为了搞明白 libco 协程切换原理(《[libco] 协程切换理解思路》),重温已经还给老师的汇编知识。
通过 lldb 调试器,在 64 位的 MacOS(x86_64)机器上调试测试程序,观察相关数据(程序汇编编码,寄存器数据,对应数据内存地址),去理解运行时栈的内存布局。
1. 程序工作流程
详细请参考:《程序工作流程(Linux)》。
1.1. 程序编译加载
高级语言通过编译器编译成低级语言指令提供给机器设备运行。
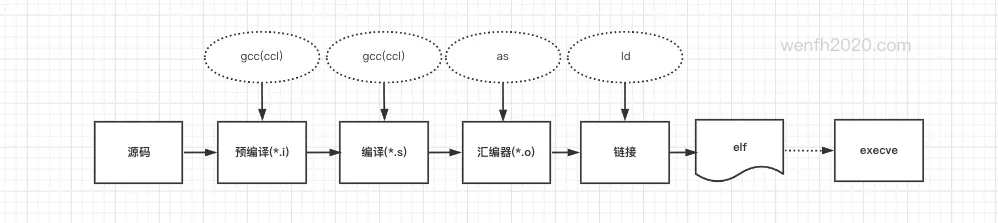
1.2. 程序运行环境
二进制程序文件被载入内存后,CPU,内存,磁盘等重要设备相互与系统协调工作,完成程序指令。
- 硬件。

- 系统。
图片来源:《程序工作流程(Linux)》
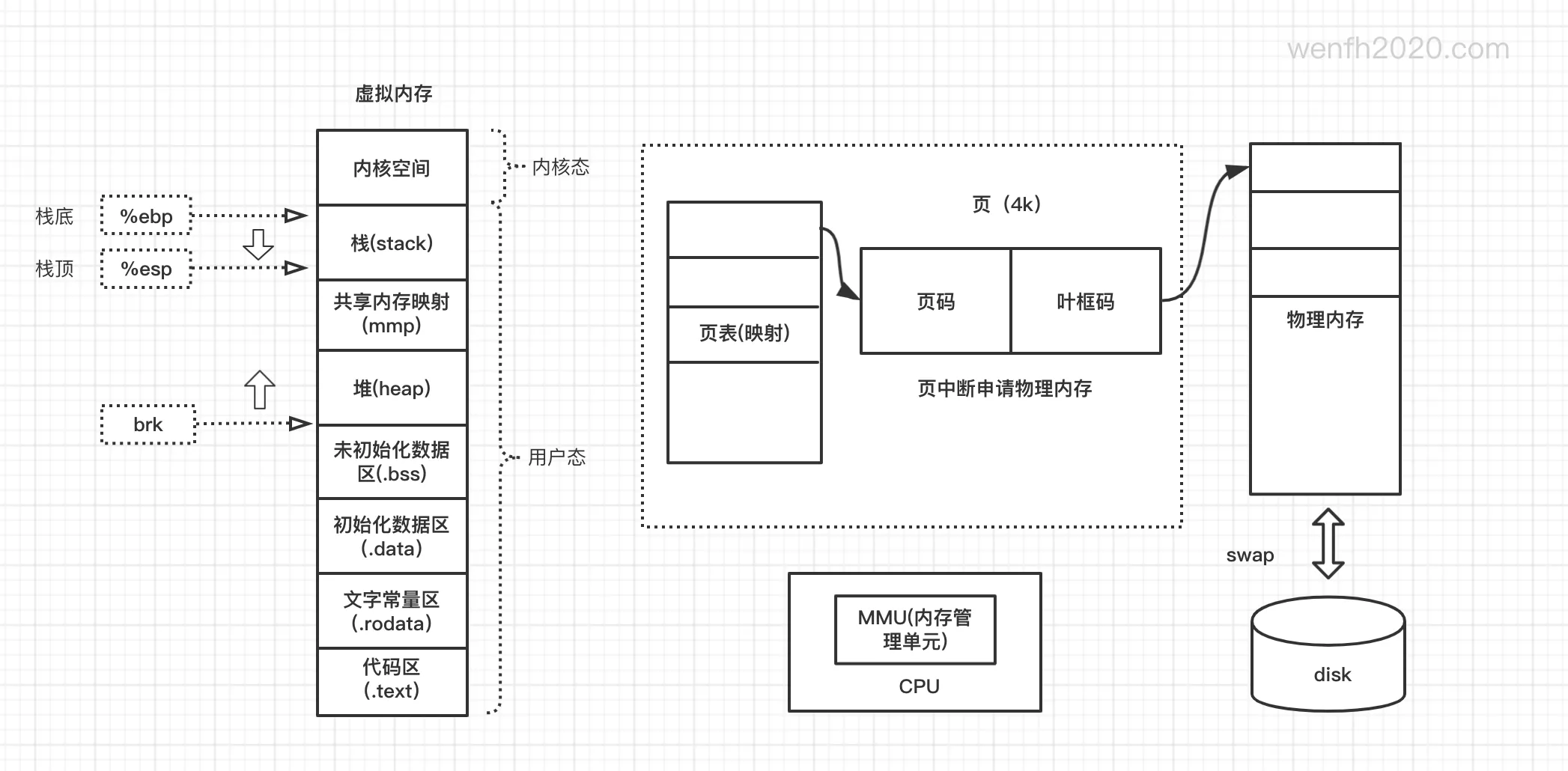
1.3. 程序虚拟内存布局
- 程序被载入内存后,以进程方式运行。
- 用户进程一般情况下不能直接访问物理内存,它通过虚拟内存进行寻址。
- 下图(红色框框区域)是进程运行时栈空间在(32 位)虚拟内存的内存分布位置。
- 栈空间特点,进栈:数据从高地址向低地址进栈;出栈:先进后出。
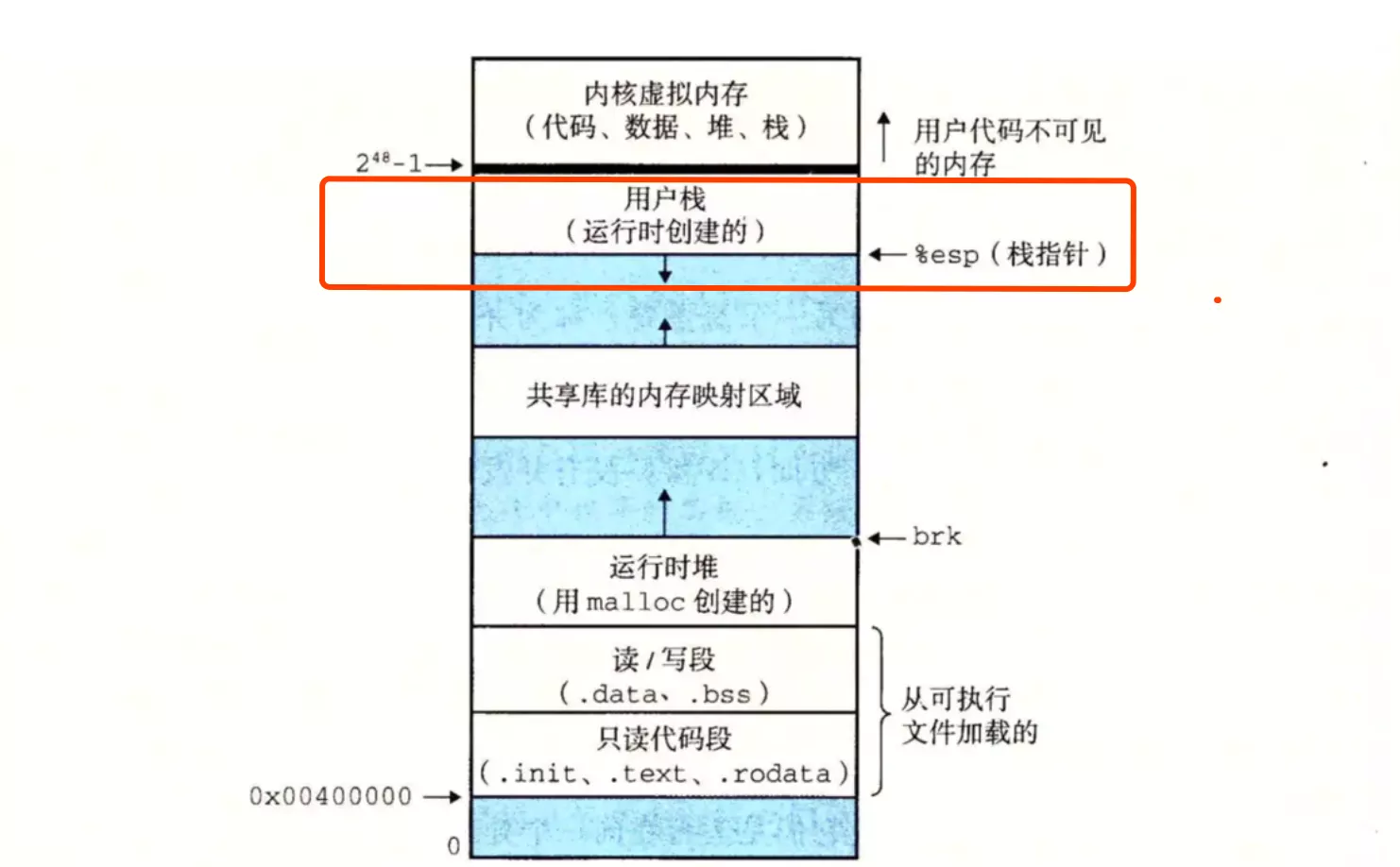
图片来源:《深入理解计算机系统》8.2.3 私有地址空间
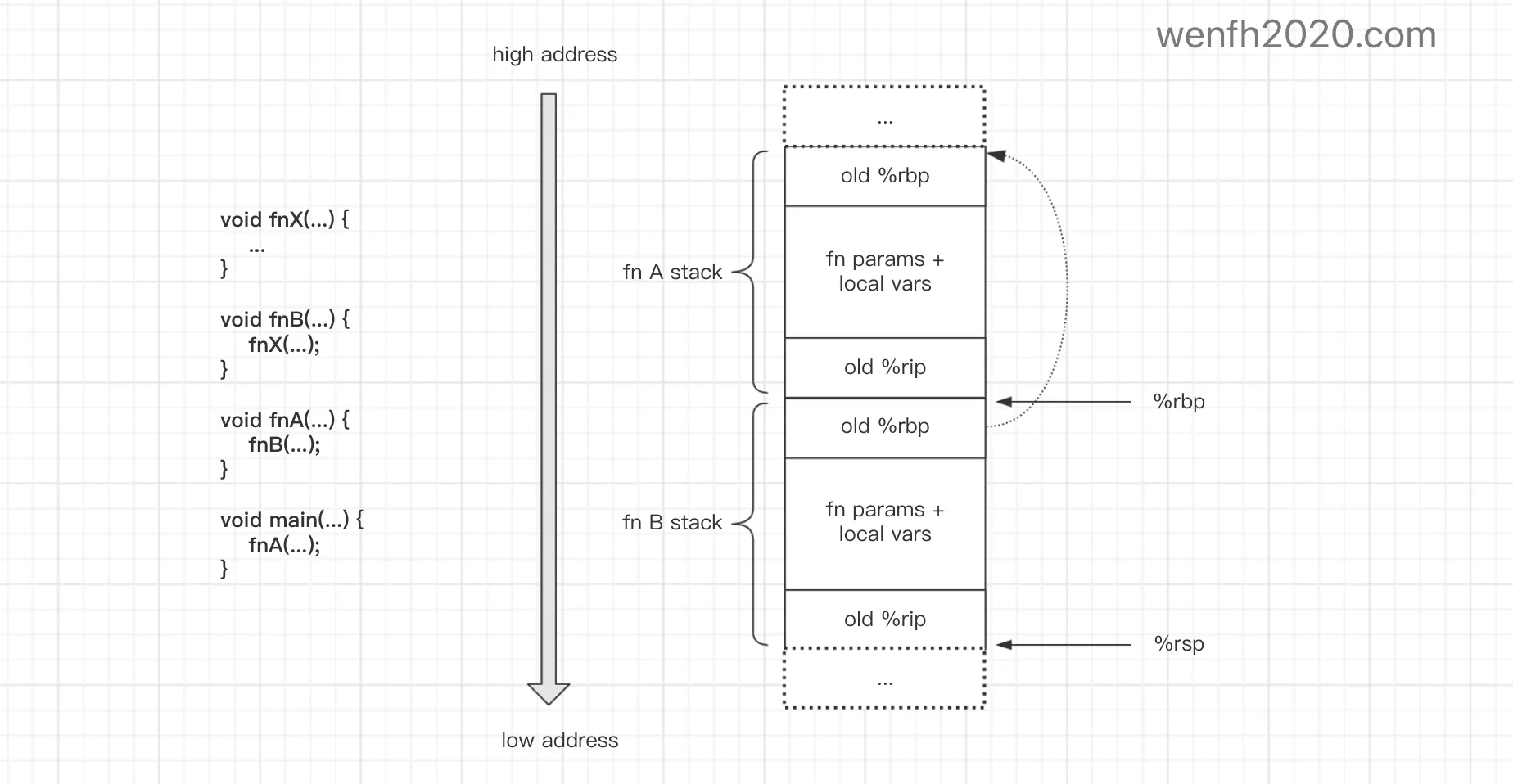
1.5. 运行时栈空间布局
下图是函数运行时,函数相关数据在内存上的布局情况。
- 函数运行时,系统会为它分配临时栈内存。
- 函数运行时,相关数据除了保存在
内存(栈内存空间),但也需要通过寄存器传递或保存数据。 - 栈内存的生命期与当前函数的生命期一样。
- 栈大小一般情况下是(%ebp/%rbp)函数基地址和 (%esp/%rsp) 函数栈顶地址之间的内存块。
有时候不一定需要函数栈顶地址,因为它可以通过函数基地址结合变量等数据计算出来。
- 栈内存保存数据:函数参数数据副本,函数内部临时变量数据,函数基地址,函数调用者运行的指令地址等等。
2. lldb 源码调试
下面将通过 lldb 调试器,分步调试 c 语言测试源码的汇编编码,搞清楚函数运行时栈内存存储布局。
2.1. 测试源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
int fnB(int z) {
int f, g;
f = z + 1;
g = f + 2;
return g;
}
int fnA(int x, int y) {
int d, e;
d = x + y;
e = fnB(d);
return e;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int a, b, c;
a = 1;
b = 2;
c = fnA(a, b);
return c;
