
inet_sk(sk)->inet_num);
/* 根据哈希值从哈希表获取对应的 slot。 */
return inet_lhash2_bucket(h, hash);
}
/* ip/port 哈希函数。 */
static inline u32 ipv4_portaddr_hash(const struct net *net,
__be32 saddr, unsigned int port) {
return jhash_1word((__force u32)saddr, net_hash_mix(net)) ^ port;
}
3.3. 查找 listen socket
tcp 客户端主动链接服务,第一次握手,服务是如何查找 listen socket 的。
- __inet_lookup_listener 从 inet_hashinfo.lhash2 对应的哈希槽上查找数据。
- 如果是 reuseport 选项,再从 sock_reuseport.socks 数组上哈希找(参考下文)。
- 堆栈。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
...
__inet_lookup_listener(struct net * net, struct inet_hashinfo * hashinfo, struct sk_buff * skb, int doff, const __be32 saddr, __be16 sport, const __be32 daddr, const unsigned short hnum, const int dif, const int sdif) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/inet_hashtables.c:309)
__inet_lookup() (/root/linux-5.0.1/include/net/inet_hashtables.h:350)
__inet_lookup_skb() (/root/linux-5.0.1/include/net/inet_hashtables.h:387)
tcp_v4_rcv(struct sk_buff * skb) (/root/linux-5.0.1/net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c:1818)
...
do_softirq() (/root/linux-5.0.1/kernel/softirq.c:337)
- 内核源码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
static inline struct sock *__inet_lookup(struct net *net,
struct inet_hashinfo *hashinfo,
struct sk_buff *skb, int doff,
const __be32 saddr, const __be16 sport,
const __be32 daddr, const __be16 dport,
const int dif, const int sdif,
bool *refcounted) {
u16 hnum = ntohs(dport);
struct sock *sk;
/* 从 established 哈希表中找连接的 socket.sock 指针。
* 第一次握手时,服务端还没将 sock 指针添加到 established 哈希表中。
* established 哈希表保存的是 TCP_ESTABLISHED <= sk->sk_state < TCP_CLOSE 状态的连接。*/
sk = __inet_lookup_established(net, hashinfo, saddr, sport,
daddr, hnum, dif, sdif);
*refcounted = true;
if (sk)
return sk;
*refcounted = false;
/* 找 listen socket。 */
return __inet_lookup_listener(net, hashinfo, skb, doff, saddr,
sport, daddr, hnum, dif, sdif);
}
struct sock *__inet_lookup_listener(struct net *net,
struct inet_hashinfo *hashinfo,
struct sk_buff *skb, int doff,
const __be32 saddr, __be16 sport,
const __be32 daddr, const unsigned short hnum,
const int dif, const int sdif) {
struct inet_listen_hashbucket *ilb2;
struct sock *result = NULL;
unsigned int hash2;
/* 通过目标 ip/port 哈希值从 hashinfo.lhash2 查找对应的 slot。*/
hash2 = ipv4_portaddr_hash(net, daddr, hnum);
ilb2 = inet_lhash2_bucket(hashinfo, hash2);
result = inet_lhash2_lookup(net, ilb2, skb, doff,
saddr, sport, daddr, hnum,
dif, sdif);
...
return result;
}
/* called with rcu_read_lock() : No refcount taken on the socket */
static struct sock *inet_lhash2_lookup(struct net *net,
struct inet_listen_hashbucket *ilb2,
struct sk_buff *skb, int doff,
const __be32 saddr, __be16 sport,
const __be32 daddr, const unsigned short hnum,
const int dif, const int sdif) {
bool exact_dif = inet_exact_dif_match(net, skb);
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk;
struct sock *sk, *result = NULL;
int score, hiscore = 0;
u32 phash = 0;
inet_lhash2_for_each_icsk_rcu(icsk, &ilb2->head) {
sk = (struct sock *)icsk;
score = compute_score(sk, net, hnum, daddr, dif, sdif, exact_dif);
/* 统计分数,获取最大匹配分数的 socket。*/
if (score > hiscore) {
if (sk->sk_reuseport) {
phash = inet_ehashfn(net, daddr, hnum, saddr, sport);
/* 在数组里,通过哈希获得 sk。 */
result = reuseport_select_sock(sk, phash, skb, doff);
if (result)
return result;
}
result = sk;
hiscore = score;
}
}
return result;
}
struct sock *reuseport_select_sock(struct sock *sk,
u32 hash,
struct sk_buff *skb,
int hdr_len) {
struct sock_reuseport *reuse;
struct bpf_prog *prog;
struct sock *sk2 = NULL;
u16 socks;
rcu_read_lock();
reuse = rcu_dereference(sk->sk_reuseport_cb);
...
