压缩列表ziplist是一个双向链表,设计主要是为了节省内存。
保存字符串,数值两种类型( It stores both strings and integer values),列表内部实现主要是对一块连续内存进行管理,列表支持列表头尾的插入或弹出结点操作。因为写操作涉及到内存重新分配,所以复杂度需要根据当前使用内存的使用情况而定,一般情况下,不建议存储大量数据。
sorted set 根据数据长度,就分别用 ziplist 和 skiplist 两种数据结构进行保存。
The ziplist is a specially encoded dually linked list that is designed to be very memory efficient. It stores both strings and integer values, where integers are encoded as actual integers instead of a series of characters. It allows push and pop operations on either side of the list in O(1) time. However, because every operation requires a reallocation of the memory used by the ziplist, the actual complexity is related to the amount of memory used by the ziplist.
1. 原理
压缩原理:举个例子,int a = 0,a 是一个整型变量,占 4 个字节。但是 a = 0,0 这个数字只需要一个 bit 保存就足够了,如果用 4 个字节(32 bit)内存去存储就有点浪费了。按照这个思路,大致可以理解压缩策略是怎么样的,详细信息看文档和源码吧。
压缩数据管理有点像数据序列化,序列化数据平常数据的传输经常用到,可以了解下
protobuf源码,看看数据是怎么打包的。压缩列表除了数据序列化外,还需要对数据进行插入删除等操作,需要增加一些额外的结构进行内存管理。
2. 结构
2.1. 列表结构
头 + 结点集合 + 尾:
<zlbytes> <zltail> <zllen> <entry> <entry> ... <entry> <zlend>
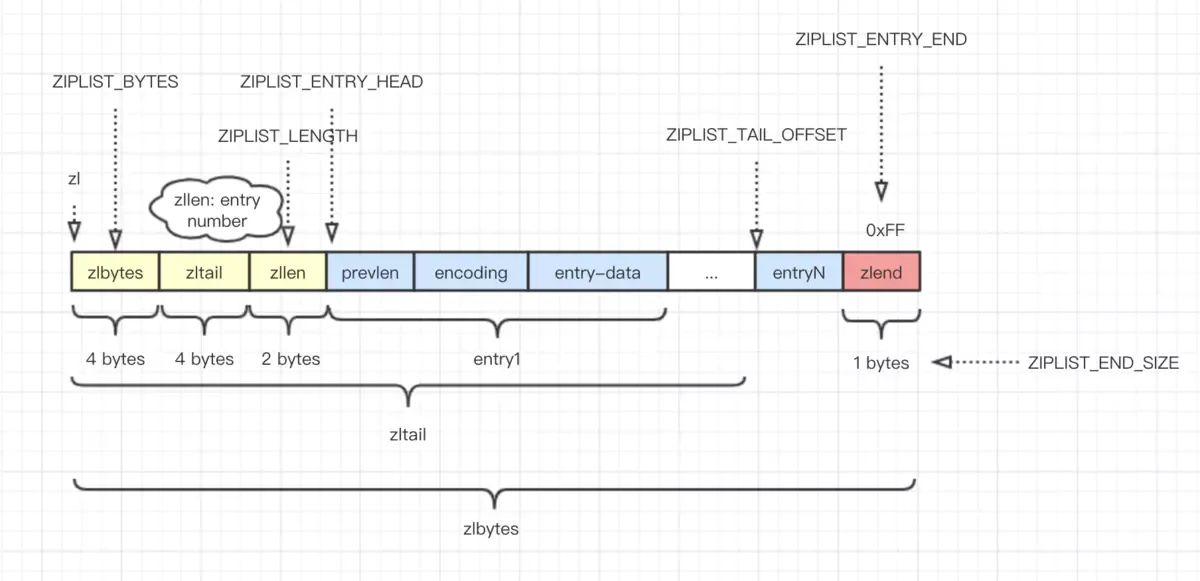
设计图来源 《redis ziplist 压缩列表内存结构》
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
/* Size of the "end of ziplist" entry. Just one byte. */
#define ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE (sizeof(uint32_t)*2+sizeof(uint16_t))
/* Size of the "end of ziplist" entry. Just one byte. */
#define ZIPLIST_END_SIZE (sizeof(uint8_t))
/* Return total bytes a ziplist is composed of. */
#define ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl) (*((uint32_t*)(zl)))
/* Return the offset of the last item inside the ziplist. */
#define ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) (*((uint32_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t))))
/* Return the length of a ziplist, or UINT16_MAX if the length cannot be
* determined without scanning the whole ziplist. */
#define ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) (*((uint16_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t)*2)))
/* Special "end of ziplist" entry. */
#define ZIP_END 255
2.2. entry
结点结构:<prevlen> <encoding> <entry-data>,但有时候数值很小,用 <encoding> 也能保存数据,不需要 <entry-data>, 即 <prevlen> <encoding>。
压缩链表的结点有点特别,这里的链表不是传统的链表,传统的链表每个结点都有 prev 或者 next 的指针,连接起来。压缩链表结点通过 prevlen 在内存上进行定位前一个结点,因为 <encoding> 存储了当前结点数据类型和数据长度,从而可以向后定位下一个结点。
2.3. prevlen
| 条件 | 长度 | 格式 |
|---|---|---|
| < 254 字节 | 1 字节 | <prevlen from 0 to 253> <encoding> <entry-dagta> |
| >= 254 字节 | 5 字节 | 0xFE <4 bytes unsigned little endian prevlen> <encoding> <entry-data> |