}
2.2. 函数汇编编码
上面 c 语言测试源码对应的函数汇编编码(lldb 调试过程中打印出来的)。
了解相关汇编指令和寄存器知识可以参考:《常用汇编知识》,《汇编语言基础:寄存器和系统调用》 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
(lldb) di -n main
test`main:
0x100000f70 <+0>: pushq %rbp
0x100000f71 <+1>: movq %rsp, %rbp
0x100000f74 <+4>: subq $0x20, %rsp
0x100000f78 <+8>: movl $0x0, -0x4(%rbp)
0x100000f7f <+15>: movl %edi, -0x8(%rbp)
0x100000f82 <+18>: movq %rsi, -0x10(%rbp)
0x100000f86 <+22>: movl $0x1, -0x14(%rbp)
0x100000f8d <+29>: movl $0x2, -0x18(%rbp)
0x100000f94 <+36>: movl -0x14(%rbp), %edi
0x100000f97 <+39>: movl -0x18(%rbp), %esi
0x100000f9a <+42>: callq 0x100000f40 ; fnA at test_stack.cpp:10
0x100000f9f <+47>: movl %eax, -0x1c(%rbp)
0x100000fa2 <+50>: movl -0x1c(%rbp), %eax
0x100000fa5 <+53>: addq $0x20, %rsp
0x100000fa9 <+57>: popq %rbp
0x100000faa <+58>: retq
(lldb) di -n fnA
test`fnA:
0x100000f40 <+0>: pushq %rbp
0x100000f41 <+1>: movq %rsp, %rbp
0x100000f44 <+4>: subq $0x10, %rsp
0x100000f48 <+8>: movl %edi, -0x4(%rbp)
0x100000f4b <+11>: movl %esi, -0x8(%rbp)
0x100000f4e <+14>: movl -0x4(%rbp), %esi
0x100000f51 <+17>: addl -0x8(%rbp), %esi
0x100000f54 <+20>: movl %esi, -0xc(%rbp)
0x100000f57 <+23>: movl -0xc(%rbp), %edi
0x100000f5a <+26>: callq 0x100000f20 ; fnB at test_stack.cpp:3
0x100000f5f <+31>: movl %eax, -0x10(%rbp)