prog = rcu_dereference(reuse->prog);
socks = READ_ONCE(reuse->num_socks);
if (likely(socks)) {
...
select_by_hash:
/* no bpf or invalid bpf result: fall back to hash usage */
if (!sk2)
/* 通过哈希获得对应的数组下标,从而获得概率相对平衡的数据。 */
sk2 = reuse->socks[reciprocal_scale(hash, socks)];
}
...
return sk2;
}
4. 连接逻辑
tcp 通信,客户端通过三次握手与服务端建立连接。
第一次握手时,服务端先创建一个轻量版本的 request_sock,第三次握手时,才会创建 sock,这样可以减少资源的消耗。(Linux 5.0.1)其实没有 半连接队列,半链接的 request_sock 指针保存于 inet_hashinfo.ehash 哈希表里,而半连接的统计数据 qlen,保存于 listen sock 的 inet_connection_sock.icsk_accept_queue 里。
三次握手后,request_sock 指针会保存于全连接队列:inet_connection_sock.icsk_accept_queue.rskq_accept_head,等待 accept。
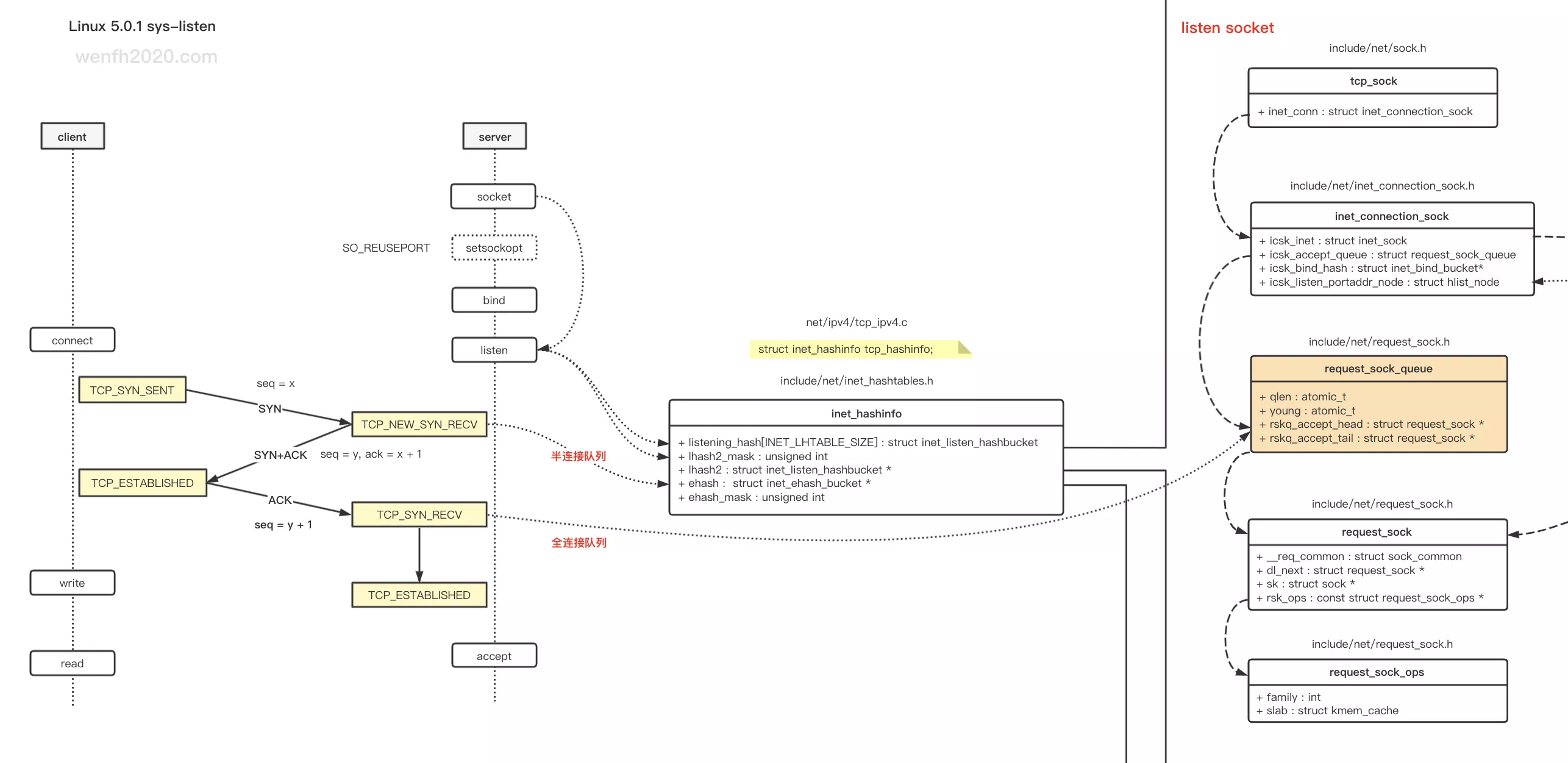
4.1. 数据结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
/* 网络链接逻辑的 socket 结构。
* inet_connection_sock - INET connection oriented sock
*
* @icsk_accept_queue: FIFO of established children
* @icsk_listen_portaddr_node: hash to the portaddr listener hashtable
*/
struct inet_connection_sock {
/* inet_sock has to be the first member! */
struct inet_sock icsk_inet;
struct request_sock_queue icsk_accept_queue; /* 半连接和全连接数据记录。 */
...
};
struct sock {
...
u32 sk_ack_backlog; /* 当前全连接队列已有数据个数。 */
u32 sk_max_ack_backlog; /* listen 的 backlog,用于限制半连接和全连接队列的长度。 */
...
}
/** struct request_sock_queue - queue of request_socks
*
* @rskq_accept_head - FIFO head of established children
