文章重点讲述 aof 持久化的应用场景。
aof 持久化,拆分上下为两章,可以先读上一章:[redis 源码走读] aof 持久化 ①。
1. 应用场景
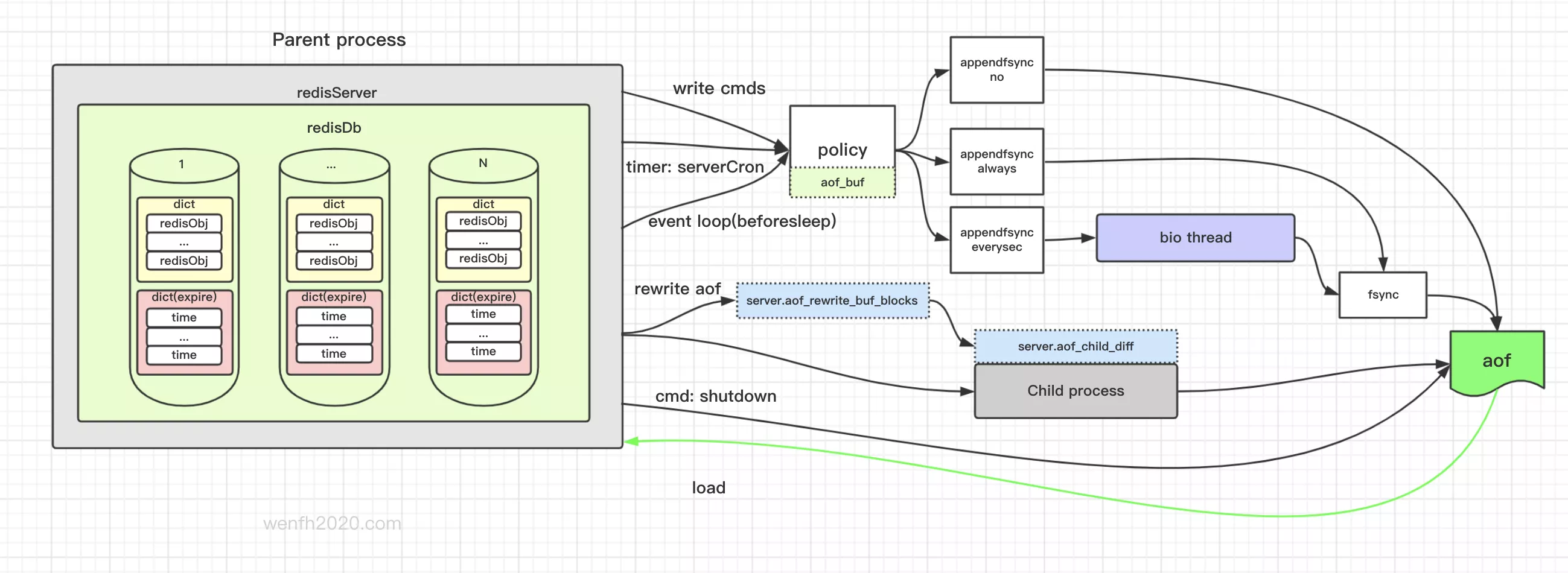
1.1. 启动加载
redis 启动,程序会模拟一个客户端加载从 aof 文件读出的命令。
aof 持久化支持 aof 和 rdb 混合模式,参考上面的
aof 和 rdb 混合结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
...
loadDataFromDisk();
...
}
void loadDataFromDisk(void) {
...
if (server.aof_state == AOF_ON) {
if (loadAppendOnlyFile(server.aof_filename) == C_OK)
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"DB loaded from append only file: %.3f seconds",(float)(ustime()-start)/1000000);
}
...
}
int loadAppendOnlyFile(char *filename) {
...
// 程序模拟一个客户端执行从 aof 文件读出的命令。
fakeClient = createAOFClient();
...
// 检查 aof 文件读取数据方式。
char sig[5];
if (fread(sig,1,5,fp) != 5 || memcmp(sig,"REDIS",5) != 0) {
// 通过 aof 方式加载数据。
if (fseek(fp,0,SEEK_SET) == -1) goto readerr;
} else {
...
// 通过 rdb 方式加载数据。
if (rdbLoadRio(&rdb,RDBFLAGS_AOF_PREAMBLE,NULL) != C_OK) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Error reading the RDB preamble of the AOF file, AOF loading aborted");
goto readerr;
}
}
/* Read the actual AOF file, in REPL format, command by command. */
while(1) {
// 根据 aof 文件数据结构,取出数据回写内存。
...
}
...