0x100000f62 <+34>: movl -0x10(%rbp), %eax
0x100000f65 <+37>: addq $0x10, %rsp
0x100000f69 <+41>: popq %rbp
0x100000f6a <+42>: retq
(lldb) di -n fnB
test`fnB:
0x100000f20 <+0>: pushq %rbp
0x100000f21 <+1>: movq %rsp, %rbp
0x100000f24 <+4>: movl %edi, -0x4(%rbp)
0x100000f27 <+7>: movl -0x4(%rbp), %edi
0x100000f2a <+10>: addl $0x1, %edi
0x100000f2d <+13>: movl %edi, -0x8(%rbp)
0x100000f30 <+16>: movl -0x8(%rbp), %edi
0x100000f33 <+19>: addl $0x2, %edi
0x100000f36 <+22>: movl %edi, -0xc(%rbp)
0x100000f39 <+25>: movl -0xc(%rbp), %eax
0x100000f3c <+28>: popq %rbp
0x100000f3d <+29>: retq
2.3. 运行时栈内存数据
调试走完 main 函数整个流程后,整理出来的运行时栈数据。有了具体的数据,抽象的运行时栈内存布局就可以很好地具体理解。
| offset | addr | data | desc |
|---|---|---|---|
| +0x30 | 0x00007ffeefbff300 | 0x00007ffeefbff512 | fn param: char* argv[2] –> “world” |
| +0x28 | 0x00007ffeefbff2f8 | 0x00007ffeefbff50c | fn param: char *argv[1] –> “hello” |
| +0x20 | 0x00007ffeefbff2f0 | 0x00007ffeefbff4d8 | fn param: char* argv[0] –> “../../../” |
| +0x18 | 0x00007ffeefbff2e8 | 3 | fn param: int argc –> 3 |
| +0x10 (%rbp) (start) | 0x00007ffeefbff2e0 | 0 | |
| +0x08 | 0x00007ffeefbff2d8 | 0x00007fff6e2f22e5 | save caller’s (%rip) libdyld.dylib`start + 1 |
| +0x00 (%rbp) (main) | 0x00007ffeefbff2d0 | 0x00007ffeefbff2e0 | main(), stack base addr. |