* @rskq_accept_tail - FIFO tail of established children
*/
struct request_sock_queue {
...
atomic_t qlen; /* 半连接队列 sk 个数。 */
atomic_t young; /* 用于超时重传。 */
/* 完成三次握手,等待 accept 的 sock。 */
struct request_sock *rskq_accept_head; /* 队列头。 */
struct request_sock *rskq_accept_tail; /* 队列尾。 */
...
};
/* 缩减版的 sock,连接过程中,三次握手的第一次握手创建,主要是为了节省资源。
* 等到第三次握手成功了,才会创建正常的 sock。
* struct request_sock - mini sock to represent a connection request
*/
struct request_sock {
struct sock_common __req_common;
...
struct request_sock *dl_next;
...
};
4.2. 半连接
- 当服务端收到客户端第一次握手 syn 请求。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
int tcp_conn_request(struct request_sock_ops *rsk_ops,
const struct tcp_request_sock_ops *af_ops,
struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) {
...
struct request_sock *req;
...
/* TW buckets are converted to open requests without
* limitations, they conserve resources and peer is
* evidently real one.
*/
if ((net->ipv4.sysctl_tcp_syncookies == 2 || inet_csk_reqsk_queue_is_full(sk))
&& !isn) {
want_cookie = tcp_syn_flood_action(sk, skb, rsk_ops->slab_name);
if (!want_cookie)
goto drop;
}
/* 检查全连接是否已满。 */
if (sk_acceptq_is_full(sk)) {
NET_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), LINUX_MIB_LISTENOVERFLOWS);
goto drop;
}
/* 第一次握手,创建缩减版的 sock:request_sock。 */
req = inet_reqsk_alloc(rsk_ops, sk, !want_cookie);
if (!req)
goto drop;
...
if (fastopen_sk) {
...