前一个结点长度,存储在本结点首部,有两种存储长度,1 字节或者 5 字节空间进行存储,具体产看前面的具体描述。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
/* Return the number of bytes used to encode the length of the previous
* entry. The length is returned by setting the var 'prevlensize'. */
#define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize) do { \
if ((ptr)[0] < ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN) { \
(prevlensize) = 1; \
} else { \
(prevlensize) = 5; \
} \
} while(0);
prevlen: 前一个结点结点长度。
prevlensize: 保存 prevlen 占用了多少内存(1/5)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
/* Return the length of the previous element, and the number of bytes that
* are used in order to encode the previous element length.
* 'ptr' must point to the prevlen prefix of an entry (that encodes the
* length of the previous entry in order to navigate the elements backward).
* The length of the previous entry is stored in 'prevlen', the number of
* bytes needed to encode the previous entry length are stored in
* 'prevlensize'. */
#define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(ptr, prevlensize, prevlen) do { \
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize); \
if ((prevlensize) == 1) { \
(prevlen) = (ptr)[0]; \
} else if ((prevlensize) == 5) { \
assert(sizeof((prevlen)) == 4); \
memcpy(&(prevlen), ((char*)(ptr)) + 1, 4); \
memrev32ifbe(&prevlen); \
} \
} while(0);
2.4. encoding
编码有两种类型:字符串/整数
The encoding field of the entry depends on the content of the entry. When the entry is a string, the first 2 bits of the encoding first byte will hold the type of encoding used to store the length of the string, followed by the actual length of the string. When the entry is an integer the first 2 bits are both set to 1. The following 2 bits are used to specify what kind of integer will be stored after this header. An overview of the different types and encodings is as follows. The first byte is always enough to determine the kind of entry.
2.4.1. 字符串
如果当结点内容是字符串,那么 <encoding> 前两个 bit 主要用来存储编码类型,剩下的保存当前字符串的字符串长度。从 <encoding> 可以获得 3 个信息:
- 编码类型。
- 结点数据内容长度。
- 整个 <encoding> 长度。
| 标识 | encoding 长度 | 字符串长度 | 描述 | 注意 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |00pppppp| | 1 byte | <= 63 字节(6 bits) | encoding 用一个字节保存,前 2 个 bit是 0,后面 6 个 bit 保存字符串长度 | |
| |01pppppp|qqqqqqqq| | 2 bytes | <= 16383 字节(14 bits) | encoding 前 2 个 bit是 0,紧接着后面 6 个 bit 保存字符串长度。 | 14 bit 数值用大端方式保存 |
| |10000000|qqqqqqqq|rrrrrrrr|ssssssss|tttttttt| | 5 bytes | >= 16384 字节 | encoding 前面一个字节是标识,后面 4 个字节保存字符串长度。 | 长度数值用大端模式保存 |