}
1.2. 写命令执行流程
- client 向 redis 服务发送写命令。
- redis 服务接收命令,进行业务处理。
- redis 服务将新的写命令追加到 aof 数据缓冲区。
- redis 服务会通过时钟,(
eventloop)事件处理前(beforeSleep)等方法将 aof 数据缓冲区落地,然后清空 aof 缓冲区。
- 流程
1
2
3
4
5
6
call(client * c, int flags) (/Users/wenfh2020/src/other/redis/src/server.c:3266)
processCommand(client * c) (/Users/wenfh2020/src/other/redis/src/server.c:3552)
...
aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop * eventLoop, int flags) (/Users/wenfh2020/src/other/redis/src/ae.c:457)
aeMain(aeEventLoop * eventLoop) (/Users/wenfh2020/src/other/redis/src/ae.c:515)
main(int argc, char ** argv) (/Users/wenfh2020/src/other/redis/src/server.c:5054)
- 执行命令,填充 aof 数据缓冲区
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
/* Command propagation flags, see propagate() function
+ PROPAGATE_NONE (no propagation of command at all)
+ PROPAGATE_AOF (propagate into the AOF file if is enabled)
+ PROPAGATE_REPL (propagate into the replication link)
*/
#define PROPAGATE_NONE 0
#define PROPAGATE_AOF 1
#define PROPAGATE_REPL 2
void call(client *c, int flags) {
...
c->cmd->proc(c);
...
if (propagate_flags != PROPAGATE_NONE && !(c->cmd->flags & CMD_MODULE))
propagate(c->cmd,c->db->id,c->argv,c->argc,propagate_flags);
...
}
void propagate(struct redisCommand *cmd, int dbid, robj **argv, int argc, int flags) {
if (server.aof_state != AOF_OFF && flags & PROPAGATE_AOF)
feedAppendOnlyFile(cmd,dbid,argv,argc);
...
}
// aof 缓冲区
struct redisServer {
...
sds aof_buf; /* AOF buffer, written before entering the event loop */
...
}
// 追加内容到 aof 文件
void feedAppendOnlyFile(struct redisCommand *cmd, int dictid, robj **argv, int argc) {
sds buf = sdsempty();
robj *tmpargv[3];
// 命令执行,需要指定到对应数据库。
if (dictid != server.aof_selected_db) {
char seldb[64];
snprintf(seldb,sizeof(seldb),"%d",dictid);
buf = sdscatprintf(buf,"*2\r\n$6\r\nSELECT\r\n$%lu\r\n%s\r\n",
(unsigned long)strlen(seldb),seldb);
server.aof_selected_db = dictid;
}
...
// 将命令格式化为 redis 命令格式,然后追加到 aof 数据缓冲区。
buf = catAppendOnlyGenericCommand(buf,argc,argv);
...
if (server.aof_state == AOF_ON)
server.aof_buf = sdscatlen(server.aof_buf,buf,sdslen(buf));
// 如果有子进程正在重写,父进程将新的数据发送给正在重写的子进程,使得重写文件数据更完备。
if (server.aof_child_pid != -1)
aofRewriteBufferAppend((unsigned char*)buf,sdslen(buf));
...
}
-
重写过程中,父进程接收到新的命令,父进程发送给子进程,对重写数据进行追加。
父子进程通过管道进行通信交互。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
void feedAppendOnlyFile(struct redisCommand *cmd, int dictid, robj **argv, int argc) {
...
// 如果有子进程正在重写,父进程将新的数据发送给正在重写的子进程,使得重写文件数据更完备。
if (server.aof_child_pid != -1)
aofRewriteBufferAppend((unsigned char*)buf,sdslen(buf));
...
}
// 将数据保存到重写缓冲区链表。然后通过父子进程管道进行数据传输
void aofRewriteBufferAppend(unsigned char *s, unsigned long len) {}
// 父进程通过管道把重写缓冲区数据,发送到子进程
void aofChildWriteDiffData(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {}
// 子进程读取父进程发送的数据。
ssize_t aofReadDiffFromParent(void) {...}
// 创建父子进程通信管道
int aofCreatePipes(void) {...}
// 父子结束通信
void aofChildPipeReadable(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {}
1.3. 定时保存
主要对延时刷新和写磁盘出现错误回写的检查刷新。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
/* Using the following macro you can run code inside serverCron() with the
* specified period, specified in milliseconds.
* The actual resolution depends on server.hz. */
#define run_with_period(_ms_) \
if ((_ms_ <= 1000 / server.hz) || \
!(cronloops % ((_ms_) / (1000 / server.hz))))
int serverCron(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData) {
...