} else {
/* 第一次握手,将 req */
tcp_rsk(req)->tfo_listener = false;
if (!want_cookie)
/* 哈希存储半连接信息。 */
inet_csk_reqsk_queue_hash_add(sk, req, tcp_timeout_init((struct sock *)req));
/* 第二次握手:发送 syn + ack。 */
af_ops->send_synack(sk, dst, &fl, req, &foc,
!want_cookie ? TCP_SYNACK_NORMAL :
TCP_SYNACK_COOKIE);
...
}
...
}
void inet_csk_reqsk_queue_hash_add(struct sock *sk, struct request_sock *req,
unsigned long timeout) {
reqsk_queue_hash_req(req, timeout);
inet_csk_reqsk_queue_added(sk);
}
/* 存储连接信息到 inet_hashinfo.ehash。
* insert a socket into ehash, and eventually remove another one
* (The another one can be a SYN_RECV or TIMEWAIT
*/
bool inet_ehash_insert(struct sock *sk, struct sock *osk) {
struct inet_hashinfo *hashinfo = sk->sk_prot->h.hashinfo;
struct hlist_nulls_head *list;
struct inet_ehash_bucket *head;
spinlock_t *lock;
bool ret = true;
WARN_ON_ONCE(!sk_unhashed(sk));
sk->sk_hash = sk_ehashfn(sk);
head = inet_ehash_bucket(hashinfo, sk->sk_hash);
list = &head->chain;
lock = inet_ehash_lockp(hashinfo, sk->sk_hash);
spin_lock(lock);
if (osk) {
WARN_ON_ONCE(sk->sk_hash != osk->sk_hash);
ret = sk_nulls_del_node_init_rcu(osk);
}
if (ret)
__sk_nulls_add_node_rcu(sk, list);
spin_unlock(lock);
return ret;
}
static void reqsk_queue_hash_req(struct request_sock *req, unsigned long timeout) {
req->num_retrans = 0;
req->num_timeout = 0;
req->sk = NULL;
/* 添加定时器。 */
timer_setup(&req->rsk_timer, reqsk_timer_handler, TIMER_PINNED);
mod_timer(&req->rsk_timer, jiffies + timeout);
/* 将 sk 指针保存于 inet_hashinfo.ehash 哈希表。 */
inet_ehash_insert(req_to_sk(req), NULL);
...
}
static inline void inet_csk_reqsk_queue_added(struct sock *sk) {
reqsk_queue_added(&inet_csk(sk)->icsk_accept_queue);
}
/* include/net/request_sock.h */
static inline void reqsk_queue_added(struct request_sock_queue *queue) {
atomic_inc(&queue->young);
/* 半连接连接个数 + 1。*/
atomic_inc(&queue->qlen);
}
- 检查队列是否已满。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
/* include/net/inet_connection_sock.h
* 判断半连接队列是否已满。*/
static inline int inet_csk_reqsk_queue_is_full(const struct sock *sk) {
return inet_csk_reqsk_queue_len(sk) >= sk->sk_max_ack_backlog;
}
static inline int inet_csk_reqsk_queue_len(const struct sock *sk) {
return reqsk_queue_len(&inet_csk(sk)->icsk_accept_queue);
}
static inline int reqsk_queue_len(const struct request_sock_queue *queue) {
return atomic_read(&queue->qlen);
}
/* 检查全连接队列是否已满。 */
static inline bool sk_acceptq_is_full(const struct sock *sk) {
return sk->sk_ack_backlog > sk->sk_max_ack_backlog;
}
4.3. 全连接队列
tcp connect 过程中,已经完成三次握手的连接。
- sock 被创建。
- 连接的 request_sock 信息会放进 listen socket 的全连接队列(inet_connection_sock.request_sock_queue.request_sock),等待 accept 函数从队列里面捞数据。
- request_sock_queue。
1
2
3
4
5
6
struct request_sock_queue {
...
struct request_sock *rskq_accept_head; /* 队列头。 */
struct request_sock *rskq_accept_tail; /* 队列尾。 */
...
};
- 管理全连接队列数据大小。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
struct inet_connection_sock {
/* inet_sock has to be the first member! */
struct inet_sock icsk_inet;
...