判断字节前面两个 bit 是否为 1,如果不是就是字符串。ZIP_STR_MASK = “1100 0000”
1
2
3
4
5
6
/* Extract the encoding from the byte pointed by 'ptr' and set it into
* 'encoding' field of the zlentry structure. */
#define ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING(ptr, encoding) do { \
(encoding) = (ptr[0]); \
if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) (encoding) &= ZIP_STR_MASK; \
} while(0)
2.4.2. 数值
当结点内容是数值,<encoding> 前两个 bit 设置成 1,接下来两个 bit 用来保存数值类型。从 <encoding> 可以获得 3 个信息:
- 编码类型。
- 数值类型。
- 数值。
| 首字节标识 | encoding 长度 | 数值长度 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| |11000000| | 3 bytes | 2 bytes | int16_t |
| |11010000| | 5 bytes | 4 bytes | int32_t |
| |11100000| | 9 bytes | 8 bytes | int64_t |
| |11110000| | 4 bytes | 3 bytes | Integer encoded as 24 bit signed (3 bytes). |
| |11111110| | 2 bytes | 1 byte | Integer encoded as 8 bit signed (1 byte). |
| |1111xxxx| | 1 byte | 4 bits | 4 bit integer, 可以存储 0 - 12, 因为 0000,1110,1111 不能使用,只能存储 1 - 13,所以保存进来的数字进行 + 1 操作,解析后需要 -1 |
| |11111111| | 1 byte | 0 bit | 列表结束符 |
2.4.3. 编解码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
#define ZIP_STR_MASK 0xc0
#define ZIP_INT_MASK 0x30
#define ZIP_STR_06B (0 << 6)
#define ZIP_STR_14B (1 << 6)
#define ZIP_STR_32B (2 << 6)
#define ZIP_INT_16B (0xc0 | 0<<4)
#define ZIP_INT_32B (0xc0 | 1<<4)
#define ZIP_INT_64B (0xc0 | 2<<4)
#define ZIP_INT_24B (0xc0 | 3<<4)
#define ZIP_INT_8B 0xfe
/* Macro to determine if the entry is a string. String entries never start
* with "11" as most significant bits of the first byte. */
#define ZIP_IS_STR(enc) (((enc) & ZIP_STR_MASK) < ZIP_STR_MASK)
/* Write the encoidng header of the entry in 'p'. If p is NULL it just returns
* the amount of bytes required to encode such a length. Arguments:
*
* 'encoding' is the encoding we are using for the entry. It could be
* ZIP_INT_* or ZIP_STR_* or between ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN and ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX
* for single-byte small immediate integers.
*
* 'rawlen' is only used for ZIP_STR_* encodings and is the length of the
* srting that this entry represents.
*
* The function returns the number of bytes used by the encoding/length
* header stored in 'p'. */
unsigned int zipStoreEntryEncoding(unsigned char *p, unsigned char encoding, unsigned int rawlen) {
unsigned char len = 1, buf[5];
if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) {
/* Although encoding is given it may not be set for strings,
* so we determine it here using the raw length. */