| -0x04 | 0x00007ffeefbff2cc | 0 | movl $0x0, -0x4(%rbp) |
| -0x08 | 0x00007ffeefbff2c8 | 3 | movl %edi, -0x8(%rbp) |
| -0x10 | 0x00007ffeefbff2c0 | 0x00007ffeefbff2f0 | ”../../../” |
| -0x14 | 0x00007ffeefbff2bc | 1 | fn param: int a –> movl $0x1, -0x14(%rbp) |
| -0x18 | 0x00007ffeefbff2b8 | 2 | fn param: int b –> movl $0x2, -0x18(%rbp) |
| -0x1c | 0x00007ffeefbff2b4 | 6 | local val: int c = fnA(a, b) |
| -0x20 (%rsp) | 0x00007ffeefbff2b0 | 0 | 16 bits alignment. |
| -0x28 |
0x00007ffeefbff2a8 | 0x0000000100000f9f | save caller’s (%rip) 0x100000f9a <+42>: callq 0x100000f40; fnA at test_stack.cpp:10 0x100000f9f <+47>: movl %eax, -0x1c(%rbp) |
| +0x00 (%rbp) (fnA) | 0x00007ffeefbff2a0 | 0x00007ffeefbff2d0 | save caller’s (%rbp) |
| -0x04 | 0x00007ffeefbff29c | 1 | fn param: int x –> movl %edi, -0x4(%rbp) |
| -0x08 | 0x00007ffeefbff298 | 2 | fn param: int y –> movl %esi, -0x8(%rbp) |
| -0x0c | 0x00007ffeefbff294 | 3 | local val: int d = x + y |
| -0x10 (%rsp) | 0x00007ffeefbff290 | 6 | local val: int e = fnB(d) |
| -0x18 | 0x00007ffeefbff288 | 0x0000000100000f5f | 0x100000f5a <+26>: callq 0x100000f20; fnB at test_stack.cpp:3 0x100000f5f <+31>: movl %eax, -0x10(%rbp) |
| -0x00 (%rbp) (%rsp) (fnB) | 0x00007ffeefbff280 | 0x00007ffeefbff2a0 | save caller’s (%rbp) |