// 如果有延时任务,定时检查刷新。
if (server.aof_flush_postponed_start) flushAppendOnlyFile(0);
// 刷新缓存到磁盘出现错误(例如:磁盘满了),定时检查回写。
// hz 频率为 10 ,这里一般每十次时钟检查一次。
run_with_period(1000) {
if (server.aof_last_write_status == C_ERR)
flushAppendOnlyFile(0);
}
...
server.cronloops++;
return 1000/server.hz;
}
1.4. 重写
服务器接收到写入操作命令会追加到 aof 文件,那么 aof 文件相当于一个流水文件。随着时间推移,文件将会越来越大。然而 aof 文件主要目的是为了持久化,并不是为了记录服务器流水。这些流水命令有可能很多是冗余的,需要重新整理——通过重写来减小 aof 文件体积。
例如下面 4 条命令,会追加记录到 aof 文件,因为对同一个 key 操作,内存里最终数据 key1 对应的数据是 4,这样前面 3 条历史命令是冗余的,通过重写功能,aof 文件只留下 key 对应的最新的 value。
1
2
3
4
set key1 1
set key1 2
set key1 3
set key1 4
1.4.1. 重写方式
- 通过命令
BGREWRITEAOF重写。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
void bgrewriteaofCommand(client *c) {
if (server.aof_child_pid != -1) {
// 当重写正在进行时,返回错误。
addReplyError(c,"Background append only file rewriting already in progress");
} else if (hasActiveChildProcess()) {
// 当有其它子进程正在进行工作时,延后执行。
server.aof_rewrite_scheduled = 1;
addReplyStatus(c,"Background append only file rewriting scheduled");
} else if (rewriteAppendOnlyFileBackground() == C_OK) {
// 异步执行重写
addReplyStatus(c,"Background append only file rewriting started");
} else {
// 重写操作失败,检查原因。
addReplyError(c,"Can't execute an AOF background rewriting. "
"Please check the server logs for more information.");
}
}
- 时钟定期检查 redis 使用内存大小,当超过配置的阈值,触发自动重写。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# redis.conf
# 触发 aof 重写的最小 aof 文件大小
# 配置 64mb,说明 aof 持久化文件,只有超过了 64 mb 才会触发重写。
auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 64mb
# 触发 aof 重写的条件
# aof 文件大小相对于上一次重写后的大小的增长百分比
# 配置 100,当 aof 文件的大小增长到上一次重写后的大小的两倍时
# (即增长了 100%)才会触发 aof 重写。
auto-aof-rewrite-percentage 100
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
int serverCron(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData) {
...
/* Trigger an AOF rewrite if needed. */
if (server.aof_state == AOF_ON &&
!hasActiveChildProcess() &&
server.aof_rewrite_perc &&
server.aof_current_size > server.aof_rewrite_min_size)
{
long long base = server.aof_rewrite_base_size ?
server.aof_rewrite_base_size : 1;
long long growth = (server.aof_current_size*100/base) - 100;
if (growth >= server.aof_rewrite_perc) {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Starting automatic rewriting of AOF on %lld%% growth",growth);
rewriteAppendOnlyFileBackground();
}
}
...
}
1.4.2. 重写实现
- 父进程 fork 子进程实现重写逻辑。
- 子进程创建 aof 临时文件存储重写子进程
fork-on-write内存到 aof 文件。 - 子进程重写完成 fork 内存数据内容后,追加在重写过程中父进程发送的新的内容。
- 子进程结束父子进程管道通信。
- 更新临时文件覆盖旧的文件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
// 父进程 fork 子进程进行 aof 重写
int rewriteAppendOnlyFileBackground(void) {
...
if ((childpid = redisFork()) == 0) {
...
if (rewriteAppendOnlyFile(tmpfile) == C_OK) {
sendChildCOWInfo(CHILD_INFO_TYPE_AOF, "AOF rewrite");
exitFromChild(0);
} else {
exitFromChild(1);
}
} else {
/* Parent */
...