if (rawlen <= 0x3f) {
if (!p) return len;
buf[0] = ZIP_STR_06B | rawlen;
} else if (rawlen <= 0x3fff) {
len += 1;
if (!p) return len;
buf[0] = ZIP_STR_14B | ((rawlen >> 8) & 0x3f);
buf[1] = rawlen & 0xff;
} else {
len += 4;
if (!p) return len;
buf[0] = ZIP_STR_32B;
buf[1] = (rawlen >> 24) & 0xff;
buf[2] = (rawlen >> 16) & 0xff;
buf[3] = (rawlen >> 8) & 0xff;
buf[4] = rawlen & 0xff;
}
} else {
/* Implies integer encoding, so length is always 1. */
if (!p) return len;
buf[0] = encoding;
}
/* Store this length at p. */
memcpy(p,buf,len);
return len;
}
/* 'encoding' field of the zlentry structure. */
#define ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING(ptr, encoding) do { \
(encoding) = (ptr[0]); \
// 如果是字符串类型,取前面两个 bit,其它 bit 是 0 \
if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) (encoding) &= ZIP_STR_MASK; \
} while(0)
#define ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN 0xf1 /* 11110001 */
#define ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX 0xfd /* 11111101 */
/* Return bytes needed to store integer encoded by 'encoding'. */
unsigned int zipIntSize(unsigned char encoding) {
switch(encoding) {
case ZIP_INT_8B: return 1;
case ZIP_INT_16B: return 2;
case ZIP_INT_24B: return 3;
case ZIP_INT_32B: return 4;
case ZIP_INT_64B: return 8;
}
if (encoding >= ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN && encoding <= ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX)
return 0; /* 4 bit immediate */
panic("Invalid integer encoding 0x%02X", encoding);
return 0;
}
/* Store integer 'value' at 'p', encoded as 'encoding' */
void zipSaveInteger(unsigned char *p, int64_t value, unsigned char encoding) {
int16_t i16;
int32_t i32;
int64_t i64;
if (encoding == ZIP_INT_8B) {
((int8_t *)p)[0] = (int8_t)value;
} else if (encoding == ZIP_INT_16B) {
i16 = value;
memcpy(p, &i16, sizeof(i16));
memrev16ifbe(p);
} else if (encoding == ZIP_INT_24B) {
i32 = value << 8;
memrev32ifbe(&i32);
memcpy(p, ((uint8_t *)&i32) + 1, sizeof(i32) - sizeof(uint8_t));
} else if (encoding == ZIP_INT_32B) {
i32 = value;
memcpy(p, &i32, sizeof(i32));
memrev32ifbe(p);
} else if (encoding == ZIP_INT_64B) {
i64 = value;
memcpy(p, &i64, sizeof(i64));
memrev64ifbe(p);
} else if (encoding >= ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN && encoding <= ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX) {
/* Nothing to do, the value is stored in the encoding itself. */
} else {
assert(NULL);
}
}
/* Decode the entry encoding type and data length (string length for strings,