};
struct inet_sock {
/* sk and pinet6 has to be the first two members of inet_sock */
struct sock sk;
...
}
struct sock {
...
u32 sk_ack_backlog; /* 当前全连接队列已有数据个数。 */
u32 sk_max_ack_backlog; /* listen 的 backlog,用于限制半连接和全连接队列的长度。 */
...
}
static inline bool sk_acceptq_is_full(const struct sock *sk) {
return sk->sk_ack_backlog > sk->sk_max_ack_backlog;
}
static inline void sk_acceptq_added(struct sock *sk) {
sk->sk_ack_backlog++;
}
- 三次握手完成后,将 request_sock 信息添加到全连接队列。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
/* net/ipv4/tcp_minisocks.c
* Process an incoming packet for SYN_RECV sockets represented as a
* request_sock. Normally sk is the listener socket but for TFO it
* points to the child socket.
*
* XXX (TFO) - The current impl contains a special check for ack
* validation and inside tcp_v4_reqsk_send_ack(). Can we do better?
*
* We don't need to initialize tmp_opt.sack_ok as we don't use the results
*/
/* 服务端第三次握手,检查 request_sock。*/
struct sock *tcp_check_req(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb,
struct request_sock *req,
bool fastopen, bool *req_stolen) {
...
/* OK, ACK is valid, create big socket and
* feed this segment to it. It will repeat all
* the tests. THIS SEGMENT MUST MOVE SOCKET TO
* ESTABLISHED STATE. If it will be dropped after
* socket is created, wait for troubles.
*/
/* 创建 sock,state: TCP_SYN_RECV。 */
child = inet_csk(sk)->icsk_af_ops->syn_recv_sock(sk, skb, req, NULL, req, &own_req);
...
/* 三次握手成功,管理全连接队列数据。 */
return inet_csk_complete_hashdance(sk, child, req, own_req);
...
}
/* 完成三次握手。 */
struct sock *inet_csk_complete_hashdance(struct sock *sk, struct sock *child,
struct request_sock *req, bool own_req) {
if (own_req) {
inet_csk_reqsk_queue_drop(sk, req);
reqsk_queue_removed(&inet_csk(sk)->icsk_accept_queue, req);
if (inet_csk_reqsk_queue_add(sk, req, child))
return child;
}
...
}
static inline void reqsk_queue_removed(struct request_sock_queue *queue,
const struct request_sock *req) {
if (req->num_timeout == 0)
atomic_dec(&queue->young);
atomic_dec(&queue->qlen);
}
/* 完成三次握手的时候 sock 已经创建了。 */
struct sock *inet_csk_reqsk_queue_add(struct sock *sk,
struct request_sock *req,
struct sock *child) {
struct request_sock_queue *queue = &inet_csk(sk)->icsk_accept_queue;
spin_lock(&queue->rskq_lock);
if (unlikely(sk->sk_state != TCP_LISTEN)) {
inet_child_forget(sk, req, child);
child = NULL;
} else {
req->sk = child;
req->dl_next = NULL;
if (queue->rskq_accept_head == NULL)
queue->rskq_accept_head = req;
else
queue->rskq_accept_tail->dl_next = req;
queue->rskq_accept_tail = req;
sk_acceptq_added(sk);
}
spin_unlock(&queue->rskq_lock);
return child;
}
static inline void sk_acceptq_added(struct sock *sk) {
sk->sk_ack_backlog++;
}
- 使用。当 listen socket (TCP) 有新的连接时,返回 EPOLLIN 可读事件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
/* net/ipv4/tcp.c
*
* Wait for a TCP event.
*
* Note that we don't need to lock the socket, as the upper poll layers
* take care of normal races (between the test and the event) and we don't
* go look at any of the socket buffers directly.
*/
__poll_t tcp_poll(struct file *file, struct socket *sock, poll_table *wait) {
...
state = inet_sk_state_load(sk);
if (state == TCP_LISTEN)
return inet_csk_listen_poll(sk);
}
/*
* LISTEN is a special case for poll..