| -0x04 | 0x00007ffeefbff27c | 3 | fn param: int z –> movl %edi, -0x4(%rbp) |
| -0x08 | 0x00007ffeefbff278 | 4 | local val: int f = z + 1 |
| -0x0c | 0x00007ffeefbff274 | 6 | local val: int g = f + 2 |
2.4. lldb
调试过程中,需要实时查看 c 测试源码,测试源码对应的汇编编码,内存地址指向的数据,各个寄存器保存的数据变化。
2.4.1. 命令
| 描述 | 命令 |
|---|---|
| 命令帮助 | help |
| 查看函数汇编编码 | di -n <fn_name> |
| 调试汇编指令 | si/ni |
| 查看寄存器数值 | register read/write <register> |
| 添加 hook 指令,打印对应的信息 | target stop-hook add |
| 读内存 | me read <addr> me read -fx -s4 -c1 <addr> |
2.4.2. 调试流程
下面是 lldb 调试流程,可以通过 si 命令,单步调试汇编指令,查看程序运行时栈内存数据,寄存器等数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
# lldb 调试 test 程序。
[wenfh2020:.../other/coroutine/test_stack]$ lldb test
(lldb) target create "test"
Current executable set to 'test' (x86_64).
# 在 main 函数下断点。
(lldb) b main
Breakpoint 1: where = test`main + 22 at test_stack.cpp:19:7, address = 0x0000000100000f86
# 调试过程中,同步打印源码对应的汇编编码,以及寄存器数据。
(lldb) target stop-hook add
Enter your stop hook command(s). Type 'DONE' to end.
# 打印汇编编码。
> di -p
# 读取寄存器数据。
> re r rip rbp rsp rdi rsi rdx rcx r8 r9 rax
Stop hook #1 added.
# 启动程序,传递两个字符串参数 "hello" "world"。
(lldb) run hello world
# main 函数调用者,运行的汇编指令。
dyld`_dyld_start:
-> 0x100003000 <+0>: popq %rdi
0x100003001 <+1>: pushq $0x0