* number of bytes used for the integer for integer entries) encoded in 'ptr'.
* The 'encoding' variable will hold the entry encoding, the 'lensize'
* variable will hold the number of bytes required to encode the entry
* length, and the 'len' variable will hold the entry length. */
#define ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(ptr, encoding, lensize, len) do { \
ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING((ptr), (encoding)); \
if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) { \
if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_06B) { \
(lensize) = 1; \
(len) = (ptr)[0] & 0x3f; \
} else if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_14B) { \
(lensize) = 2; \
(len) = (((ptr)[0] & 0x3f) << 8) | (ptr)[1]; \
} else if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_32B) { \
(lensize) = 5; \
(len) = ((ptr)[1] << 24) | \
((ptr)[2] << 16) | \
((ptr)[3] << 8) | \
((ptr)[4]); \
} else { \
panic("Invalid string encoding 0x%02X", (encoding)); \
} \
} else { \
(lensize) = 1; \
(len) = zipIntSize(encoding); \
} \
} while(0);
3. 调试
我们可以先通过调试去走一次程序逻辑,观察该数据结构的内存管理,了解下 ziplistNew, ziplistPush 等接口的工作流程。
调试为了编译通过,适当增减部分代码。
1
2
gcc -g ziplist.c sds.c zmalloc.c util.c sha1.c -o ziplist -I../deps/lua/src
sudo gdb ziplist
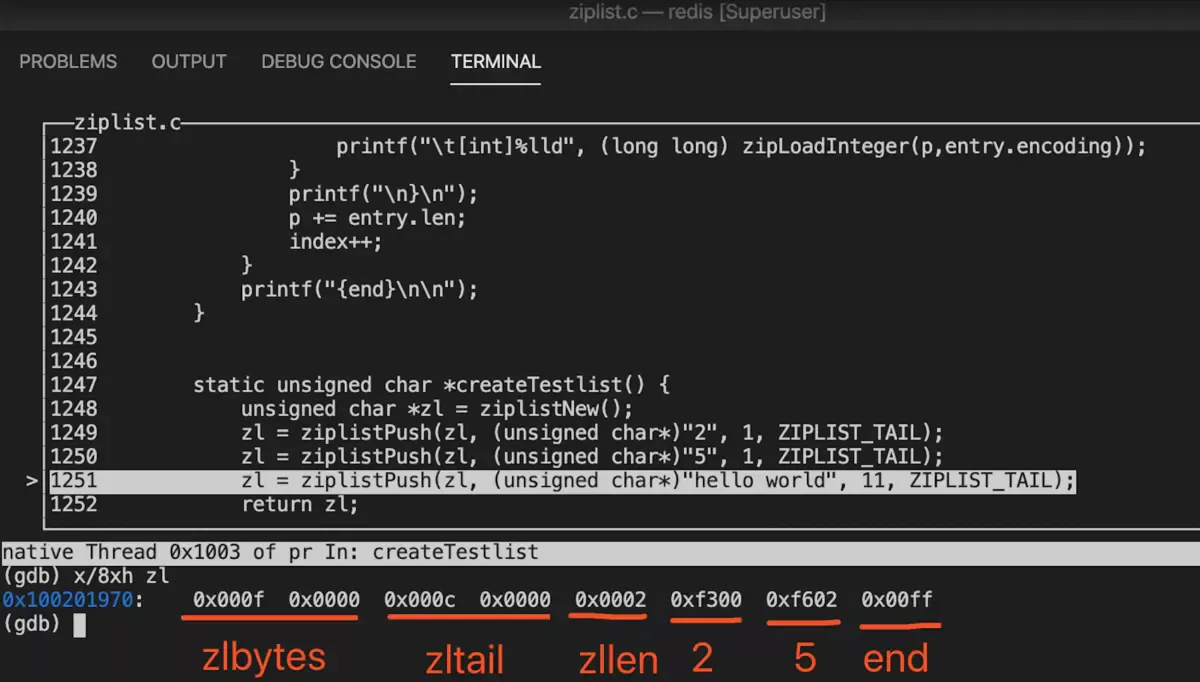
3.1. 调试中间插入结点
详细可以查看 ziplistInsert 接口源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
static unsigned char *createTestlist() {
unsigned char *zl = ziplistNew();
zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)"2", 1, ZIPLIST_TAIL);
zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)"5", 1, ZIPLIST_TAIL);
unsigned char test[1024];
memset(test, 'a', sizeof(test));
// 插入中间
unsigned char* p = ziplistIndex(zl, 0);
p = ziplistNext(zl, p);
zl = ziplistInsert(zl, p, test, sizeof(test));
return zl;
}
int main() {
unsigned char *zl = createTestlist();
ziplistRepr(zl);
zfree(zl);
}
结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
{total bytes 1046} {num entries 3}
{tail offset 1039}
{
addr 0x7fb31680060a,
index 0,
offset 10,
hdr+entry len: 2,
hdr len 2,
prevrawlen: 0,
prevrawlensize: 1,
payload 0
bytes: 00|f3|
[int]2
}
{
addr 0x7fb31680060c,
index 1,
offset 12,
hdr+entry len: 1027,
hdr len 3,
prevrawlen: 2,
prevrawlensize: 1,
payload 1024
bytes: 02|44|00|61|61|...|61|
[str]aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa...
}
{
addr 0x7fb316800a0f,
index 2,
offset 1039,
hdr+entry len: 6,
hdr len 6,
prevrawlen: 1027,
prevrawlensize: 5,
payload 0
bytes: fe|03|04|00|00|f6|
[int]5
}
{end}
主要画了部分令人费解的地方。