*/
static inline __poll_t inet_csk_listen_poll(const struct sock *sk) {
return !reqsk_queue_empty(&inet_csk(sk)->icsk_accept_queue) ?
(EPOLLIN | EPOLLRDNORM) : 0;
}
static inline bool reqsk_queue_empty(const struct request_sock_queue *queue) {
return queue->rskq_accept_head == NULL;
}
5. backlog 限制设置
关于全连接和半连接的限制设置,可以参考:TCP 半连接队列和全连接队列满了会发生什么?又该如何应对?,这个帖子说得比较详细和通俗易懂。
5.1. somaxconn
listen 的 backlog 参数最大不能超过 somaxconn。它用于限制 tcp 的全连接队列和半连接队列的长度。
1
2
3
# /etc/sysctl.conf
net.core.somaxconn = 2048
# /sbin/sysctl -p
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
static struct ctl_table netns_core_table[] = {
{
.procname = "somaxconn",
.data = &init_net.core.sysctl_somaxconn,
.maxlen = sizeof(int),
.mode = 0644,
.extra1 = &zero,
.proc_handler = proc_dointvec_minmax
},
{ }
};
int __sys_listen(int fd, int backlog) {
struct socket *sock;
int err, fput_needed;
int somaxconn;
sock = sockfd_lookup_light(fd, &err, &fput_needed);
if (sock) {
somaxconn = sock_net(sock->sk)->core.sysctl_somaxconn;
/* backlog 最大不能超过 somaxconn。 */
if ((unsigned int)backlog > somaxconn)
backlog = somaxconn;
err = security_socket_listen(sock, backlog);
if (!err)
err = sock->ops->listen(sock, backlog);
fput_light(sock->file, fput_needed);
}
return err;
}
/* include/net/inet_connection_sock.h
* 判断半连接队列是否已满。*/
static inline int inet_csk_reqsk_queue_is_full(const struct sock *sk) {
return inet_csk_reqsk_queue_len(sk) >= sk->sk_max_ack_backlog;
}
/* 检查全连接队列是否已满。 */
static inline bool sk_acceptq_is_full(const struct sock *sk) {
return sk->sk_ack_backlog > sk->sk_max_ack_backlog;
}
5.2. tcp_max_syn_backlog
tcp_max_syn_backlog 在系统配置中设置,用于检查 syn 半连接队列健康情况,当服务端接收到一定数量的 syn 包,要检查新旧包是否有冲突,如有冲突就丢弃新包,这样就要避免洪水攻击。
1
2
3
# /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 2048
# /sbin/sysctl -p
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
static int __net_init tcp_sk_init(struct net *net) {
...
net->ipv4.sysctl_max_syn_backlog = max(128, cnt / 256);
...
}
struct netns_ipv4 {
...
int sysctl_max_syn_backlog;
...
}
static struct ctl_table ipv4_net_table[] = {
...
{
.procname = "tcp_max_syn_backlog",
.data = &init_net.ipv4.sysctl_max_syn_backlog,
.maxlen = sizeof(int),
.mode = 0644,
.proc_handler = proc_dointvec
},
...
}
/* 服务端收到客户端的第一次握手 syn 包。 */
int tcp_conn_request(struct request_sock_ops *rsk_ops,
const struct tcp_request_sock_ops *af_ops,
struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) {
...
if (!want_cookie && !isn) {
/* Kill the following clause, if you dislike this way. */
if (!net->ipv4.sysctl_tcp_syncookies &&
/* 半连接长度如果超过 syn back 长度的 3/4 */
(net->ipv4.sysctl_max_syn_backlog - inet_csk_reqsk_queue_len(sk) <
(net->ipv4.sysctl_max_syn_backlog >> 2)) &&
/* tcp_peer_is_proven - PAWS 检查机制。 */
!tcp_peer_is_proven(req, dst)) {
/* Without syncookies last quarter of
* backlog is filled with destinations,
* proven to be alive.
* It means that we continue to communicate
* to destinations, already remembered
* to the moment of synflood.
*/
pr_drop_req(req, ntohs(tcp_hdr(skb)->source),
rsk_ops->family);
goto drop_and_release;
}
isn = af_ops->init_seq(skb);
}
...
}