0x100003003 <+3>: movq %rsp, %rbp
0x100003006 <+6>: andq $-0x10, %rsp
rip = 0x0000000100003000 dyld`_dyld_start
rbp = 0x0000000000000000
rsp = 0x00007ffeefbff2e0
rdi = 0x0000000000000000
rsi = 0x0000000000000000
rdx = 0x0000000000000000
rcx = 0x0000000000000000
r8 = 0x0000000000000000
r9 = 0x0000000000000000
rax = 0x0000000000000000
Process 9282 launched: '/Users/wenfh2020/src/other/coroutine/test_stack/test' (x86_64)
# main 函数运行指令。
test`main:
-> 0x100000f86 <+22>: movl $0x1, -0x14(%rbp)
0x100000f8d <+29>: movl $0x2, -0x18(%rbp)
0x100000f94 <+36>: movl -0x14(%rbp), %edi
0x100000f97 <+39>: movl -0x18(%rbp), %esi
# 寄存器数据。
rip = 0x0000000100000f86 test`main + 22 at test_stack.cpp:19:7
rbp = 0x00007ffeefbff2d0
rsp = 0x00007ffeefbff2b0
rdi = 0x0000000000000003
rsi = 0x00007ffeefbff2f0
rdx = 0x00007ffeefbff310
rcx = 0x00007ffeefbff448
r8 = 0x0000000000000000
r9 = 0x0000000000000000
rax = 0x0000000100000f70 test`main at test_stack.cpp:17
# c 源码。
Process 9282 stopped
* thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = breakpoint 1.1
frame #0: 0x0000000100000f86 test`main(argc=3, argv=0x00007ffeefbff2f0) at test_stack.cpp:19:7
16
17 int main(int argc, char** argv) {
18 int a, b, c;
-> 19 a = 1;
20 b = 2;
21 c = fnA(a, b);
22 return c;
Target 0: (test) stopped.