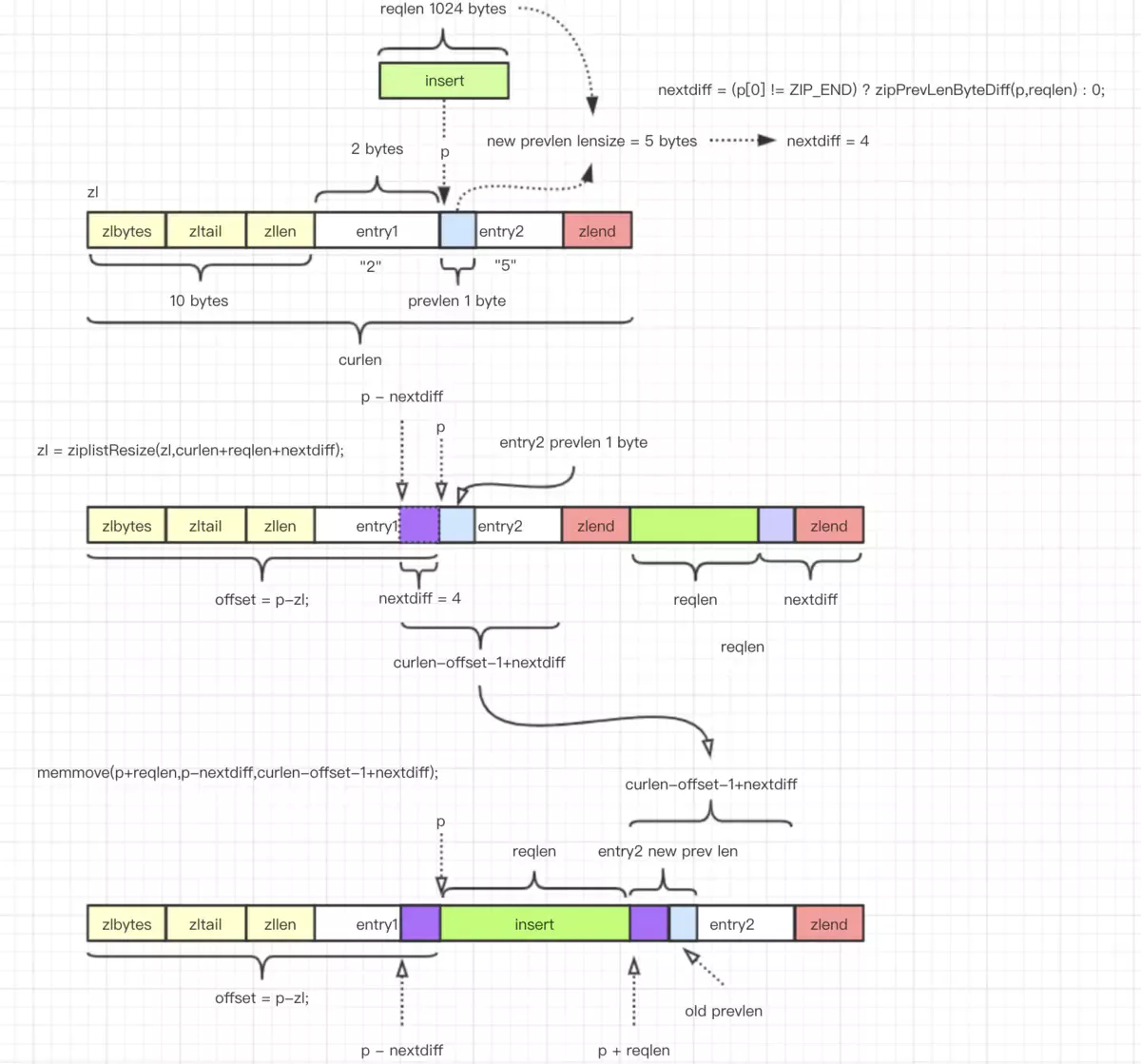
设计图来源 《redis ziplist 压缩列表加新工作流程》
4. 接口
可以通过 sorted set (t_zset.c)源码理解 ziplist 的使用。
4.1. 插入结点
根据 p 指定的位置,插入数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
/* Insert item at "p". */
unsigned char *__ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen) {
// 获取当前整个内存长度
size_t curlen = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl)), reqlen;
unsigned int prevlensize, prevlen = 0;
size_t offset;
int nextdiff = 0;
unsigned char encoding = 0;
long long value = 123456789; /* initialized to avoid warning. Using a value
that is easy to see if for some reason
we use it uninitialized. */
zlentry tail;
// 如果不是结束结点,那么就从当前结点获取前一个结点的长度。如果是结束结点,就取末结点长度(末结点不是结束结点)。
/* Find out prevlen for the entry that is inserted. */
if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen);
} else {
// 末结点
unsigned char *ptail = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl);
if (ptail[0] != ZIP_END) {
prevlen = zipRawEntryLength(ptail);
}
}
// 获取内容长度,字符串会先尝试转化为整型。
/* See if the entry can be encoded */
if (zipTryEncoding(s,slen,&value,&encoding)) {
/* 'encoding' is set to the appropriate integer encoding */
reqlen = zipIntSize(encoding);
} else {
/* 'encoding' is untouched, however zipStoreEntryEncoding will use the
* string length to figure out how to encode it. */
reqlen = slen;
}
/* We need space for both the length of the previous entry and
* the length of the payload. */
reqlen += zipStorePrevEntryLength(NULL,prevlen);
reqlen += zipStoreEntryEncoding(NULL,encoding,slen);
// 插入位置的后一个结点的<prevlen>发生改变, nextdiff 计算 <prevlen> 的 lensize 相差多少。
/* When the insert position is not equal to the tail, we need to
* make sure that the next entry can hold this entry's length in
* its prevlen field. */
int forcelarge = 0;
nextdiff = (p[0] != ZIP_END) ? zipPrevLenByteDiff(p,reqlen) : 0;
// 减少插入位置后续结点的 <prevlen> lensize 连锁反应频繁调用 ziplistResize 损耗性能。强制 forcelarge 写入。
// 该问题,详见:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000018878466?utm_source=tag-newest
if (nextdiff == -4 && reqlen < 4) {
nextdiff = 0;
forcelarge = 1;
}
/* Store offset because a realloc may change the address of zl. */
offset = p-zl;
zl = ziplistResize(zl,curlen+reqlen+nextdiff);
p = zl+offset;
/* Apply memory move when necessary and update tail offset. */
if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
/* Subtract one because of the ZIP_END bytes */
memmove(p+reqlen,p-nextdiff,curlen-offset-1+nextdiff);
/* Encode this entry's raw length in the next entry. */
if (forcelarge)