}
return C_OK; /* unreached */
}
// 重写 aof 实现逻辑
int rewriteAppendOnlyFile(char *filename) {
rio aof;
FILE *fp;
char tmpfile[256];
char byte;
// 创建 aof 临时文件。
snprintf(tmpfile,256,"temp-rewriteaof-%d.aof", (int) getpid());
fp = fopen(tmpfile,"w");
if (!fp) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING, "Opening the temp file for AOF rewrite in rewriteAppendOnlyFile(): %s", strerror(errno));
return C_ERR;
}
server.aof_child_diff = sdsempty();
rioInitWithFile(&aof,fp);
// 逐步将文件缓存刷新到磁盘。
if (server.aof_rewrite_incremental_fsync)
rioSetAutoSync(&aof,REDIS_AUTOSYNC_BYTES);
startSaving(RDBFLAGS_AOF_PREAMBLE);
// 根据配置,重写文件内容方式,rdb 或者 aof,aof 存储方式支持 rdb 和 aof 内容兼容在同一个 aof 文件。
if (server.aof_use_rdb_preamble) {
int error;
if (rdbSaveRio(&aof,&error,RDBFLAGS_AOF_PREAMBLE,NULL) == C_ERR) {
errno = error;
goto werr;
}
} else {
if (rewriteAppendOnlyFileRio(&aof) == C_ERR) goto werr;
}
// 进程内存更新完毕,刷新文件到磁盘。
if (fflush(fp) == EOF) goto werr;
if (fsync(fileno(fp)) == -1) goto werr;
// 子进程接收父进程发送的新数据。
int nodata = 0;
mstime_t start = mstime();
while(mstime()-start < 1000 && nodata < 20) {
if (aeWait(server.aof_pipe_read_data_from_parent, AE_READABLE, 1) <= 0) {
nodata++;
continue;
}
nodata = 0; /* Start counting from zero, we stop on N *contiguous*
timeouts. */
aofReadDiffFromParent();
}
// 子进程通知父进程不要发新的数据了。
if (write(server.aof_pipe_write_ack_to_parent,"!",1) != 1) goto werr;
if (anetNonBlock(NULL,server.aof_pipe_read_ack_from_parent) != ANET_OK)
goto werr;
// 父进程收到子进程的结束通知,发送确认给子进程。
if (syncRead(server.aof_pipe_read_ack_from_parent,&byte,1,5000) != 1 ||
byte != '!') goto werr;
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Parent agreed to stop sending diffs. Finalizing AOF...");
/* Read the final diff if any. */
aofReadDiffFromParent();
// 子进程接收父进程发送的内容缓存在缓冲区,将缓冲区内容追加到重写 aof 文件后。
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,
"Concatenating %.2f MB of AOF diff received from parent.",
(double) sdslen(server.aof_child_diff) / (1024*1024));
if (rioWrite(&aof,server.aof_child_diff,sdslen(server.aof_child_diff)) == 0)
goto werr;
// 内容写入文件完毕,刷新文件缓存到磁盘。
if (fflush(fp) == EOF) goto werr;
if (fsync(fileno(fp)) == -1) goto werr;
if (fclose(fp) == EOF) goto werr;
// 新的重写 aof 文件,覆盖旧的文件。
if (rename(tmpfile,filename) == -1) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Error moving temp append only file on the final destination: %s", strerror(errno));
unlink(tmpfile);
stopSaving(0);
return C_ERR;
}
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"SYNC append only file rewrite performed");
stopSaving(1);
return C_OK;
werr:
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Write error writing append only file on disk: %s", strerror(errno));
fclose(fp);
unlink(tmpfile);
stopSaving(0);
return C_ERR;
}
2. 调试
我一直认为:看文档和结合源码调试是理解一个项目的最好方法。
-
gdb 调试,在自己感兴趣的地方设下断点,通过调试熟悉 redis aof 持久化工作流程。
调试方法可以参考我的帖子: 用 gdb 调试 redis

- 开启日志
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# redis.conf
# Specify the server verbosity level.
# This can be one of:
# debug (a lot of information, useful for development/testing)
# verbose (many rarely useful info, but not a mess like the debug level)
# notice (moderately verbose, what you want in production probably)
# warning (only very important / critical messages are logged)
loglevel notice
# Specify the log file name. Also the empty string can be used to force
# Redis to log on the standard output. Note that if you use standard
# output for logging but daemonize, logs will be sent to /dev/null
logfile "redis.log"
3. 总结
- aof 文件存储 RESP 命令,新数据追加到文件末。
- aof 存储为了避免冗余,需要设置重写处理。
- aof 有三种存储策略,默认每秒存盘一次。根据自己的使用场景,选择存储策略。
- 每秒存盘策略和重写功能通过多线程异步处理,保证主线程高性能。
- 关注 redis 的博客,多看 redis.conf 配置项,里面有很多信息量。
- aof 持久化文件支持 aof 和 rdb 方式混合存储,可以快速重写,并且减少 aof 体积。
- aof 与 rdb 相比文件体积大,但是容灾能力强,出现问题丢失数据少。