...
# 单步运行汇编指令。
(lldb) si
test`fnA:
-> 0x100000f44 <+4>: subq $0x10, %rsp
0x100000f48 <+8>: movl %edi, -0x4(%rbp)
0x100000f4b <+11>: movl %esi, -0x8(%rbp)
0x100000f4e <+14>: movl -0x4(%rbp), %esi
# 程序指令寄存器跳转到 fnA 函数。
rip = 0x0000000100000f44 test`fnA(int, int) + 4 at test_stack.cpp:10
rbp = 0x00007ffeefbff2a0
rsp = 0x00007ffeefbff2a0
rdi = 0x0000000000000001
rsi = 0x0000000000000002
rdx = 0x00007ffeefbff310
rcx = 0x00007ffeefbff448
r8 = 0x0000000000000000
r9 = 0x0000000000000000
rax = 0x0000000100000f70 test`main at test_stack.cpp:17
Process 9282 stopped
* thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = instruction step into
frame #0: 0x0000000100000f44 test`fnA(x=0, y=0) at test_stack.cpp:10
7 return g;
8 }
9
-> 10 int fnA(int x, int y) {
11 int d, e;
12 d = x + y;
13 e = fnB(d);
Target 0: (test) stopped.
# 读取 rsp 指向的内存的数据。
(lldb) me read -fx -s8 -c1 0x00007ffeefbff2a0
0x7ffeefbff2a0: 0x00007ffeefbff2d0
# 打印函数调用堆栈。
(lldb) bt
* thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = instruction step into
* frame #0: 0x0000000100000f44 test`fnA(x=0, y=0) at test_stack.cpp:10
frame #1: 0x0000000100000f9f test`main(argc=3, argv=0x00007ffeefbff2f0) at test_stack.cpp:21:9
frame #2: 0x00007fff6e2f22e5 libdyld.dylib`start + 1
(lldb) f 1
frame #1: 0x0000000100000f9f test`main(argc=3, argv=0x00007ffeefbff2f0) at test_stack.cpp:21:9
18 int a, b, c;
19 a = 1;
20 b = 2;
-> 21 c = fnA(a, b);
22 return c;
23 }
24
...
Target 0: (test) stopped.
(lldb) si
test`fnB:
-> 0x100000f2d <+13>: movl %edi, -0x8(%rbp)
0x100000f30 <+16>: movl -0x8(%rbp), %edi
0x100000f33 <+19>: addl $0x2, %edi
0x100000f36 <+22>: movl %edi, -0xc(%rbp)
rip = 0x0000000100000f2d test`fnB(int) + 13 at test_stack.cpp:5:7
rbp = 0x00007ffeefbff280
rsp = 0x00007ffeefbff280
rdi = 0x0000000000000004
rsi = 0x0000000000000003
rdx = 0x00007ffeefbff310
rcx = 0x00007ffeefbff448
r8 = 0x0000000000000000
r9 = 0x0000000000000000
rax = 0x0000000100000f70 test`main at test_stack.cpp:17
Process 9282 stopped
* thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = instruction step into
frame #0: 0x0000000100000f2d test`fnB(z=3) at test_stack.cpp:5:7
2
3 int fnB(int z) {
4 int f, g;
-> 5 f = z + 1;
6 g = f + 2;
7 return g;
8 }
Target 0: (test) stopped.
# 打印寄存器 edi 数据。
(lldb) re r edi
edi = 0x00000004
(lldb)