zipStorePrevEntryLengthLarge(p+reqlen,reqlen);
else
zipStorePrevEntryLength(p+reqlen,reqlen);
/* Update offset for tail */
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+reqlen);
/* When the tail contains more than one entry, we need to take
* "nextdiff" in account as well. Otherwise, a change in the
* size of prevlen doesn't have an effect on the *tail* offset. */
zipEntry(p+reqlen, &tail);
if (p[reqlen+tail.headersize+tail.len] != ZIP_END) {
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+nextdiff);
}
} else {
/* This element will be the new tail. */
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(p-zl);
}
// <entr> 保存了 <prevlen>,前结点改变了,导致长度也改变了,后面的结点连锁反映,也需要修改 <prevlen>
/* When nextdiff != 0, the raw length of the next entry has changed, so
* we need to cascade the update throughout the ziplist */
if (nextdiff != 0) {
offset = p-zl;
zl = __ziplistCascadeUpdate(zl,p+reqlen);
p = zl+offset;
}
/* Write the entry */
p += zipStorePrevEntryLength(p,prevlen);
p += zipStoreEntryEncoding(p,encoding,slen);
if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) {
memcpy(p,s,slen);
} else {
zipSaveInteger(p,value,encoding);
}
ZIPLIST_INCR_LENGTH(zl,1);
return zl;
}
5. 问题
-
分配内存。
ziplist 插入删除数据需要重新分配内存。
-
耦合问题。
ziplist 为了在连续内存上进行数据管理,对数据进行压缩,节省内存开销,也减少内存碎片。但是 prevlen 作为数据结点对组成部分,跟其它结点严重耦合,只要在链表中间插入或者删除结点,有可能需要遍历更新插入或删除位置后续的所有结点
<prevlen>。 -
复杂度
指针的偏移考验的是技术功底。ziplist 实现算是比较复杂了(对我而言)。如果用传统的双向链表实现要简单不少的,压缩目的还是能达到的,结点间的耦合比较小。
-
效率问题。
列表重点是压缩,是一个列表,插入删除数据,效率不高,需要重新分配内存。因为是列表,查找结点复杂度 O(n)。在
sorted set的实现中,对skiplist的使用是有限制的。redis.conf
1 2
zset-max-ziplist-entries 128 zset-max-ziplist-value 64
t_zset.c
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
void zaddGenericCommand(client *c, int flags) { ... zobj = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,key); if (zobj == NULL) { if (xx) goto reply_to_client; /* No key + XX option: nothing to do. */ if (server.zset_max_ziplist_entries == 0 || server.zset_max_ziplist_value < sdslen(c->argv[scoreidx+1]->ptr)) { zobj = createZsetObject(); } else { zobj = createZsetZiplistObject(); } dbAdd(c->db,key,zobj); } else { if (zobj->type != OBJ_ZSET) { addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr); goto cleanup; } } } int zsetAdd(robj *zobj, double score, sds ele, int *flags, double *newscore) { ... zobj->ptr = zzlInsert(zobj->ptr,ele,score); if (zzlLength(zobj->ptr) > server.zset_max_ziplist_entries || sdslen(ele) > server.zset_max_ziplist_value) zsetConvert(zobj,OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST); ... }


